Electro-optical device and method of driving the same
a technology of optical devices and optical components, applied in the direction of optics, static indicating devices, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as extreme difficulty
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0078] Preferred Embodiment 1
[0079] In this embodiment, a wall mounted television set was manufactured by using the liquid crystal device utilizing the circuit structure as shown in FIG. 5, which will be described infra. Polycrystalline silicon that received laser annealing was used for TFT at the time of manufacturing.
[0080] The actual arrangement or structure of electrodes etc. corresponding to this circuit structure is shown in FIG. 6, for one picture element. The manufacturing method of the liquid crystal panel used in the first preferred embodiment will be first explained with reference to FIGS. 7 and 8. FIGS. 7 and 8 are cross sectional views and plan views of the liquid crystal panel, respectively. Referring to FIG. 7(A), a silicon oxide film was manufactured at a thickness of 1000-3000 angstroms as a blocking layer 51 by magnetron RF (high frequency) sputtering, on a glass substrate 50, which is not expensive such as quartz, and which can bear the thermal treatment of no mo...
embodiment 2
[0106] Preferred Embodiment 2
[0107] In this embodiment, a wall mounted television set manufactured by using a liquid crystal display device having a circuit structure as shown in FIG. 5, will be explained. Polycrystalline silicon subjected to laser annealing was used for TFT.
[0108] The manufacturing of a TFT part will be described infra according to FIG. 9. Referring to FIG. 9(A), a silicon oxide film was manufactured as a blocking layer 101 on an inexpensive glass substrate 100 which bears the heat treatment of not more than 700° C., e.g. approximately 600° C., at a thickness of 1000-3000 angstroms by magnetron RF (high frequency) sputtering. The conditions for the process were: in 100% oxygen atmosphere; the temperature for film formation was 15° C.; output was 400-800 W; and, pressure was 0.5 Pa. The rate of film formation was 30-100 angstroms / min, when quartz or single crystalline silicon was used as a target.
[0109] A silicon film 102 was manufactured thereon by plasma CVD. Th...
embodiment 3
[0124] Preferred Embodiment 3
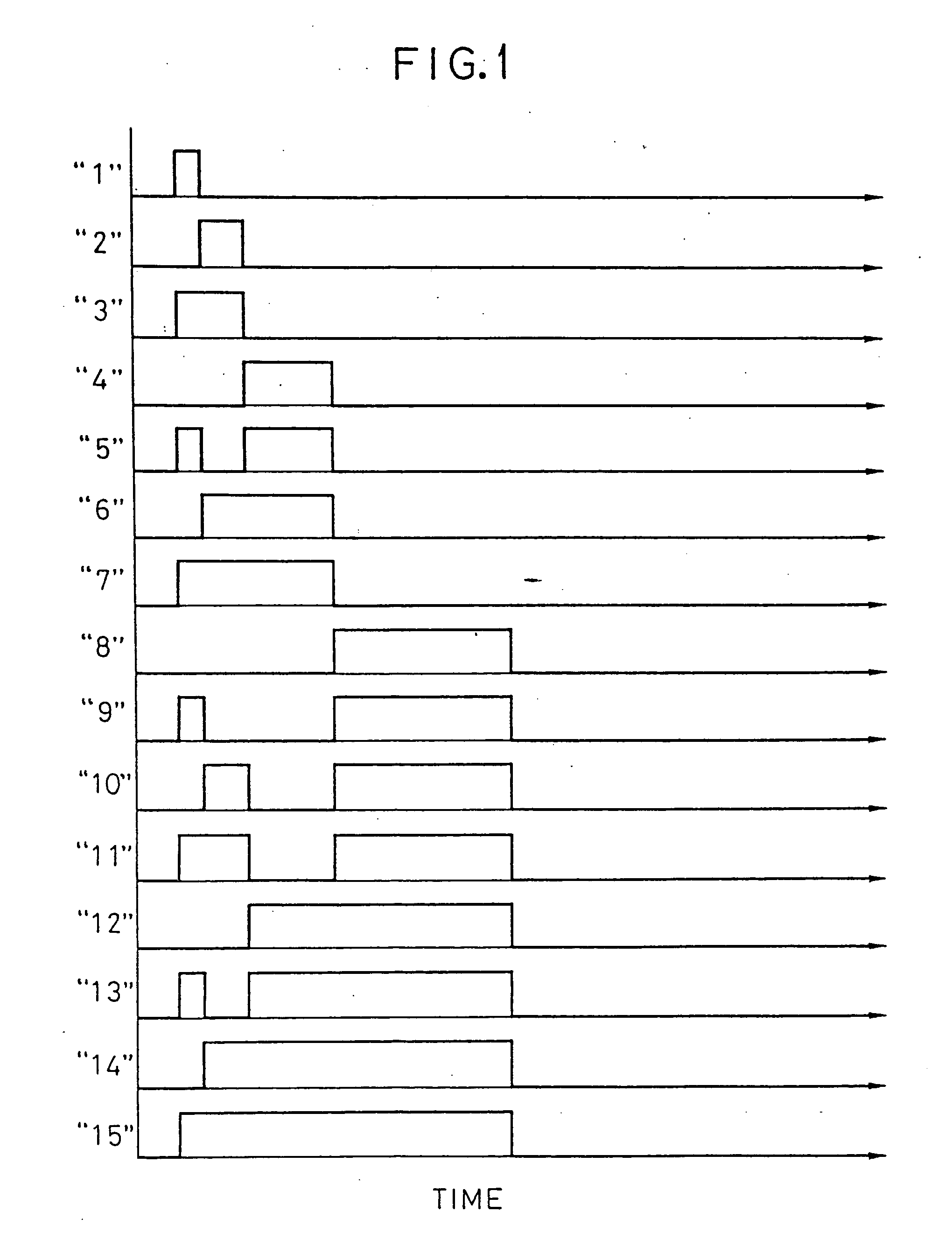
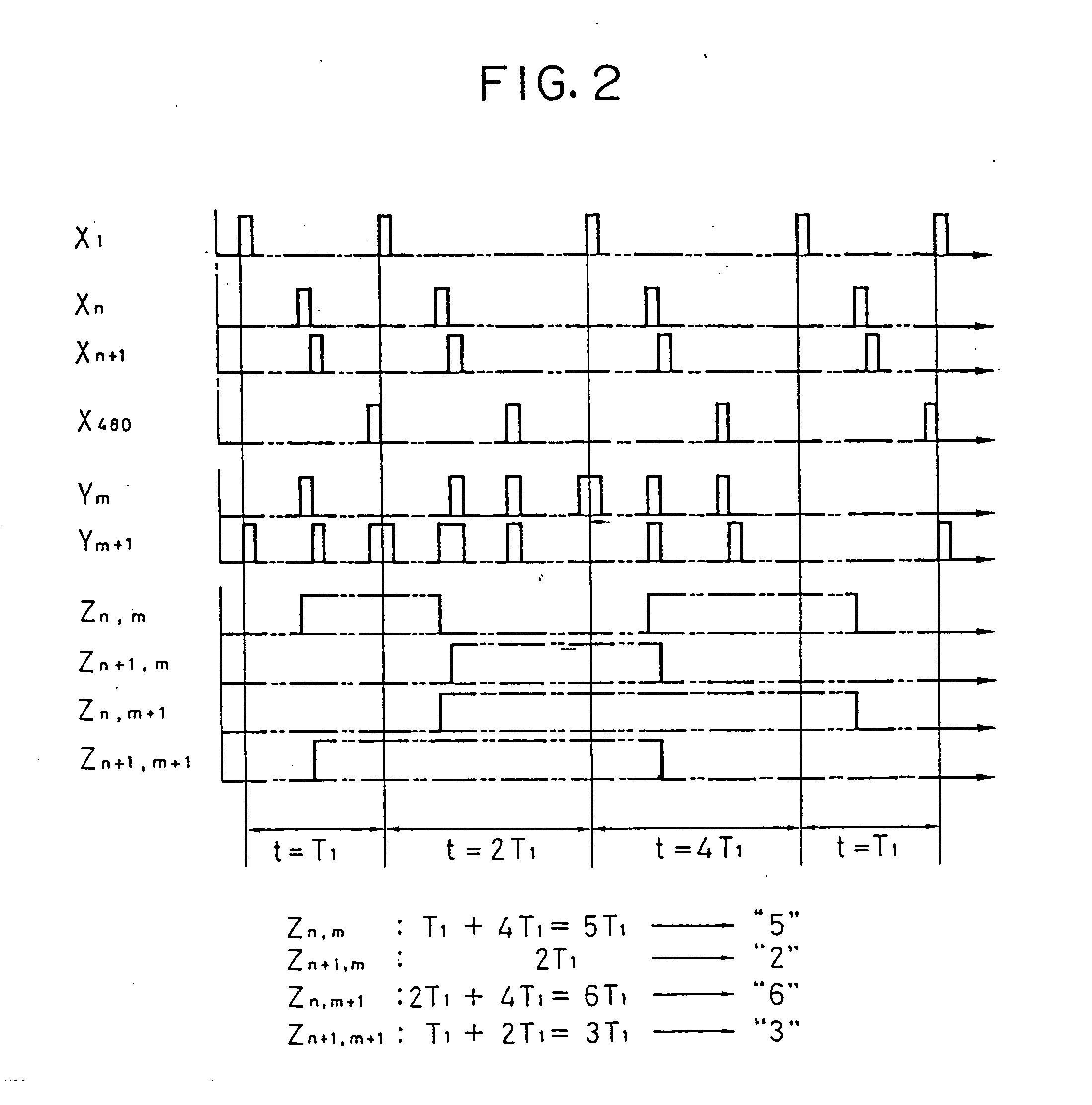
[0125] A device used when an actual monochrome television (NTSC) was driven in accordance with the present invention, is shown in FIGS. 20, 21 and 23, and examples of driving signals are shown in FIGS. 22 and 24.
