Mask pattern inspecting method, inspection apparatus, inspecting data used therein and inspecting data generating method
a mask pattern and mask technology, applied in the direction of photomechanical equipment, instruments, image enhancement, etc., can solve the problems of inability to obtain desirable diffusion profiles, reduce accuracy in etching, and also the formation of diffusion layers, so as to shorten the etching and reduce the cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
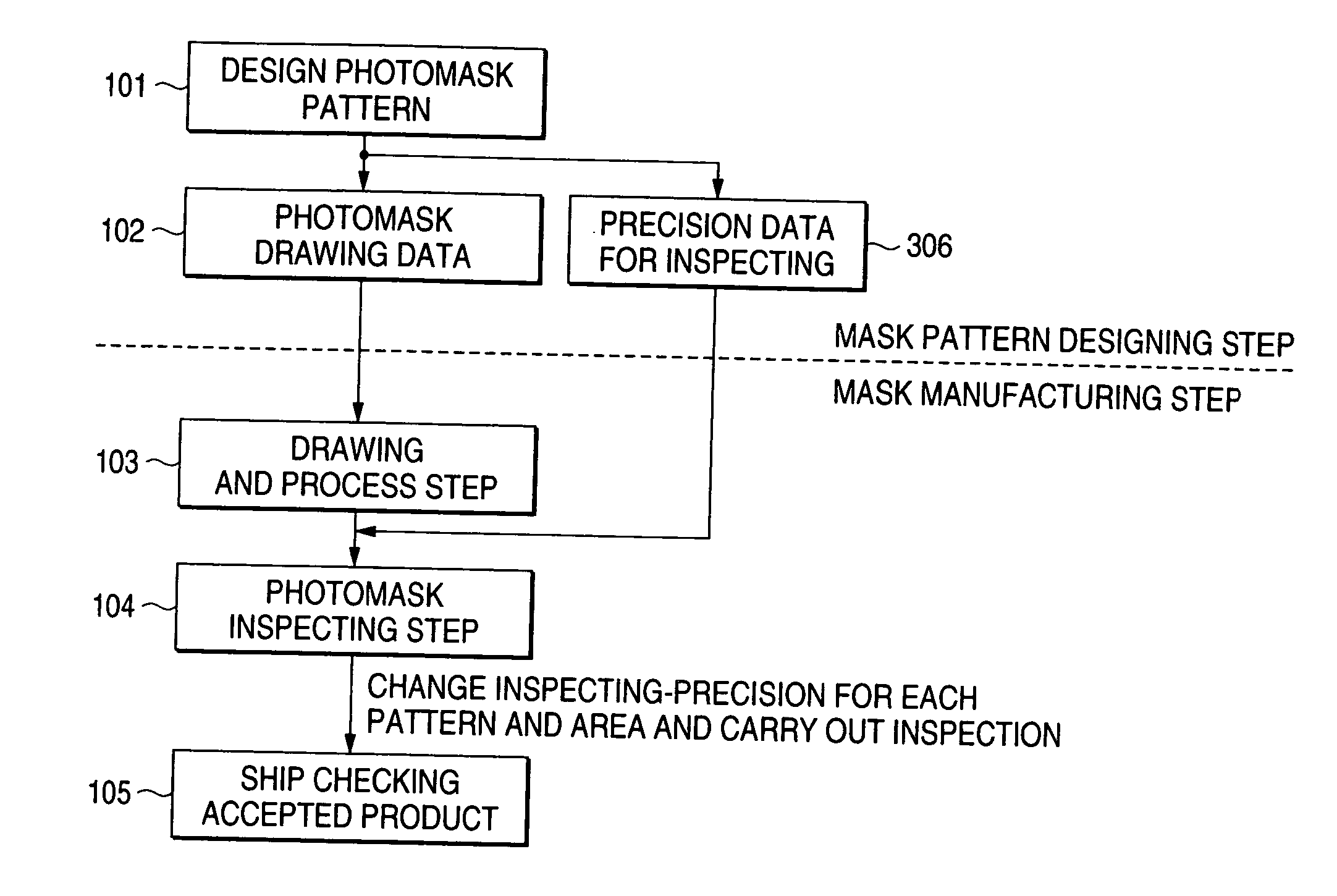
[0098] In a photomask inspecting method according to the invention, when inspecting a photomask for a semiconductor integrated circuit formed based on drawing pattern data, a drawing pattern of the semiconductor integrated circuit is classified into a plurality of ranks in accordance with a predetermined reference and is thus extracted, inspecting accuracy is determined for each of the ranks, and quality of the photomask is decided depending on whether the determined inspecting accuracy is satisfied.
