Method and System for Forming a Non-Circular Borehole
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
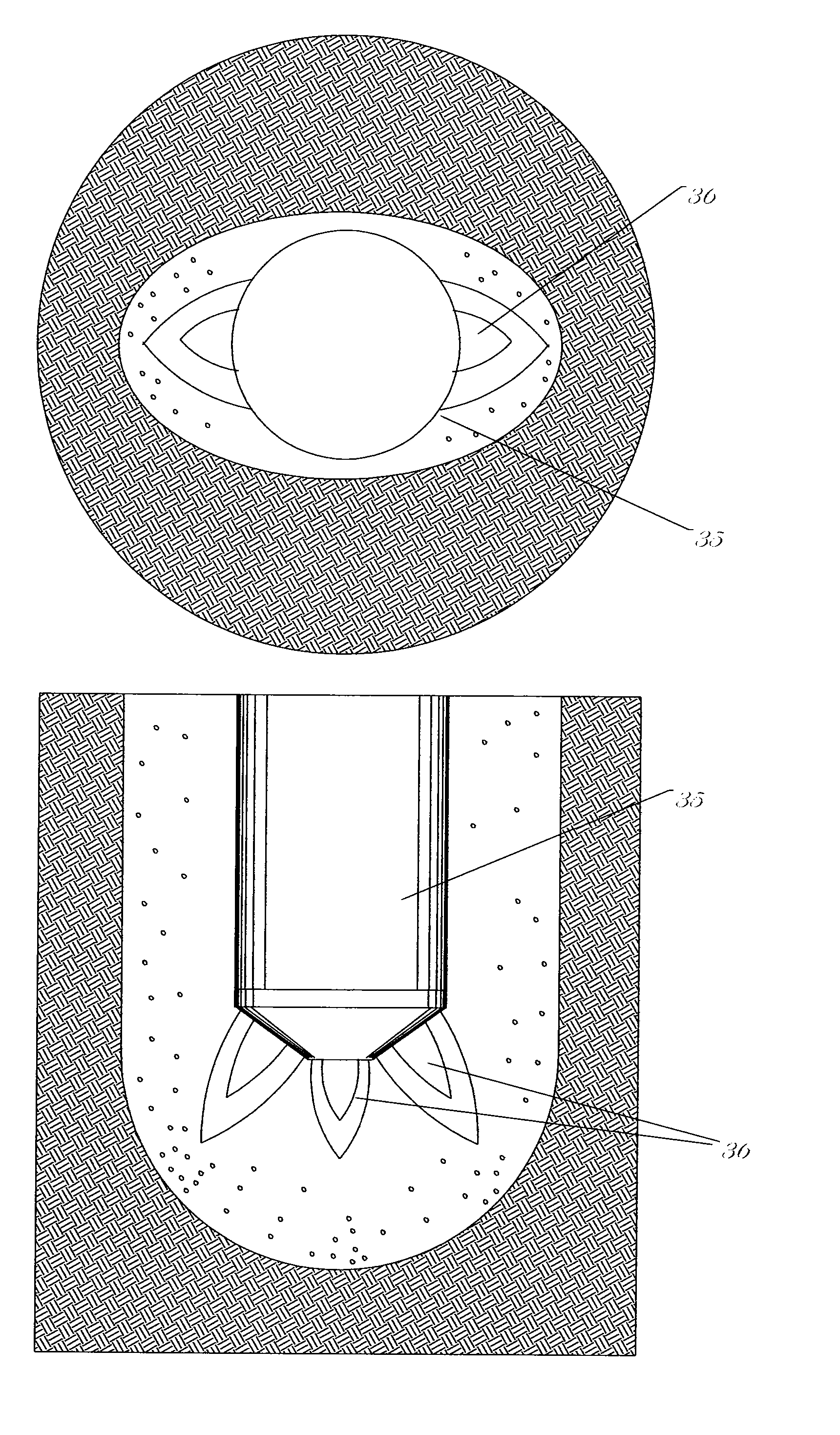
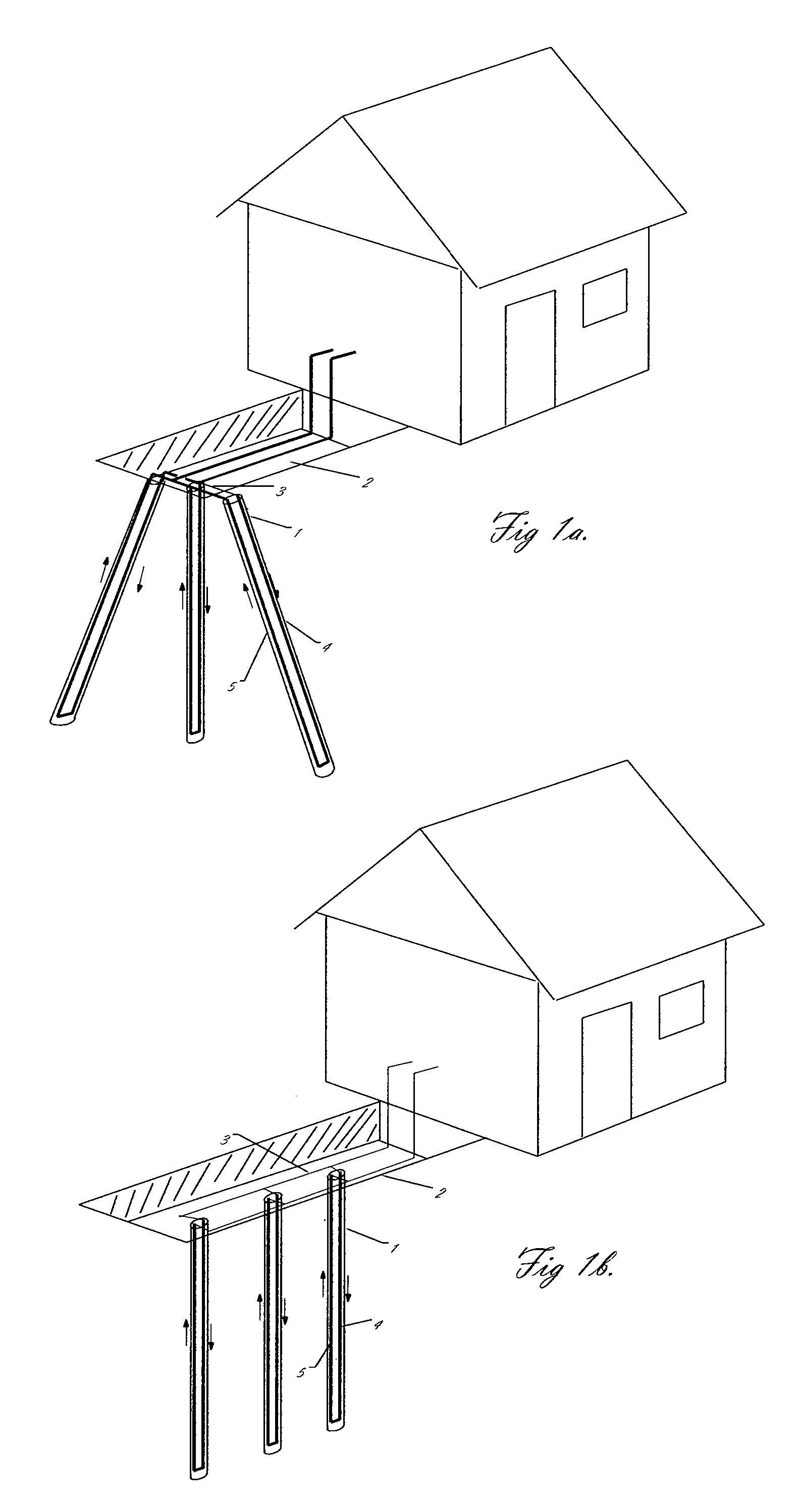
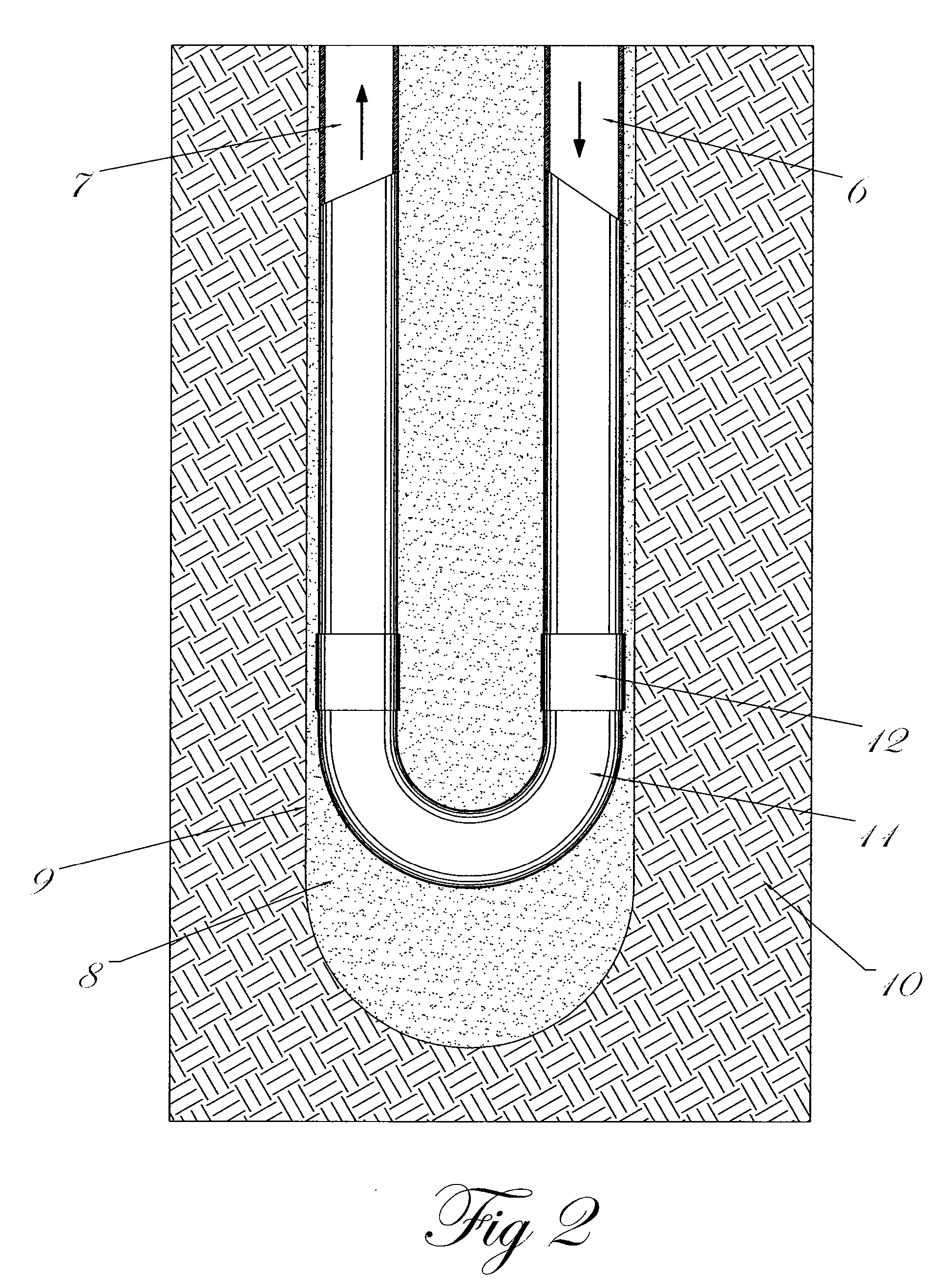
[0039]FIGS. 1a and 1b show the general layout of a geothermal heat pump system which is one such system where oval (e.g., non-circular) boreholes may be beneficial. It should be noted that there exist a number of different ways for locating the boreholes in such a system, and that the general layout of the hole orientation is not critical to the disclosed embodiments of the present invention. In the particular version shown, the heat exchange drill holes are oriented outward from a more or less central point in an excavated trench 2 where the heat exchanger tubes are connected together into a manifold system 3. The out-flowing 4 and in-flowing 5 tubes or pipes are connected to the manifold system 3. The holes are directed from substantially central location to simplify the attachment of the flow tubes to a manifold and to minimize the damage to the terrain around the drill site. A trench is typically used to hide the connection holes and tubing. The flow tubes are typically connecte...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com