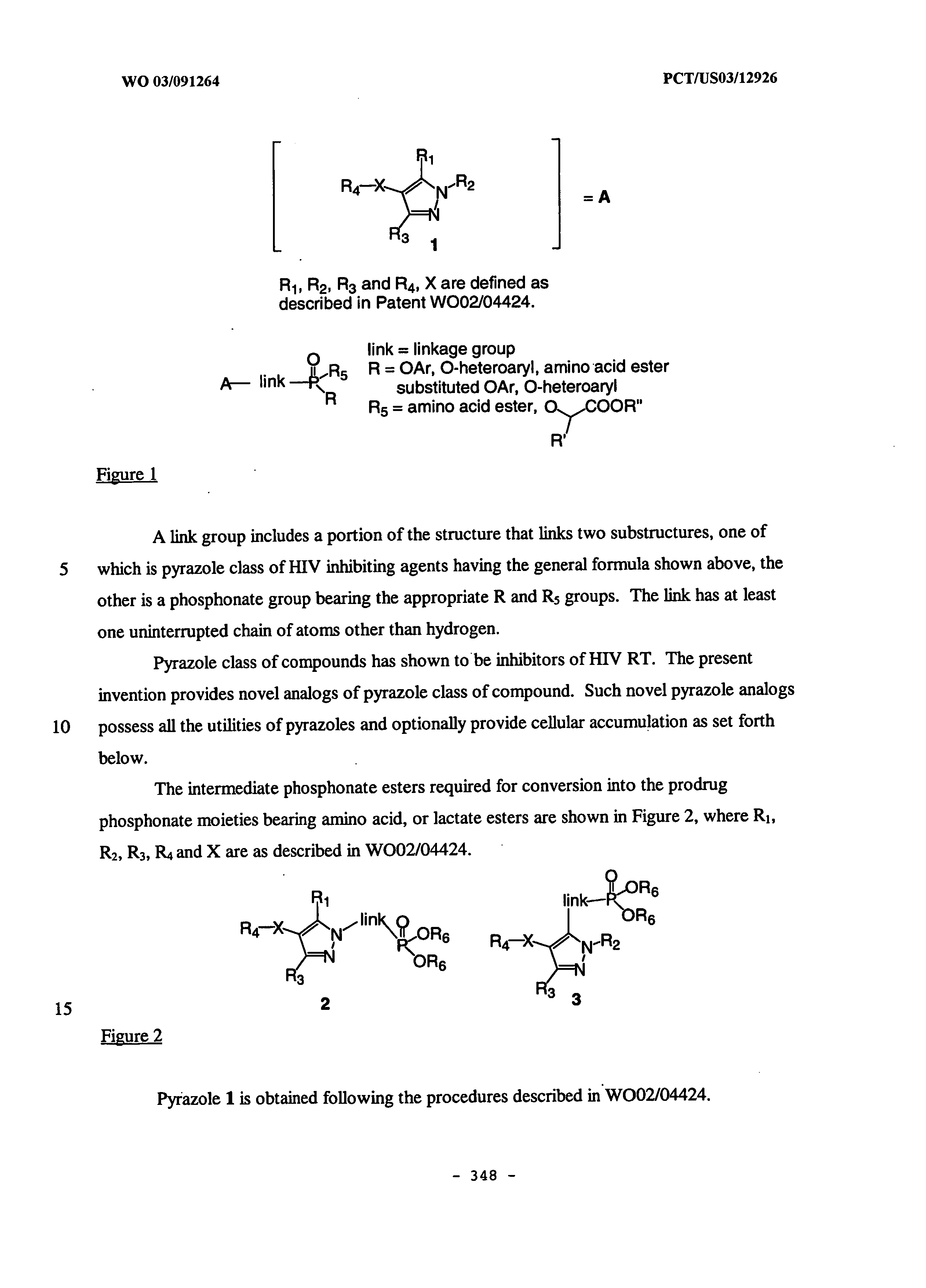
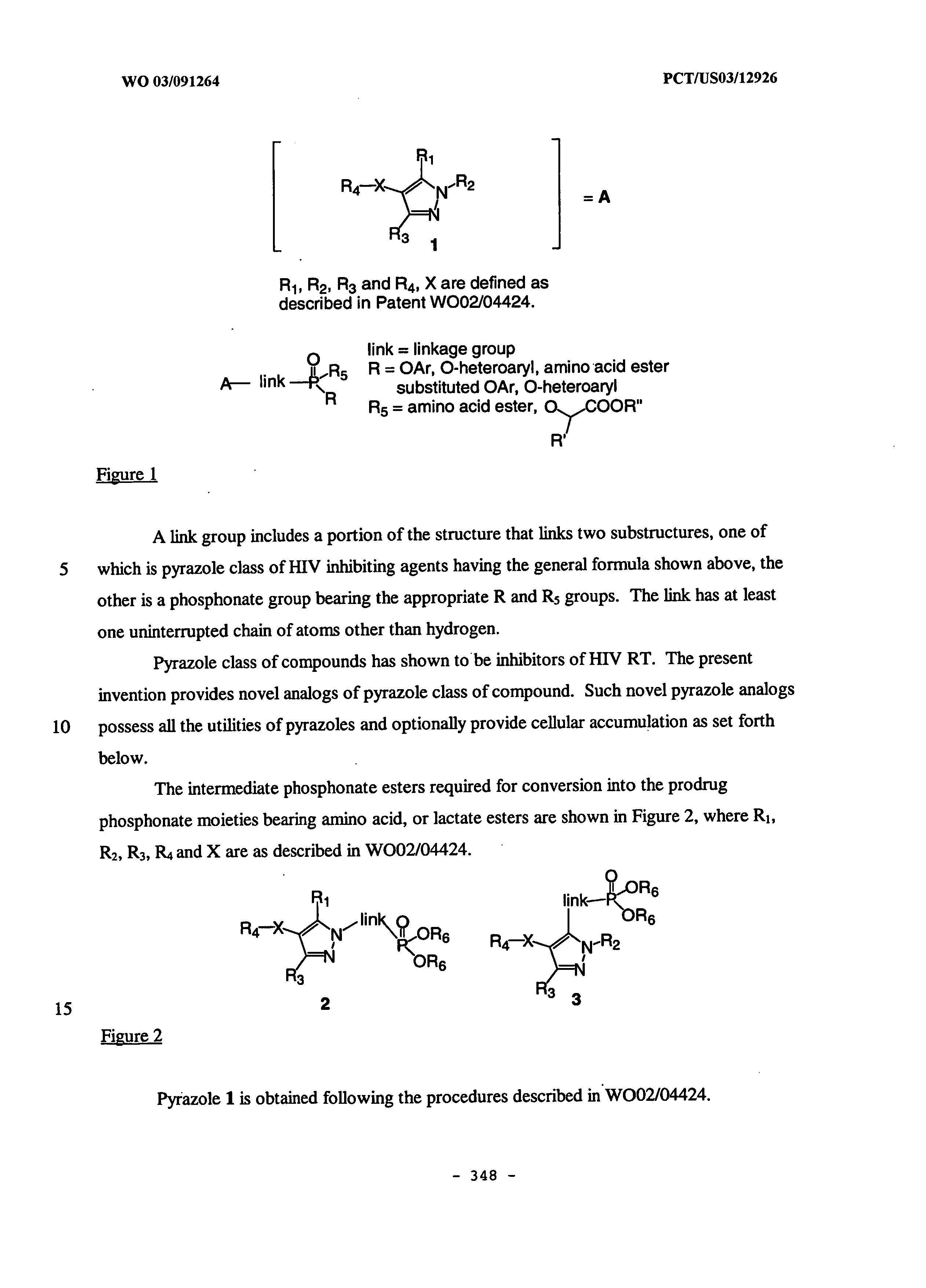
Non nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
a reverse transcriptase inhibitor and nucleoside technology, applied in the field of compounds with antiviral activity, can solve the problems of limited usefulness of resistant strains, 30 to 50% of patients currently fail combination therapy, and major public health problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
accumulation embodiment
A Cellular Accumulation Embodiment
[0232] Another embodiment of the invention is directed toward a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor compound capable of accumulating in human PBMCs. Accumulation in human PBMCs is described in the examples herein. Typically, the compounds of this embodiment further comprise a phosphonate or phosphonate prodrug. More typically, the phosphonate or phosphonate prodrug has the structure A3 as described herein. Each of the preferred embodiments of A3 described herein is a preferred embodiment of A3 in the present embodiment.
[0233] Optionally, the compounds of this embodiment demonstrate improved intracellular half-life of the compounds or intracellular metabolites of the compounds in human PBMCs when compared to analogs of the compounds not having the phosphonate or phosphonate prodrug. Typically, the half-life is improved by at least about 50%, more typically at least in the range 50-100%, still more typically at least about 100%, more typic...
example 1
