Thin, double-wall molded seat frame system
a seat frame and double-wall technology, applied in the field of vehicular seats, can solve the problems of large mass of steel seat frame, large weight of molded seat frame, and large molding thickness of molded seat frame, and achieve the effect of facilitating the incorporation of reinforcement structure and good structural performan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] A preferred embodiment of a thin, double wall molded seat frame system according to the invention is generally shown in the drawing figures and discussed below.
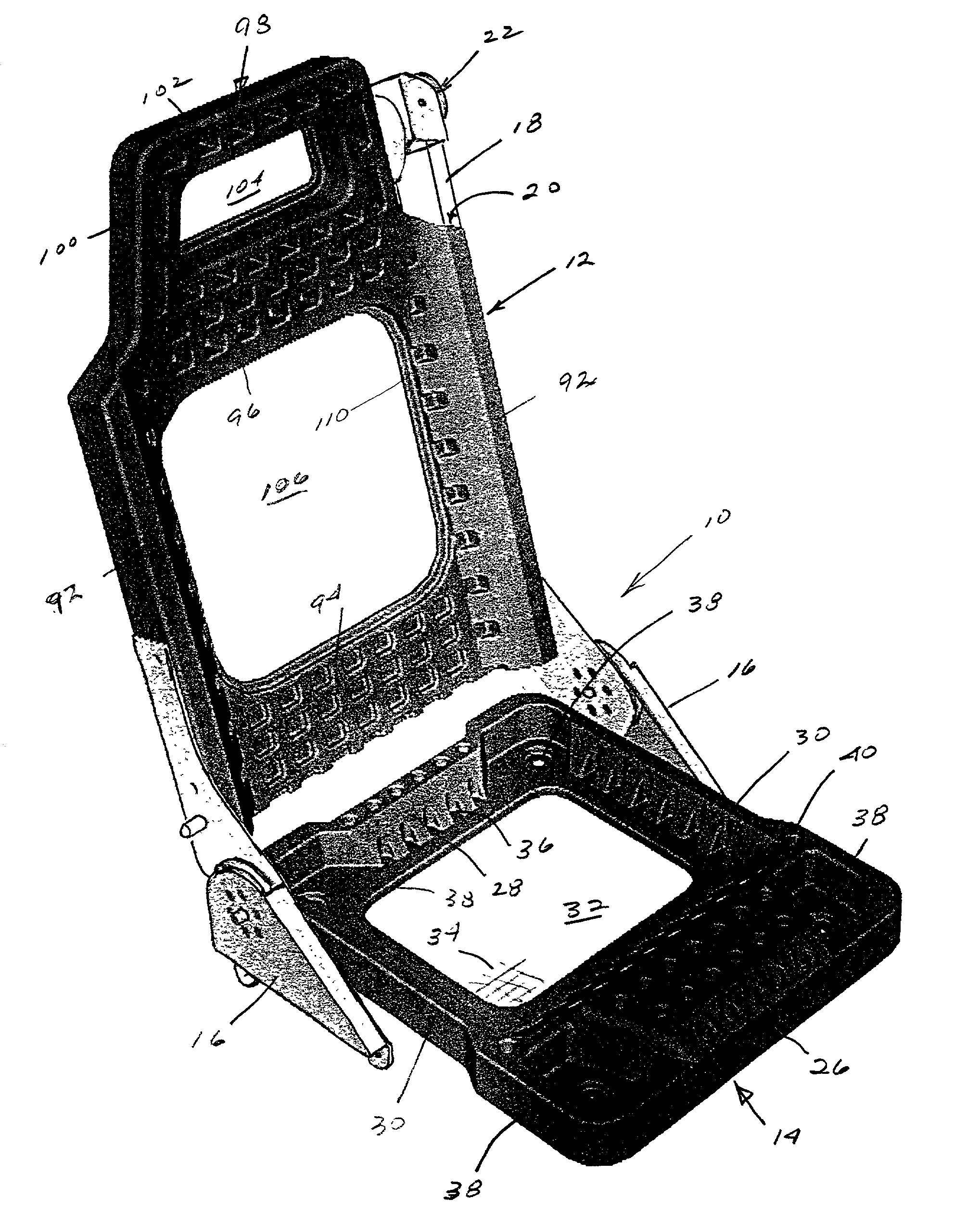
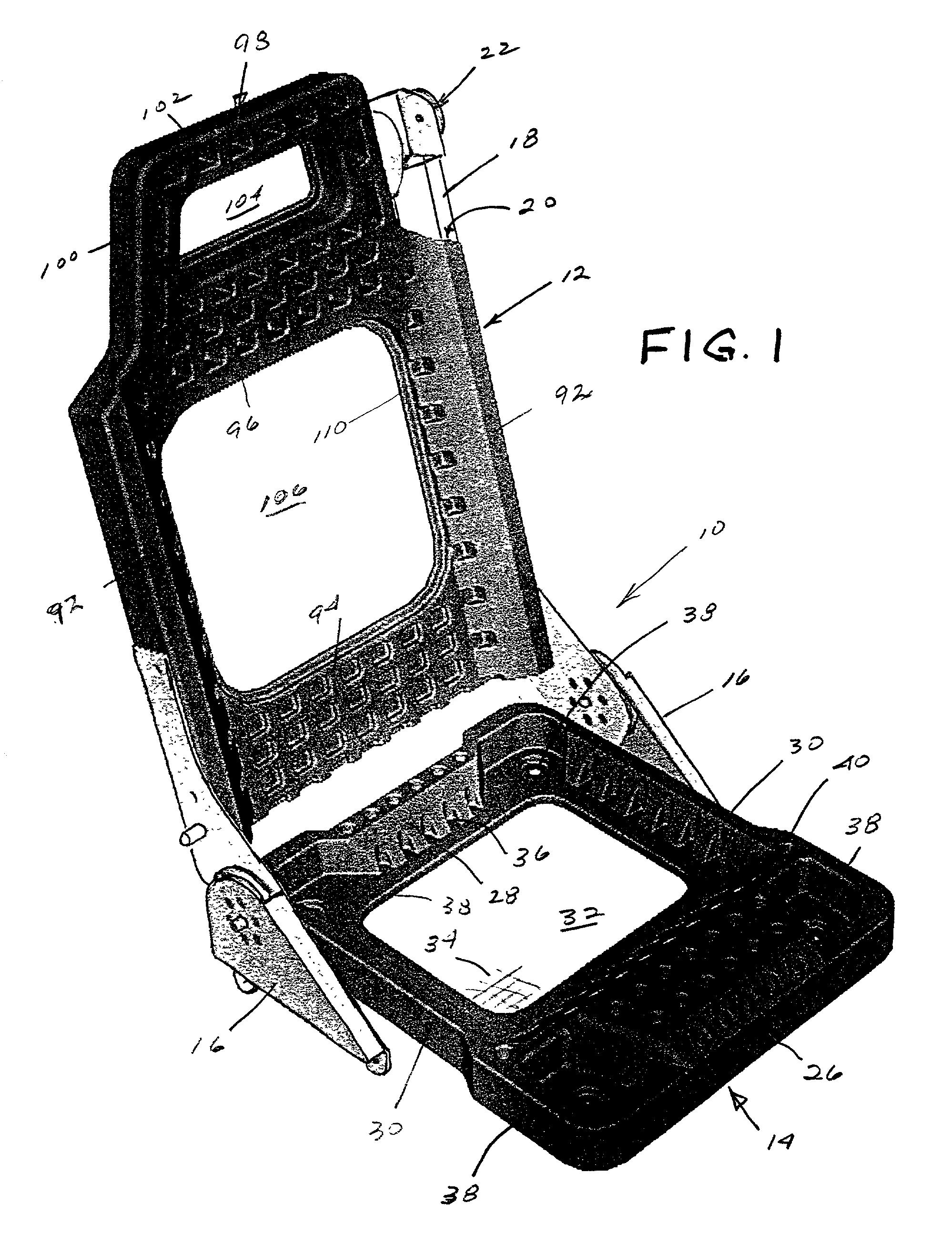
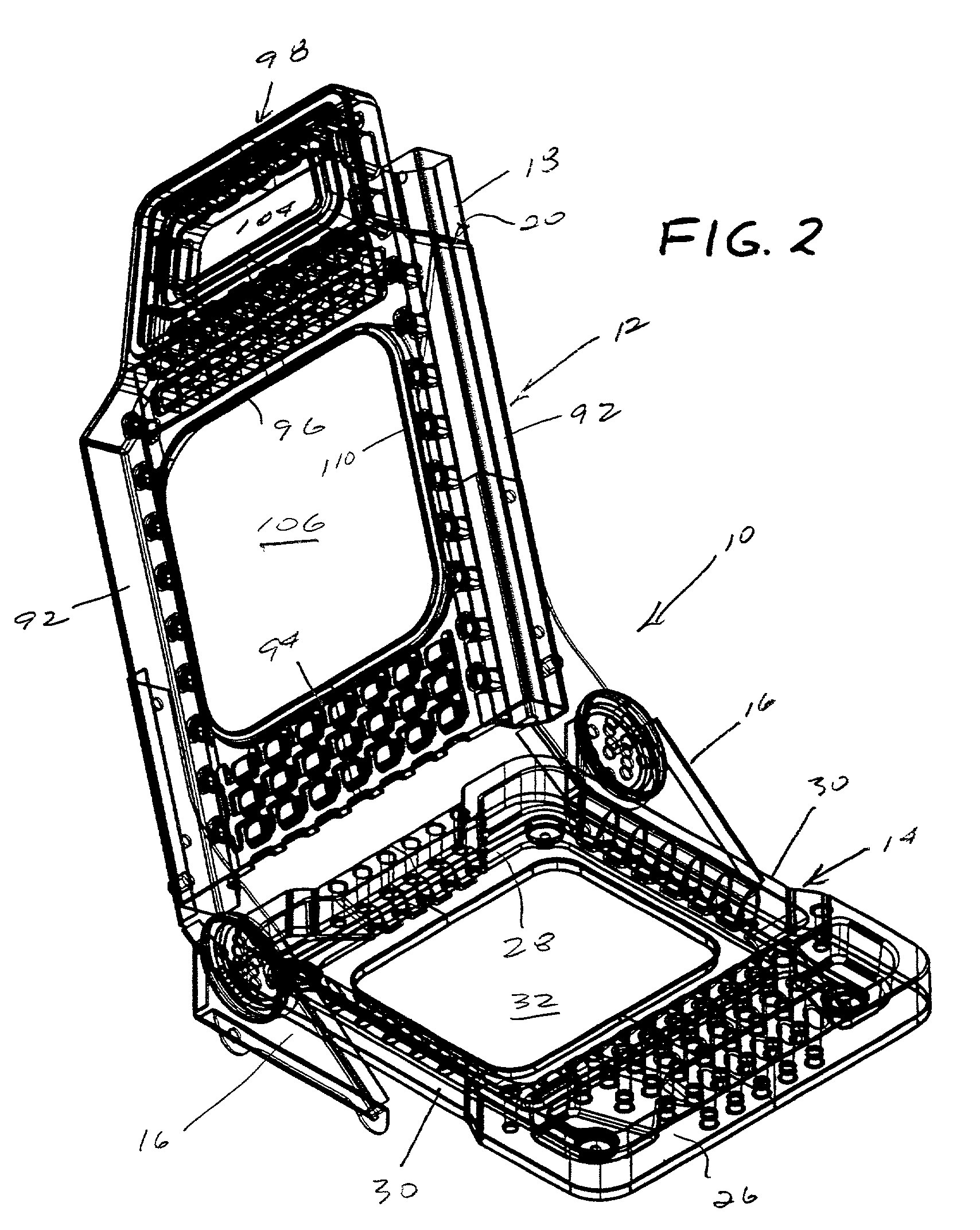
[0028] Referring to the drawings, FIG. 1 is a perspective view of a double wall seat frame assembly 10 constructed in accordance with the present invention. Seat frame assembly includes a seat back 12, a seat pan 14 and a recliner mechanism 16 interconnecting the seat back and seat frame. The recliner mechanism is known.
[0029] A reinforcement tower 18 extends through an internal cavity 20 on one side of the seat back. In FIG. 1, tower 18 is a restraint tower for a seat that incorporates an integral restraint system, wherein the safety belt is attached directly to the seat back. A seat belt retractor housing 22 is mounted on the top of tower 18. Where an integral restraint system is not employed, a conventional reinforcement tower 24 (FIG. 13) is employed instead of the longer restraint tower 18. The shorter reinforce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com