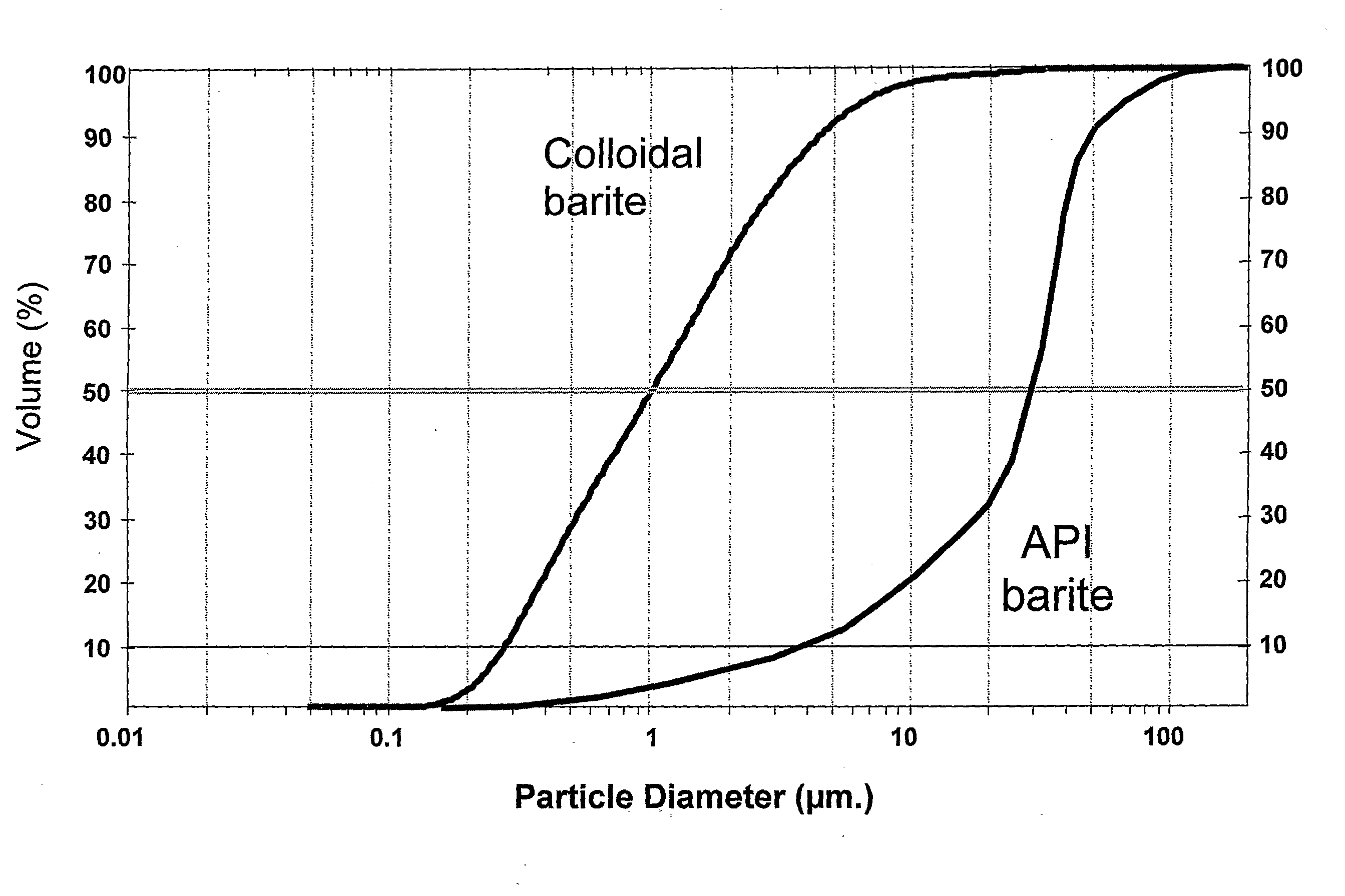
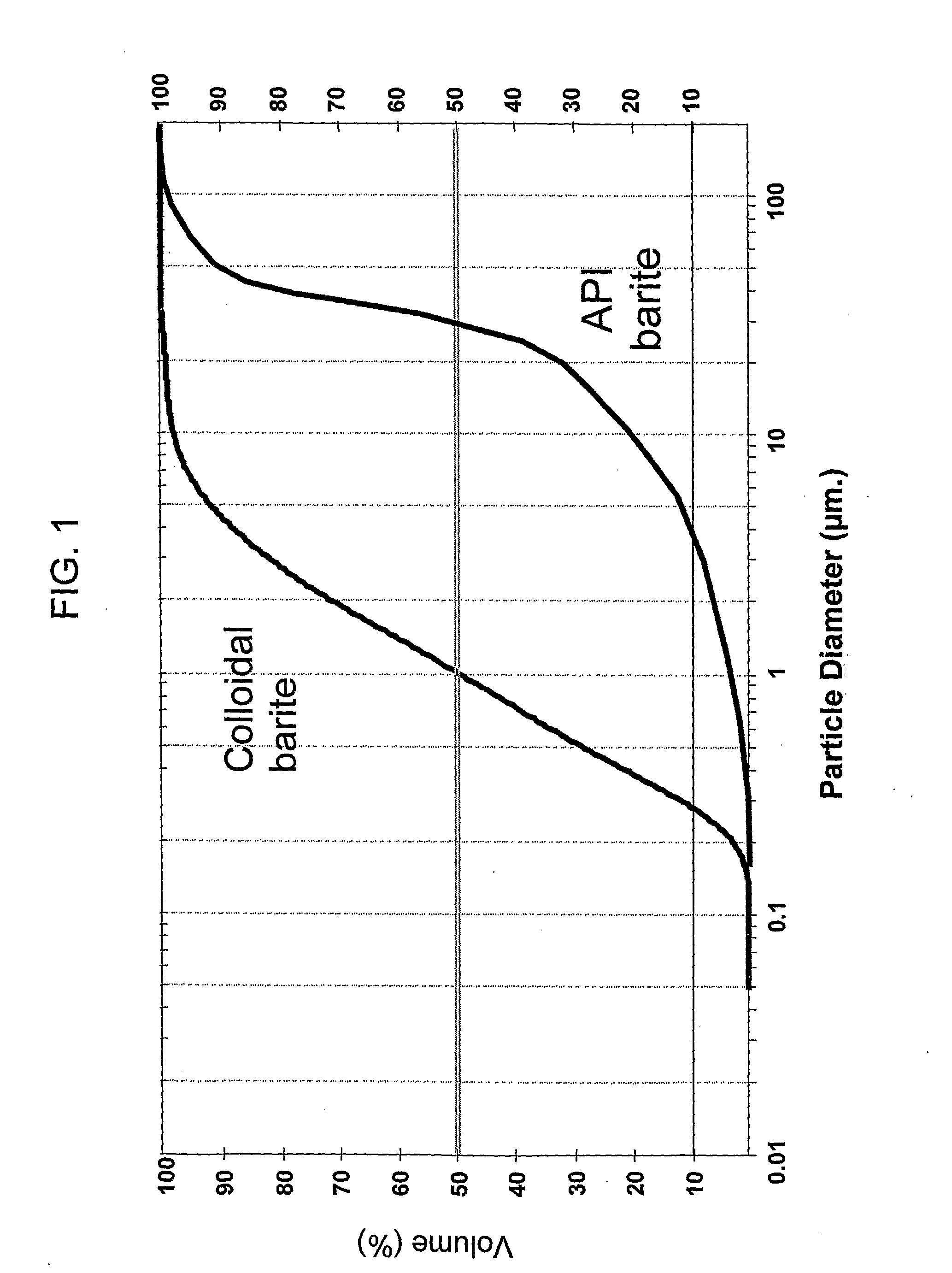
Additive For Reducing Torque On A Drill String
a technology of additive and drill string, which is applied in the direction of lubricant composition, chemistry apparatus and processes, base materials, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the toxicity and irritation level of fluids, difficult environmental compliance in specific areas of the world, and high cost, and achieve the effect of reducing the torque of drill string
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0030]22 ppg [2.63 g / cm3] fluids based on barium sulfate and water were prepared using standard barite and colloidal barite according to the invention. The 22 ppg slurry of API grade barite and water was made with no gelling agent to control the inter-particle interactions (Fluid #1). Fluid #2 is also based on standard API barite but with a post-addition of two pounds per barrel (5.7 kilograms per cubic meter) IDSPERSE XT. Fluid #3 is 100% new lubricating / weighting agent with 67% w / w of particles below 1 micron in size and at least 90% less than 2 microns. The results are provided in table I.
TABLE IViscosity at various shear rates(rpm of agitation):YieldDial reading or “Fann Units” for:PlasticPoint600200100Viscositylb / 100 ft2#rpm300 rpmrpmrpm6 rpm3 rpmmPa · s(Pascals)12501601249225169070 (34)2265105642611160−55 (−26)365382717322711 (5)
[0031]For Fluid #1 the viscosity is very high and the slurry was observed to filter very rapidly. (If further materials were added to reduce the flui...
example 21
