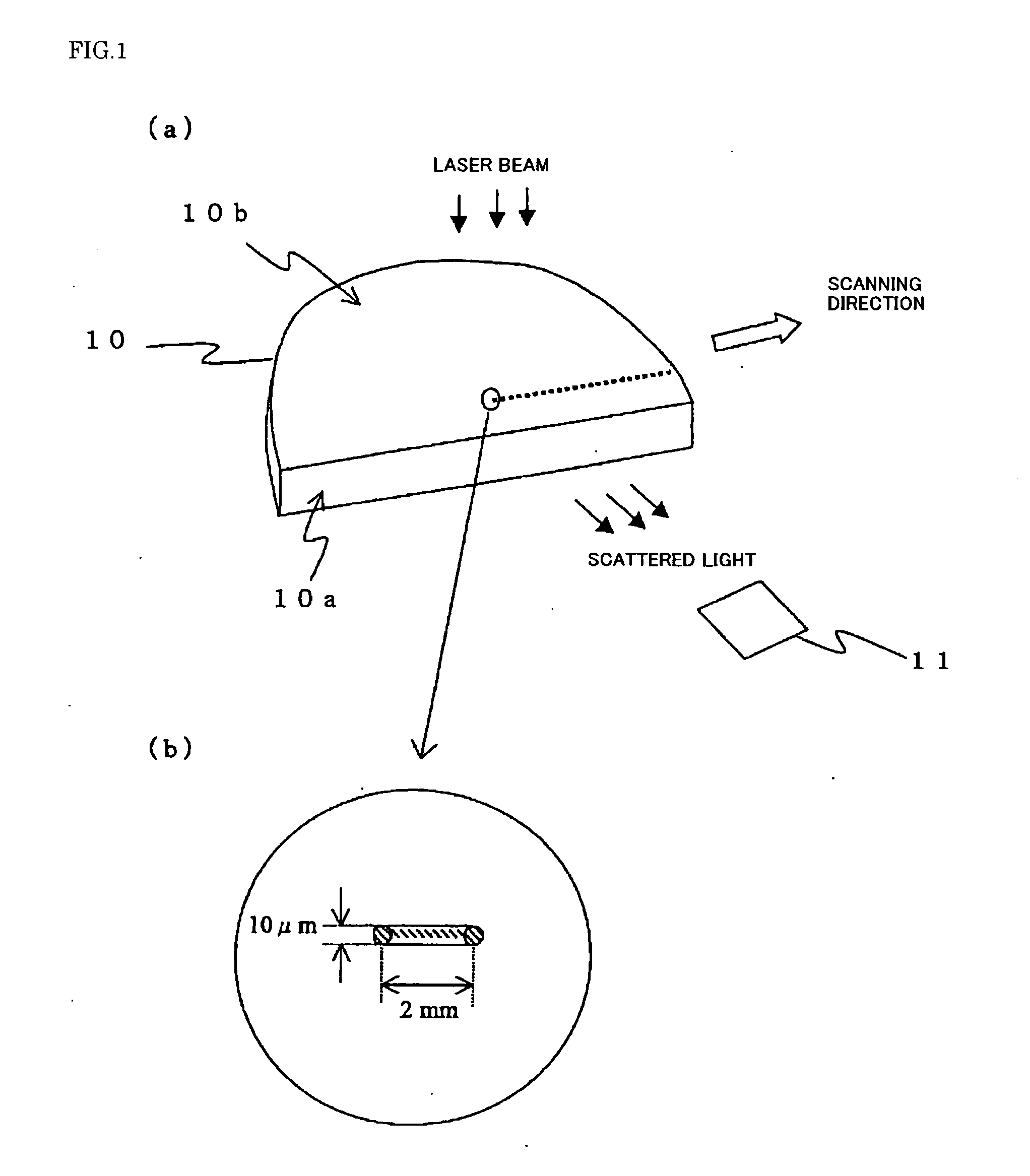
Evaluation Method for Crystal Defect in Silicon Single Crystal Wafer
a single crystal wafer and crystal defect technology, applied in the testing/measurement of individual semiconductor devices, semiconductor/solid-state devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of labor and cost, small crystal defects, and inability to detect such crystal defects by examination, so as to reduce labor and cost, the effect of small void defects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
experiment 1
[0045]An example of examining a relationship between crystal defects detected by the infrared laser scattering tomograph method according to the present invention and crystal defects detected by the conventional Cu deposition method will be described.
[0046]First, a silicon single crystal having a diameter 300 mm and a crystal orientation 100> was pulled upwardly by the CZ method. As crystal growth conditions, and a growth rate was selected in such a manner that DSODs alone are present without an FPD, thereby producing a single crystal.
[0047]After silicon single crystal growth, the grown silicon single crystal was ground by a cylindrical grinder to remove a cone part and a tail part of the single crystal, and then a crystal fixed-diameter part was cut into a length of approximately 25 cm to provide a single crystal block.
