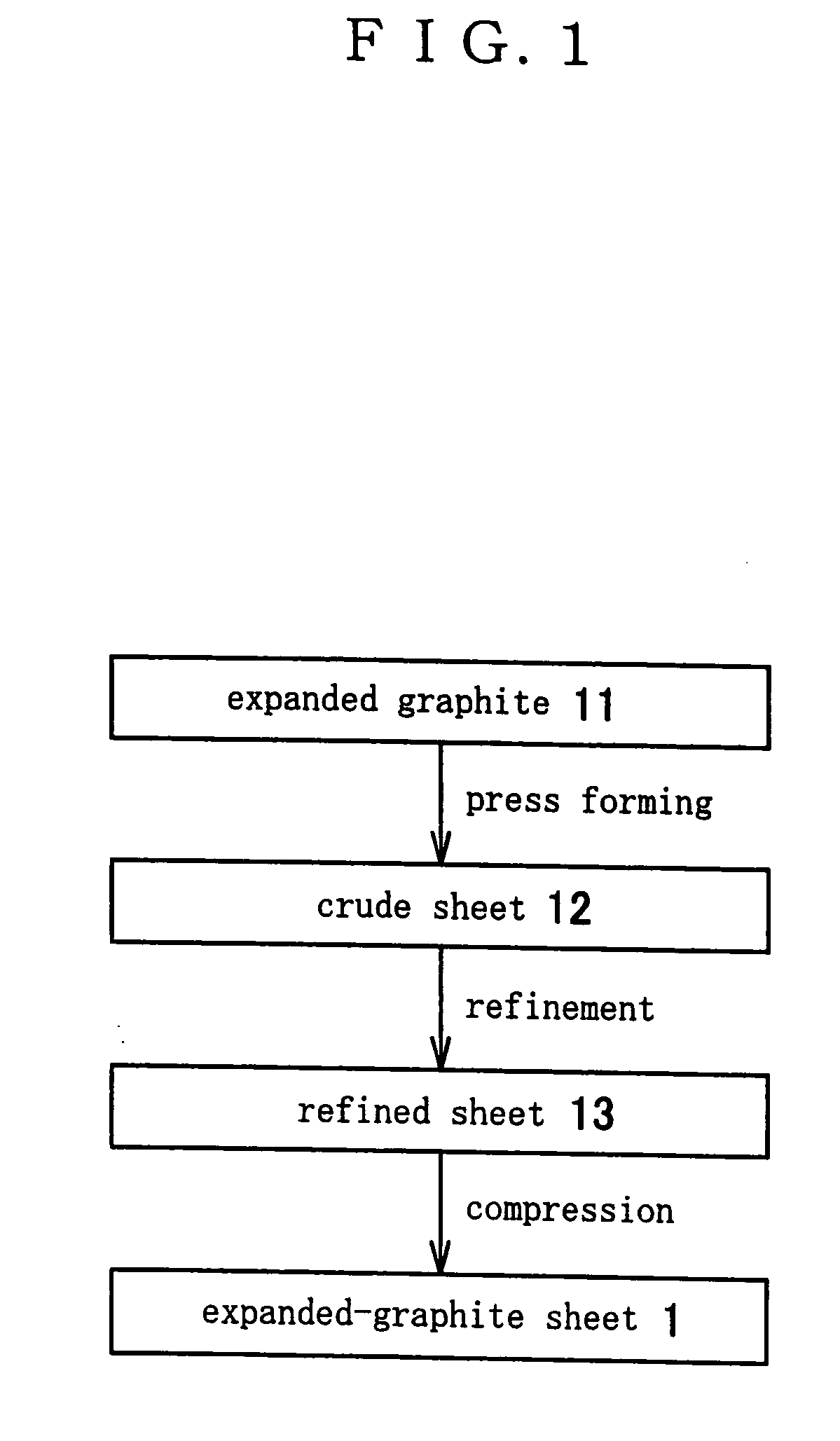
Expanded-graphite sheet
a graphite sheet and expansion technology, applied in the direction of magnetic/electric field screening, modification by conduction heat transfer, chemical instruments and processes, etc., can solve the problems of low graphite sheet production efficiency, high cost of polymer films, and long time-consuming films, etc., to achieve high thermal conductivity, and high thermal conductivity in parallel direction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0047] The thermal conductivities in parallel direction, electromagnetic-wave-shielding effect, and surface roughness of expanded-graphite sheets of the present invention were compared with those of expanded-graphite sheets currently in use. The expanded-graphite sheets of the present invention were made by compressing refined sheets at a rolling speed of 1-2 m / min and had the bulk density of 1.9 Mg / m3. The expanded-graphite sheets currently in use were made by compressing refined sheets at rolling speeds of 3-10 m / min and had the bulk density of 1.0 Mg / m3.