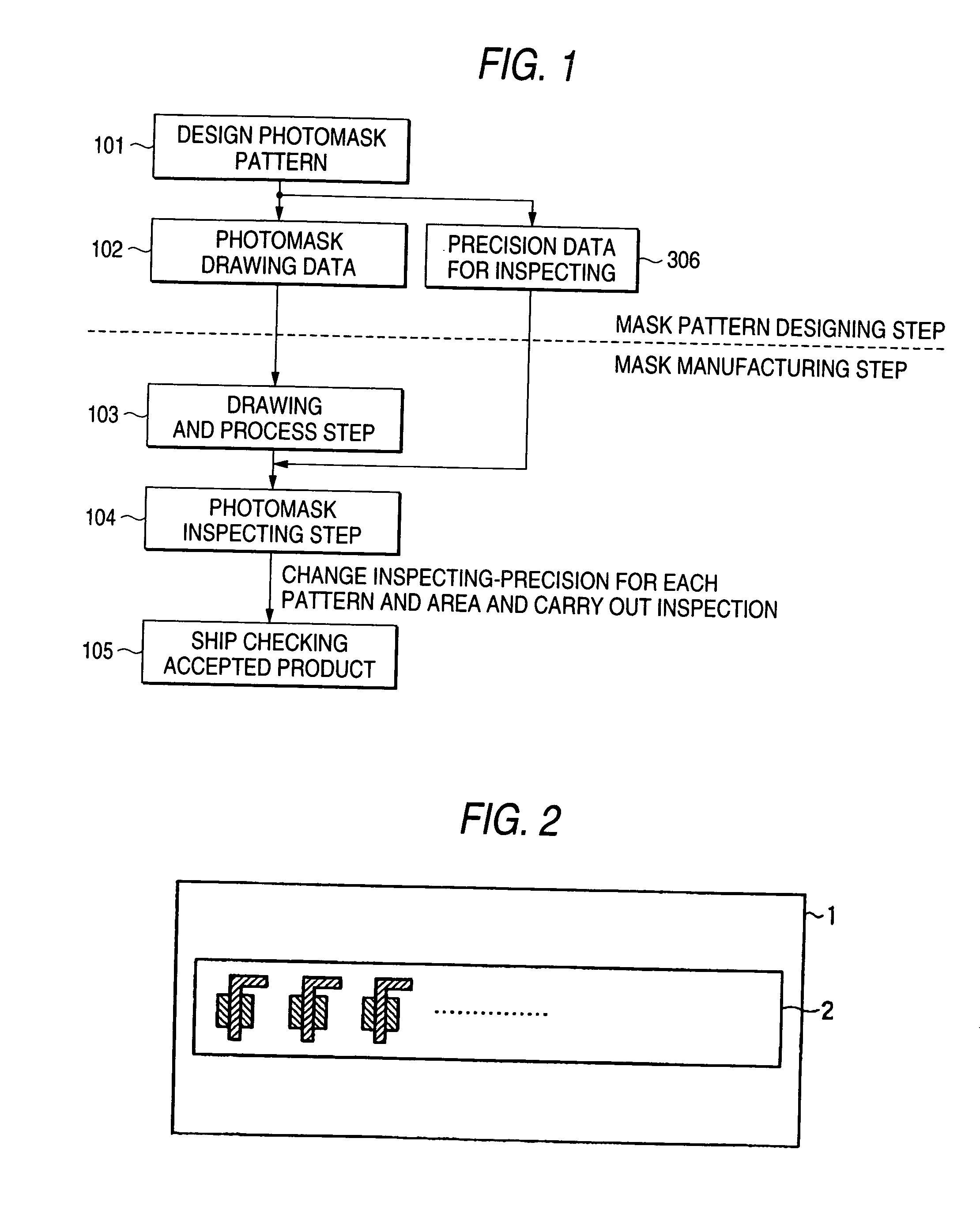
[0099]FIG. 1 shows a photomask inspecting flow according to the embodiment. While constant accuracy is specified from a design rule over a whole photomask in a conventional inspecting flow, inspecting accuracy data 306 are separately formed based on a photomask pattern obtained at a photomask pattern design step 101 and the inspection of the photomask is executed based on an inspecting accuracy reference set for each pattern area on the basis of the inspecting accuracy data 306.