[0555] To a solution of 2-aminoethylphosphonic acid (810 where n=2, 1.26 g, 10.1 mmol) in 2N NaOH (10.1 mL, 20.2 mmol) was added benzyl chloroformate (1.7 mL, 12.1 mmol). See Scheme 5. After the reaction mixture was stirred for 2 d at room temperature, the mixture was partitioned between Et2O and water. The aqueous phase was acidified with 6N HCl until pH=2. The resulting colorless solid was dissolved in MeOH (75 mL) and treated with Dowex 50WX8-200 (7 g). After the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes, it was filtered and evaporated under reduced pressure to give carbamate 28 (2.37 g, 91%) as a colorless solid.
[0556] To a solution of carbamate 28 (2.35 g, 9.1 mmol) in pyridine (40 mL) was added phenol (8.53 g, 90.6 mmol) and 1,3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (7.47 g, 36.2 mmol). After the reaction mixture was warmed to 70° C. and stirred for 5 h, the mixture was diluted with CH3CN and filtered. The filtrate was concentrated under reduced pressure and diluted with EtOAc. The organic phase...
example 10
[0570]
[0571] To a solution of alcohol 15 (42 mg, 0.10 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (5 mL) was added triethylamine (24 μL, 0.17 mmol) and bis(4-nitrophenyl) carbonate (46 mg, 0.15 mmol). See Scheme 18. After the reaction mixture was stirred for 4 h at room temperature, the mixture was partitioned between CH2Cl2 and water. The organic phase was dried over Na2SO4, filtered, and evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude product was chromatographed on silica gel (eluting 60-70% EtOAc / hexane) to give carbonic acid 5-(3,5-dichloro-phenylsulfanyl)-4-isopropyl-1-pyridin-4-ylmethyl-1H-imidazol-2-ylmethyl ester 4-nitro-phenyl ester 16 (47 mg, 82%) as a colorless oil.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com