[0009] Briefly, the present invention provides a
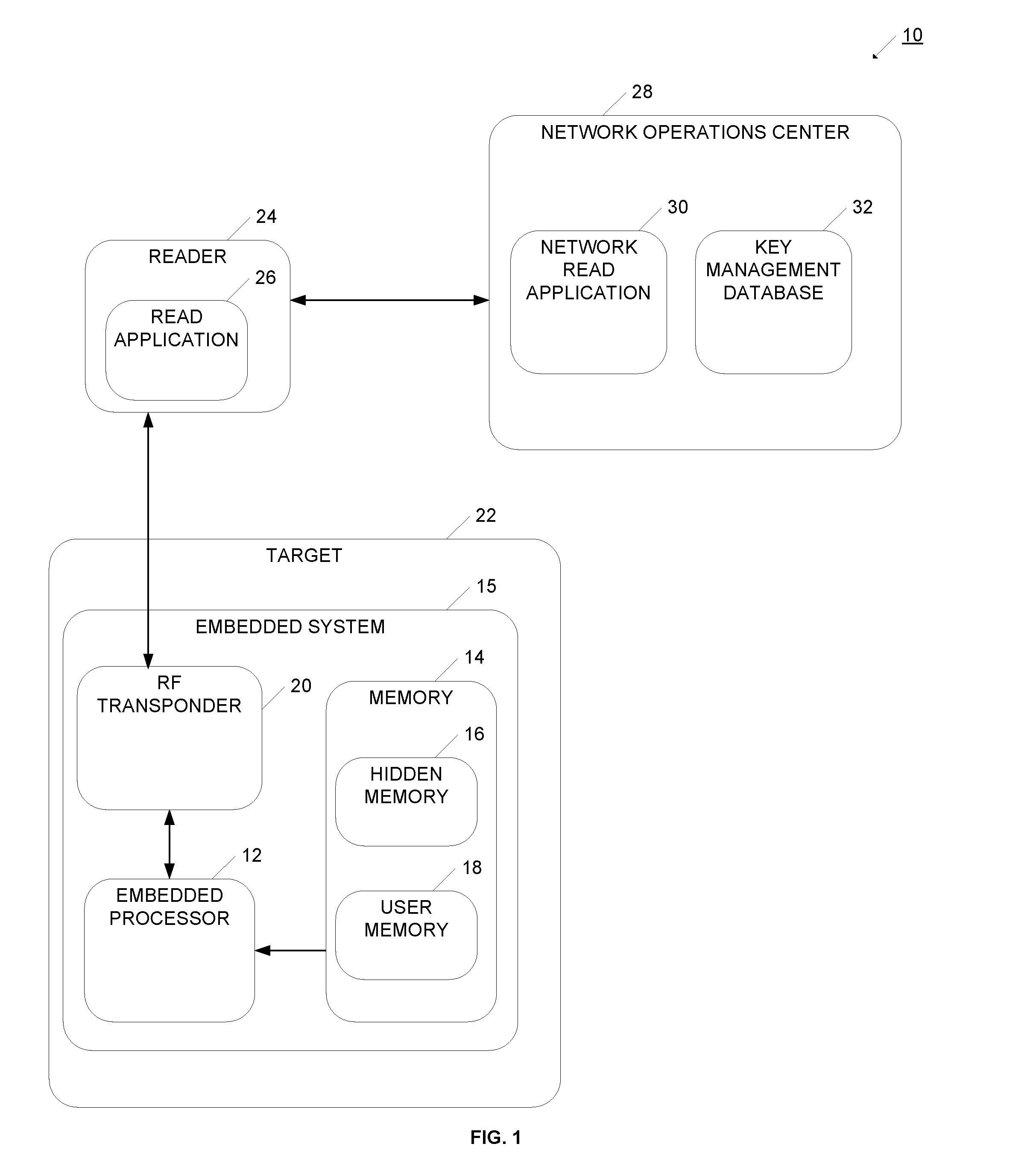
system for authenticating and securing product transactions. An integrated circuit is attached to a target, such as an
optical disc or electronic device. The integrated circuit has an RF
transceiver that is capable of establishing communication with an associated reading device. The integrated circuit also has a hidden memory, which can not be read externally, and a user memory. The hidden memory stores an authentication message, while the user memory stores readable authentication information. The hidden authentication message and the authentication information are related through a cryptographic process. However, even though the integrated circuit benefits from the cryptographic security, the integrated circuit only operates relatively simple logic operations. In this way, a highly secure transaction is enabled without requiring significant
processing power or time at the integrated circuit. When the integrated circuit is placed near the reader, the reader reads the authentication information, and with the cooperation of a network operation center, uses the authentication information to derive an activation code. The reader passes the activation code to the integrated circuit, which compares the activation code to its hidden activation message. If they have a proper relationship, the communication has been authenticated, and the integrated circuit proceeds to perform an action.