[0100] ...
second embodiment
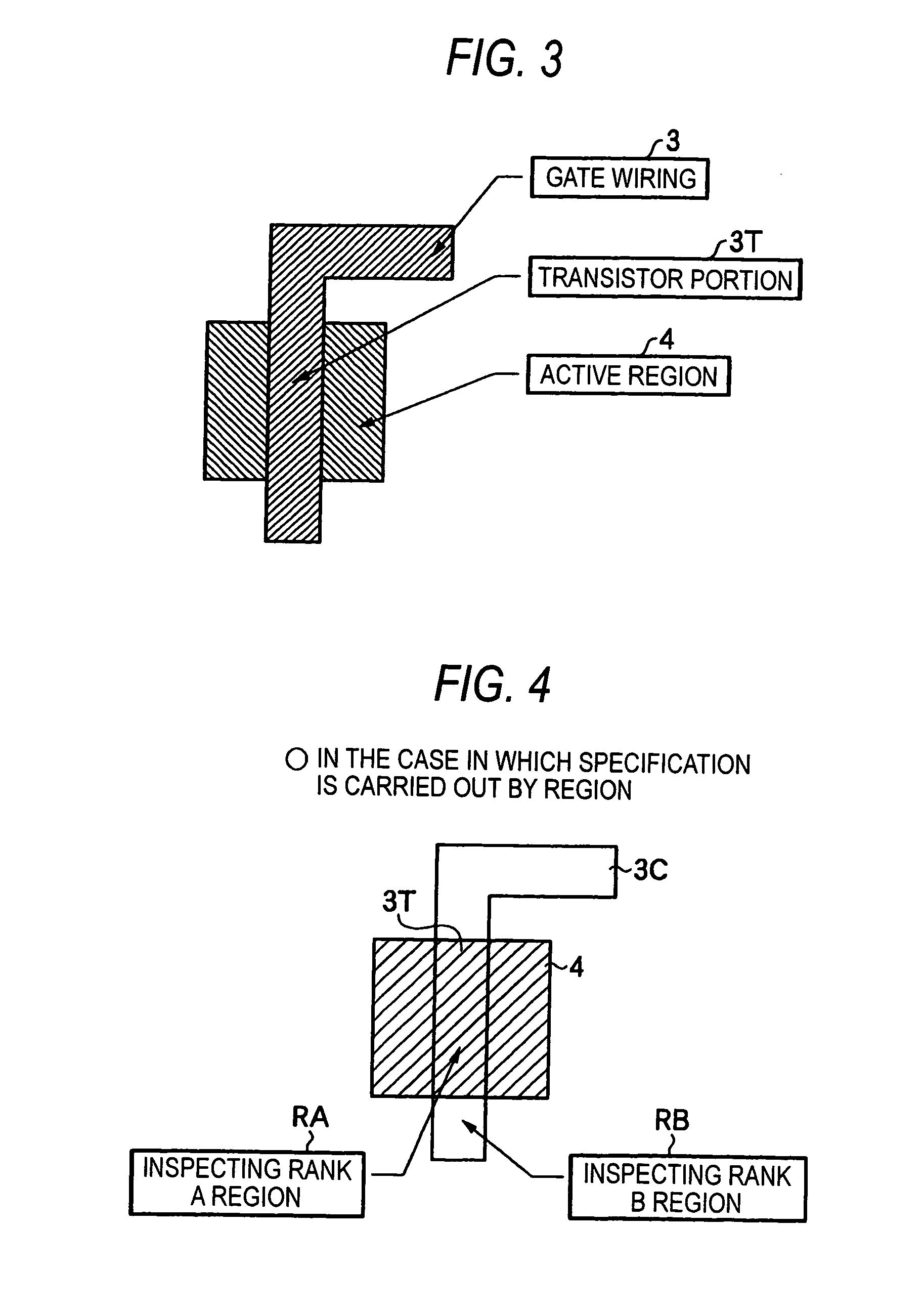
[0118] While the classification of the inspecting rank is specified for each region in the first embodiment, it may be specified for each pattern.
[0119] More specifically, as shown in FIG. 6, only the gate pattern of a region constituting a true gate region in the gate wiring 3 is set to be an An inspecting rank pattern PA corresponding to an inspecting rank with high accuracy, and the other patterns are set to be a B inspecting rank pattern PB corresponding to a lower rank.
[0120] Also in this case, at a photomask inspecting step, the embodiment is the same as the first embodiment except that a method of extracting inspecting data and an inspecting reference are different.
[0121] By this method, similarly, a channel length can reliably be maintained and a photomask of high quality can be implemented in a short time at a low cost in the same manner as in the first embodiment. By this method, particularly, it is possible to produce an advantage that data indicative of an inspecting ...
third embodiment
[0122] While the classification of the inspecting rank is specified for each region in the first embodiment, moreover, it may be specified by the edge of a pattern.
[0123] More specifically, as shown in FIG. 7, only the gate pattern edge of a region constituting a true gate region in a gate wiring 3 is set to be an An inspecting rank edge EA corresponding to an inspecting rank with high accuracy, and the other patterns are set to be a B inspecting rank edge EB corresponding to a lower rank.
[0124] Also in this case, the embodiment is the same as the first embodiment except that a method of extracting inspecting data and an inspecting reference are different at a photomask inspecting step.
[0125] According to this method, it is possible to obtain an advantage that a deciding rank can be set every edge as compared with the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| shape | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com