[0034]Experiments were conducted to examine the effect of the post addition of the chosen polymer dispersant to a slurry comprising weighting agents of the same colloidal particle size. A milled barite (D50˜4 um) and a milled calcium carbonate (70% by weight of the particles of less than 2 μm) were selected, both of which are of similar particle size to the invention related herein. The slurries were prepared at an equivalent particle volume fraction of 0.282 and compared to the product of the present invention (new barite). See table II.
[0035]The rheologies were measured at 120° F. (49° C.), thereafter an addition of 6 ppb (17.2 kg / m3) IDSPERSE XT was made. The rheologies of the subsequent slurries were finally measured at 120° F. (see table III) with additional API fluid loss test.
TABLE IIVolume#MaterialDispersantDensity (ppg)Fractionwt / wt4New baritewhile grinding16.0 [1.92 g / cm3]0.2820.6255Milled baritenone16.0 [1.92 g / cm3]0.2820.6256Milled baritepost-addition16.0 [1.92 g / cm3]0.2...
example 3
[0038]In the following example, two 13.0 ppg fluid formulations are compared, one weighted with conventional API barite and the second weighted with polymer coated colloidal barite (PCC barite) made in accordance with the teachings of the present invention, as a 2.2 sg liquid slurry. Other additives in the formulation are included to provide additional control of pH, fluid loss, rheology, inhibition to reactive shale and claystones. These additives are available from M-I Drilling Fluids.
PRODUCTFluid AFluid BPCC baritelbs / bbl320.0API baritelbs / bbl238.1Freshwaterlbs / bbl175.0264.2Soda Ashlbs / bbl0.40.4Celpol ESLlbs / bbl3.54.2Flotrollbs / bbl3.50Defoam NSlbs / bbl0.40KCllbs / bbl32.936.1Glydril; MClbs / bbl10.510.5Duotec NSlbs / bbl0.11.4
[0039]The fluids were heat aged statically for 48 hrs at 104° F. with the following exemplary results.
Fluid AFluid BFANN 35 Reading (120° F.)InitialAgedInitialAged600 rpm56627365300 rpm36415247200 rpm28334239100 rpm19233129 6 rpm571110 3 rpm4698PV (cps)20212118YP (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com