Chromatographic Rectification of Ethanol
a technology of chromatographic rectification and ethanol, which is applied in the direction of distillation, separation of dispersed particles, and separation of processes, etc., can solve the problems of unsuitable for smaller-scale production needs, and achieve the effects of reducing energy and shipping costs, reducing pollution, and reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
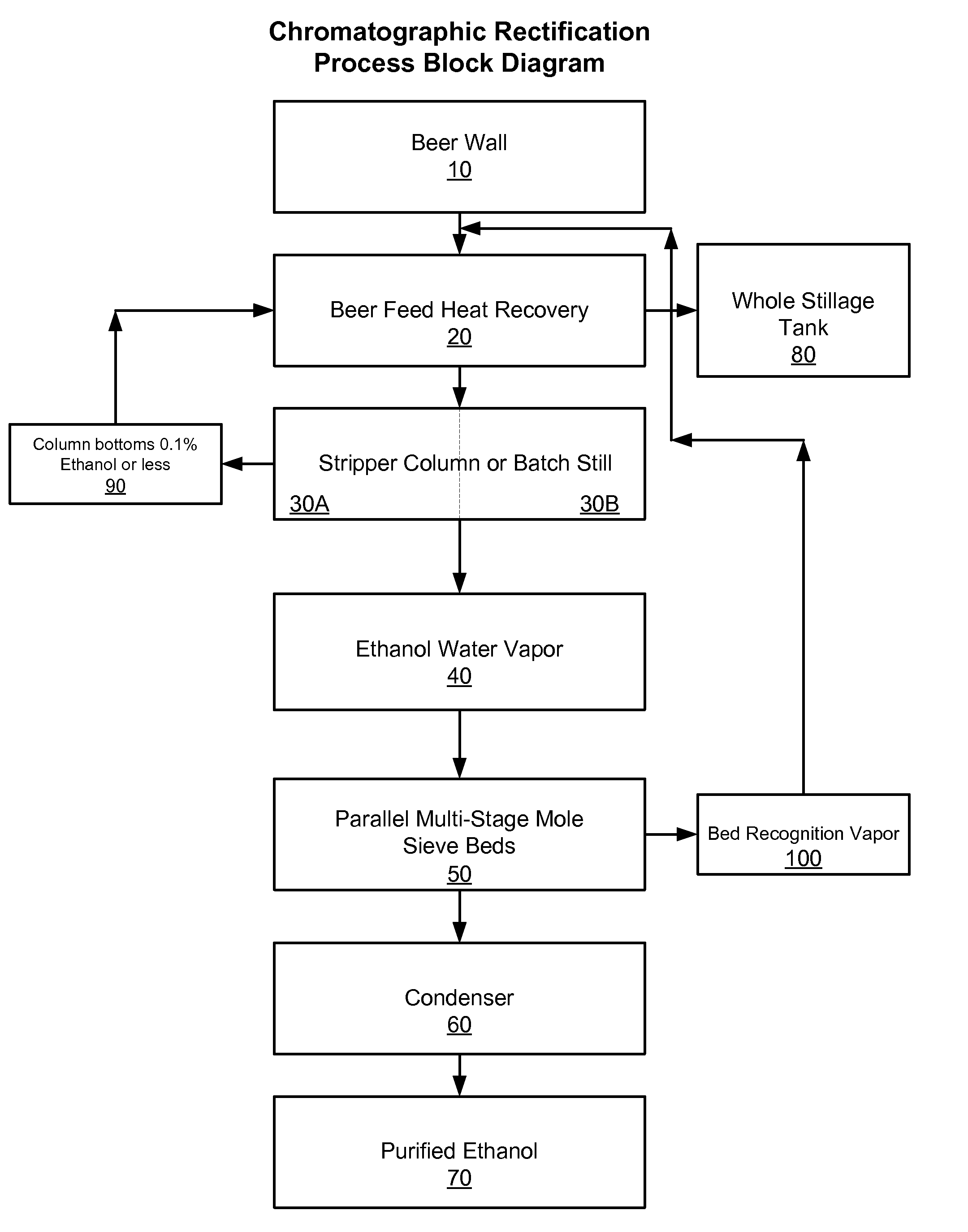
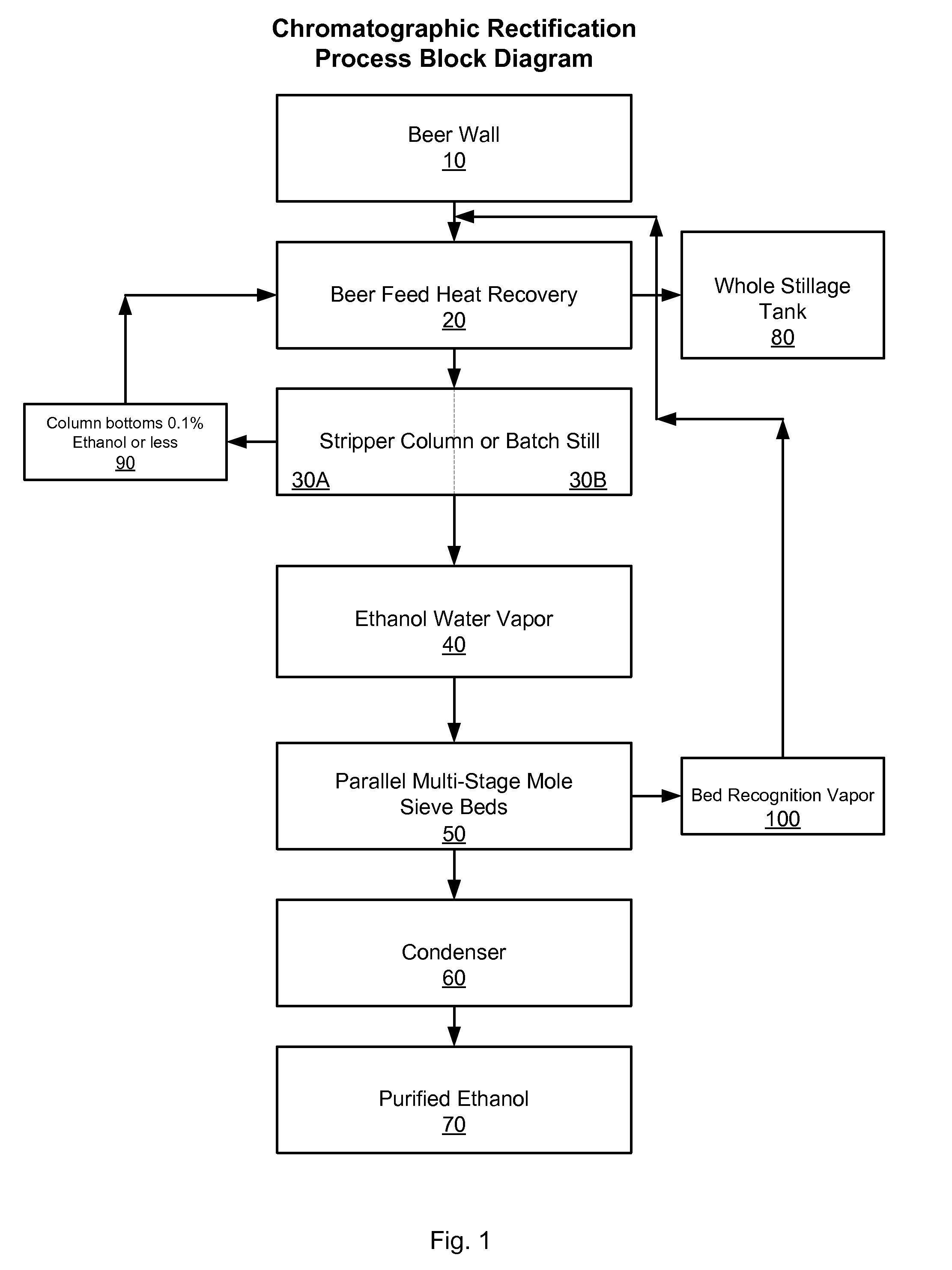
[0011]Definitions. As used in this description and the accompanying claims, the following terms shall have the meanings indicated, unless the context otherwise requires:
[0012]“Beer” means, in the context of this application, any cellulose, hemi-cellulose or fermentable sugar source (such as grains) that has been allowed to ferment into an ethanol-containing aqueous mixture, and includes ethanol from recovery of gums.
[0013]“Molecular sieve” means, in the context of this application, naturally occurring or synthetic compounds that have extremely porous structures, separate molecules on the basis of size by adsorbing the molecules into the porous spaces in the structures, and are commonly used to remove water and other impurities from liquids and gases. Naturally occurring molecular sieves are porous mineral crystals consisting of aluminum and silicon, particularly crystalline metal aluminosilicates having a three-dimensional interconnecting network of silica and alumina tetrahedral. S...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| energy | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com