[0126] A screen of the television and a peripheral circuit thereof are shown in FIG. 20, and the size of the matrix of the screen is 720×480. FIFO is thus of 720×480×3=1036800 bits, and a driver and a shift register of X-line are of 480 dots, while those of Y-line are of 720 dots. A data shift register of Y-line was of 16 bits×45. The timings of these were controlled by a sequence controller of gradation driving of LCD.
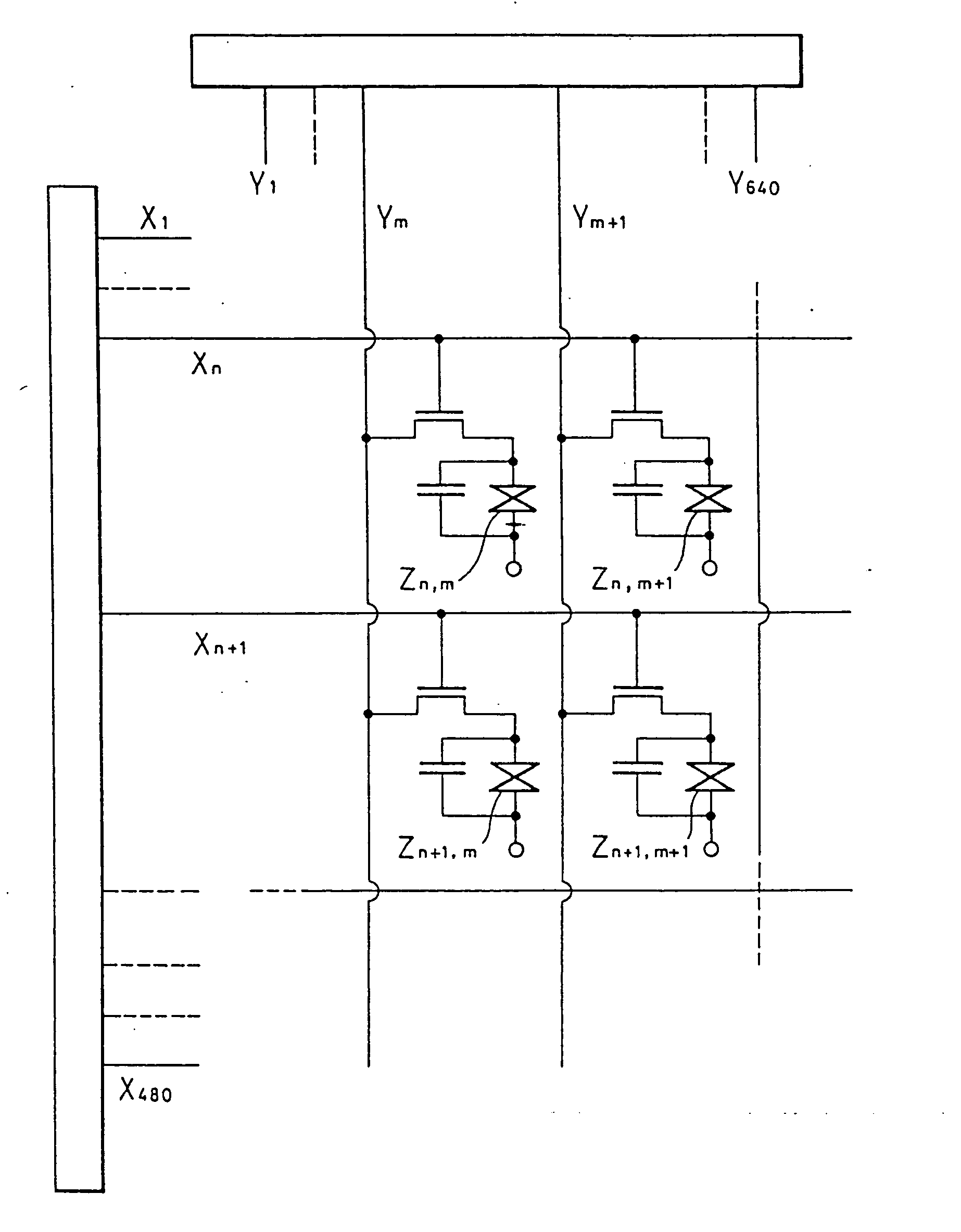
[0127] A polysilicon TFT CMOS (complementary field effect device) transfer gate circuit was used to form a matrix of the screen. The schematic circuit diagram related to the four picture elements is shown in FIG. 23. At the time of manufacturing, a normal low temperature thermal annealing crystallization method was adopted. The d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| response time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| response time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| voltage | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com