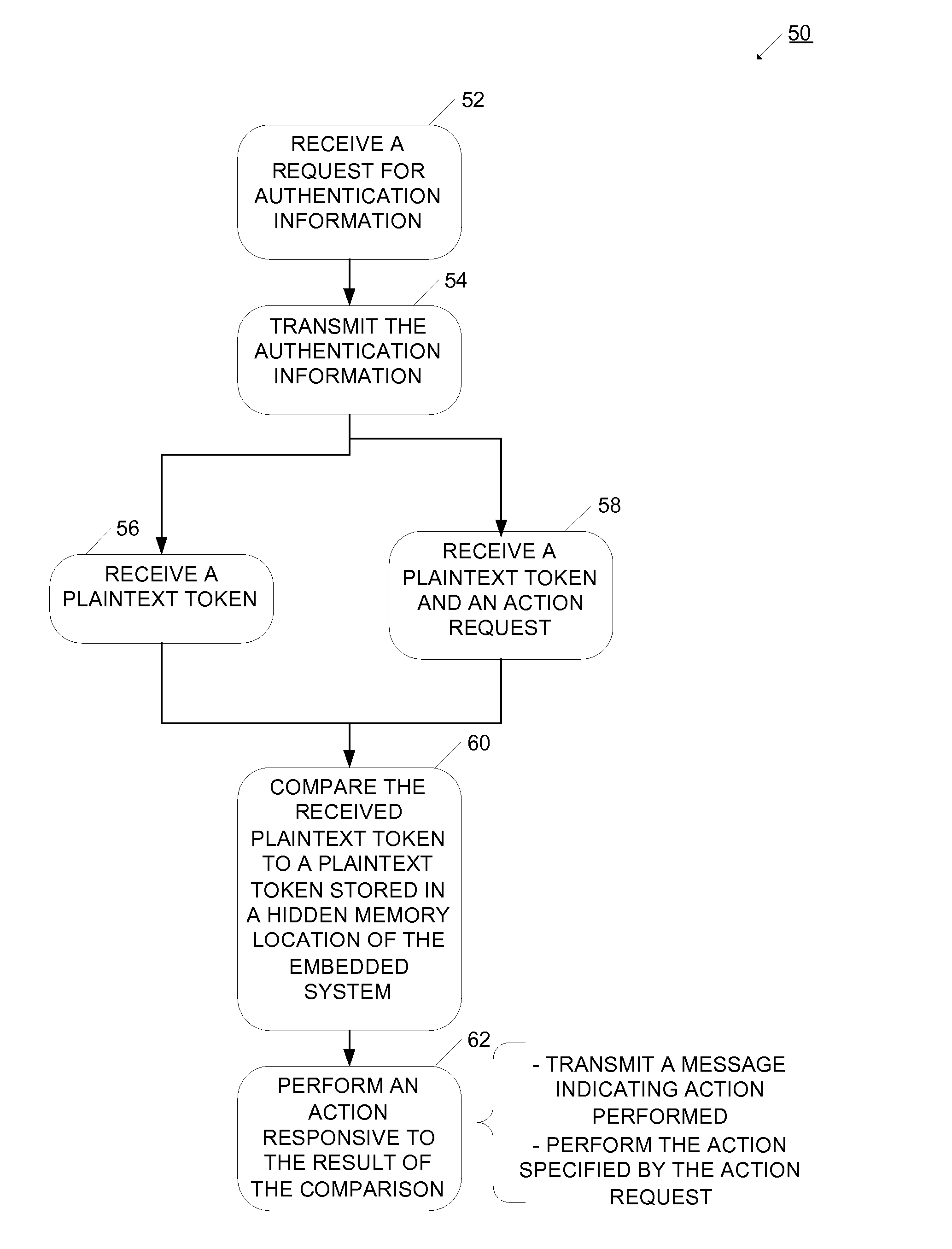
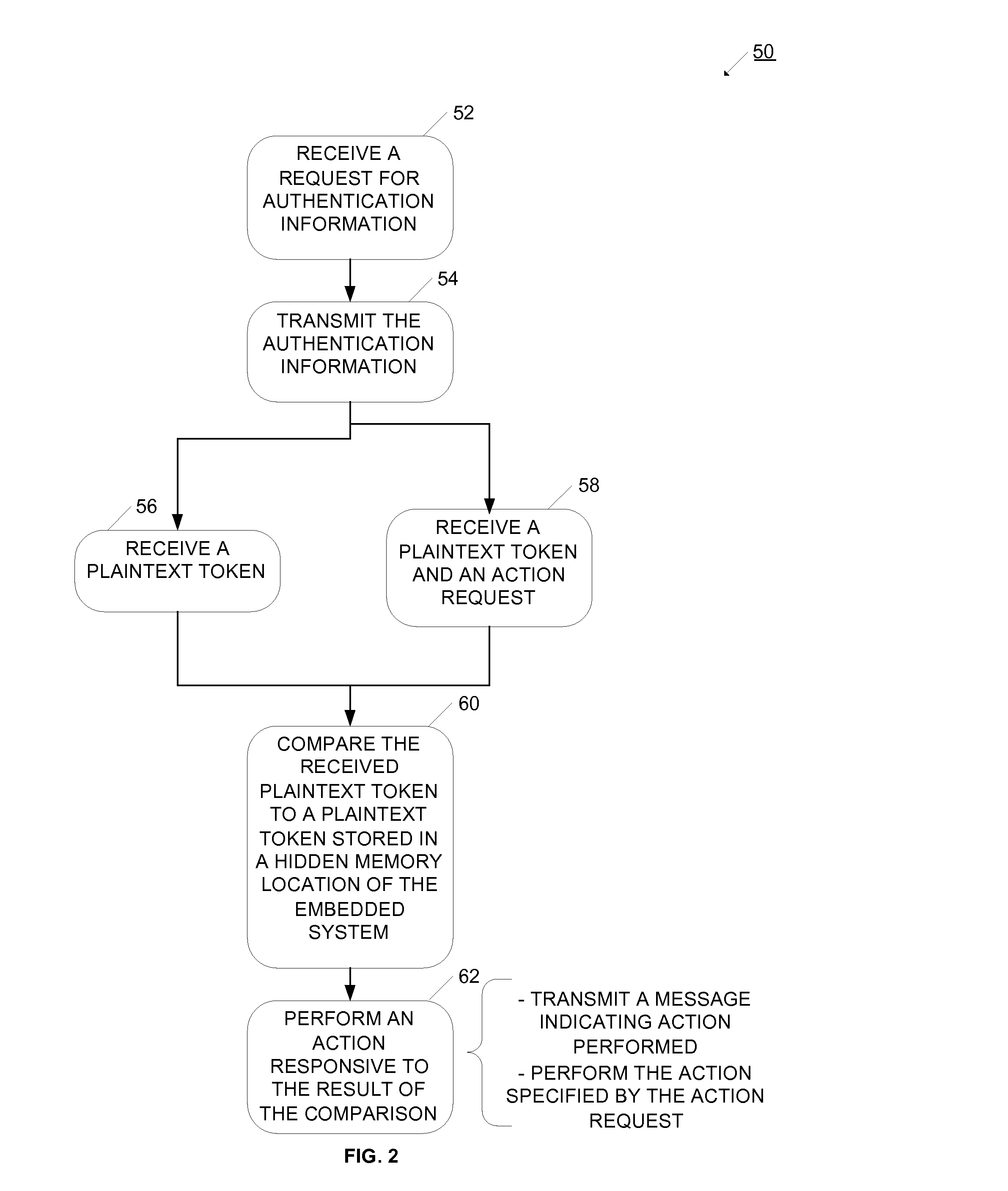
[0010] In one example, a random
plaintext number is stored as the hidden authentication message, and the user memory has authentication information that includes an identifier, as well as an encrypted version of the
plaintext number. When the integrated circuit is placed near a reader, the reader reads the authentication information, which is sent to a network operation center. The network operation center uses the identification information to retrieve a decryption key, and uses the key to decrypt the encrypted message to derive the
plaintext number. The plaintext number is sent to the reader, which communicates it to the integrated circuit. The integrated circuit does a simple logical compare between the received number and the hidden number, and if they match, the integrated circuit proceeds to perform an action. The action may be, for example, activating or deactivating the product the circuit is attached to. The hidden authentication message and the authentication information are related through a cryptographic process. In this example, the integrated circuit benefits from the cryptographic security, even though the integrated circuit only operates a relatively simple logic operation. In this way, a highly secure transaction is enabled without requiring significant
processing power or time at the integrated circuit.
[0011] In another example, an authentication code is stored as the hidden authentication message, and the user memory has authentication information that includes identifiers, as well as a public key that can be used to recreate the authentication code. When the integrated circuit is placed near a reader, the reader reads the authentication information, which is sent to a network operation center. The network operation center uses the identification information to retrieve a private key, and uses the public key, private key and other authentication information generate the authentication code. The authentication code is sent to the reader, which communicates it to the integrated circuit. The integrated circuit does a simple logical compare between the received code and the hidden code, and if they match, the integrated circuit proceeds to perform an action. The action may be, for example, activating or deactivating the product it is attached to. The hidden authentication message and the authentication information are related through a cryptographic process. In this example, the integrated circuit benefits from the cryptographic security, even though the integrated circuit only operates a relatively simple logic operation. In this way, a highly secure transaction is enabled without requiring significant processing power or time at the integrated circuit.
[0013] Advantageously, the present invention enables a highly secure and authenticated transaction, even when the authorizing circuit is operating in a low-power, low processing capability environment. This means that an RFID tag or other RF-enabled integrated circuit may be used to communicate sensitive information, and become an integral part of a secure transaction process. This enables an RF-enabled circuit to perform secured actions, thereby allowing manufacturers to enforce distribution and use rules
 Login to View More
Login to View More  Login to View More
Login to View More