[0048]A wafer of approximately 1 mm was sliced from the cone side of this single crystal block by a slicer, a surface of this wafer was ground approximately 300 μm b...
experiment 2
[0057]Another example of examining a relationship between crystal defects detected by the infrared laser scattering tomograph method according to the present invention and crystal defects detected by the conventional Cu deposition method will now be explained.
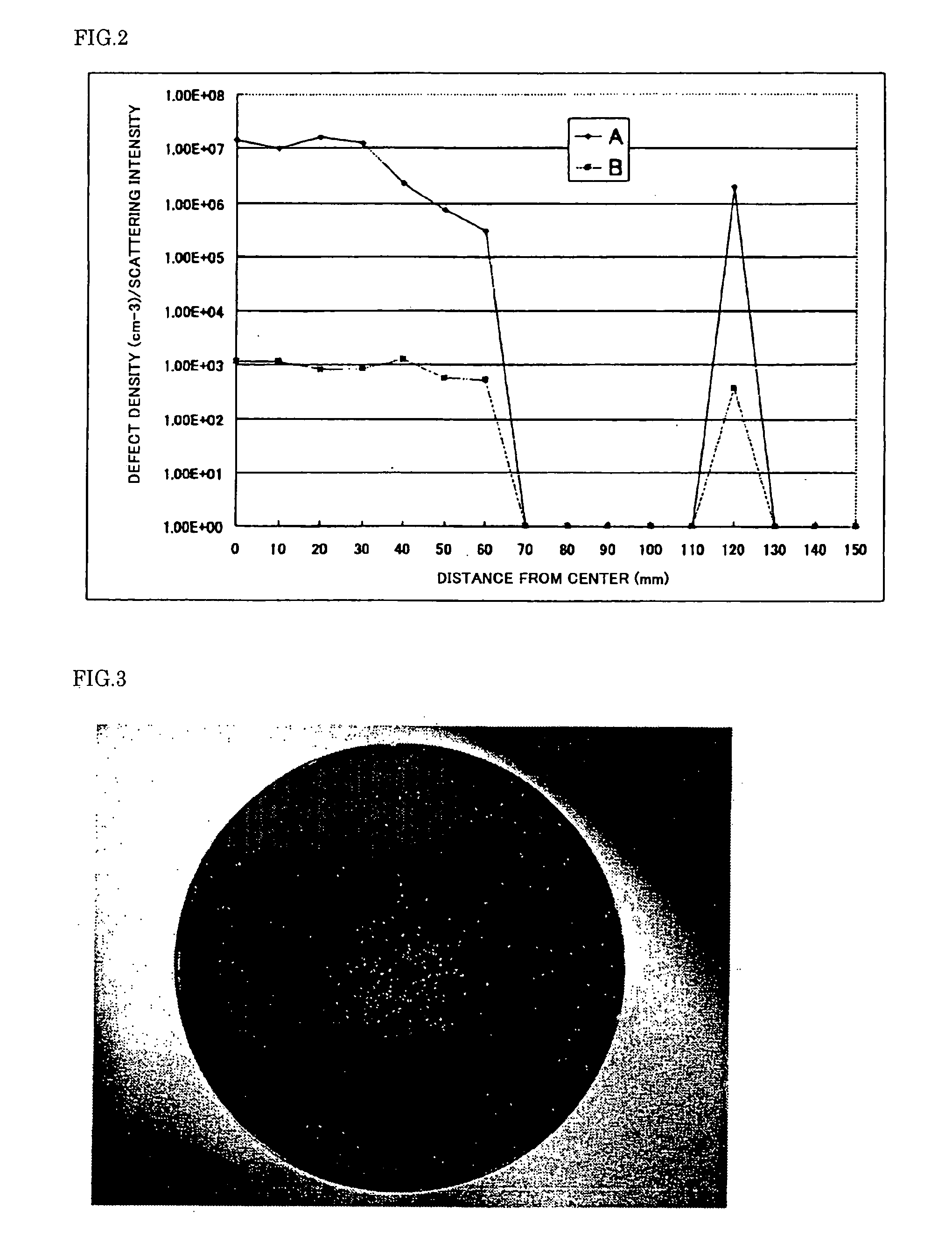
[0058]Like Experiment 1, two single crystal blocks (A, B) were cut from a silicon single crystal having a diameter 300 mm and a crystal orientation 100> pulled by the CZ method, and silicon single crystal wafers were sliced from the single crystal blocks (A, B).
[0059]Moreover, like Experiment 1, a silicon single crystal wafer for evaluation was made, and evaluation of crystal defects based on the infrared laser scattering tomograph method and evaluation of crystal defects based on the Cu deposition method were carried out.
[0060]FIG. 4 shows its result. Here, horizontal axis in FIG. 4 represents a distance from the wafer center, and vertical axis represents a defect density and a scattering intensity.
[0061]In FIG. 4, a line grap...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com