[0048] The thermal diffusivity of the expanded-graphite sheet was found by using the laser flash method and its thermal conductivity was calculated from the thermal diffusivity so found. Nine test pieces 25 mm by 25 mm were cut off from the 200-by-200 mm expanded-graphite sheet, and the mean thermal conductivity of the nine test pieces was calculated.
[0049] The electromagnetic-wave-shielding effect of the expanded-graphite sheet...
second embodiment
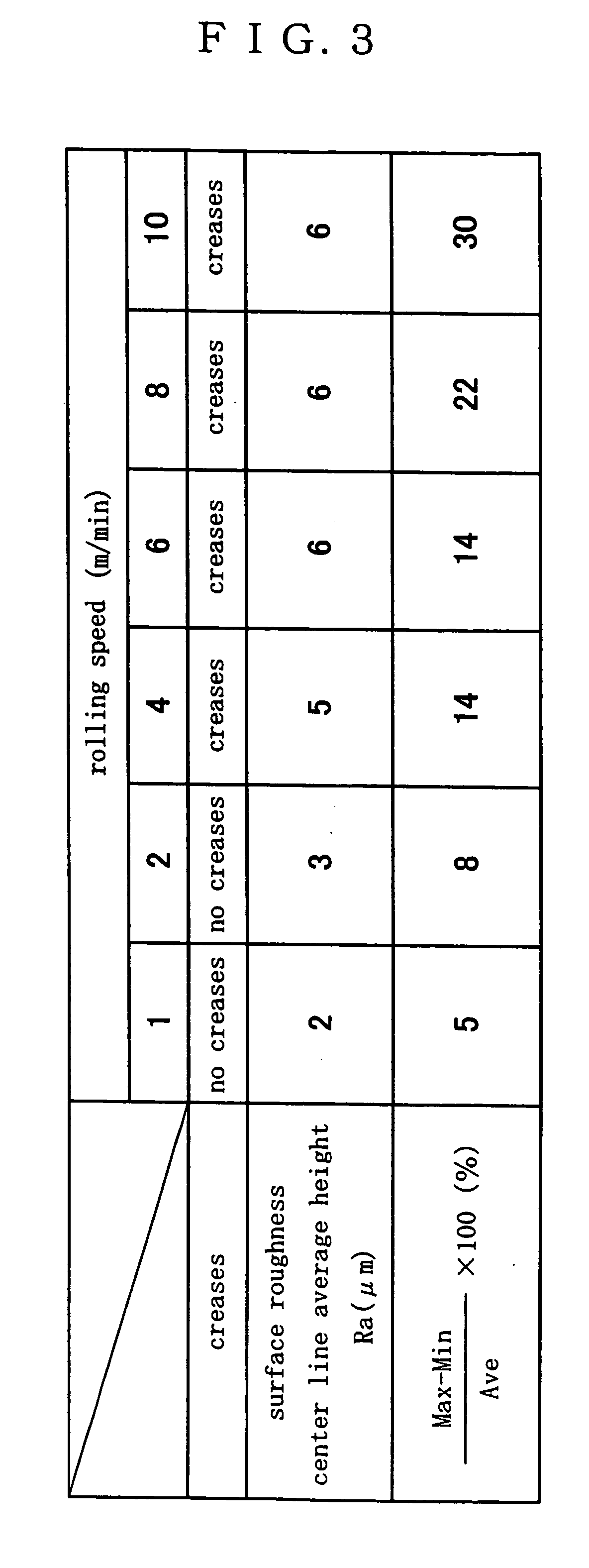
[0055] Refined sheets of the thickness of 1.0 mm and the bulk density of 1.0 Mg / m3 were compressed into expanded-graphite sheets of the thickness of 0.5 mm and the bulk density of 1.9 Mg / m3 in the rolling-speed range of 1-10 m / min to ascertain the effects of the rolling speed on the surface roughness, creases, and thermal conductivity of the expanded-graphite sheets.
[0056] As to the dispersion of thermal conductivity, nine test pieces were cut off from the expanded-graphite sheet of each of the rolling speeds of 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, and 10 m / min and the difference between the highest and lowest conductivities of the nine test pieces was divided by the mean conductivity of the nine test pieces.
[0057] As shown in FIG. 3, as the rolling speed increased, the center line average height and the dispersion of thermal conductivity increased. When the rolling speed increased from 2 m / min to 4 m / min, the center line average height and the dispersion of thermal conductivity almost doubled. This in...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| surface roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com