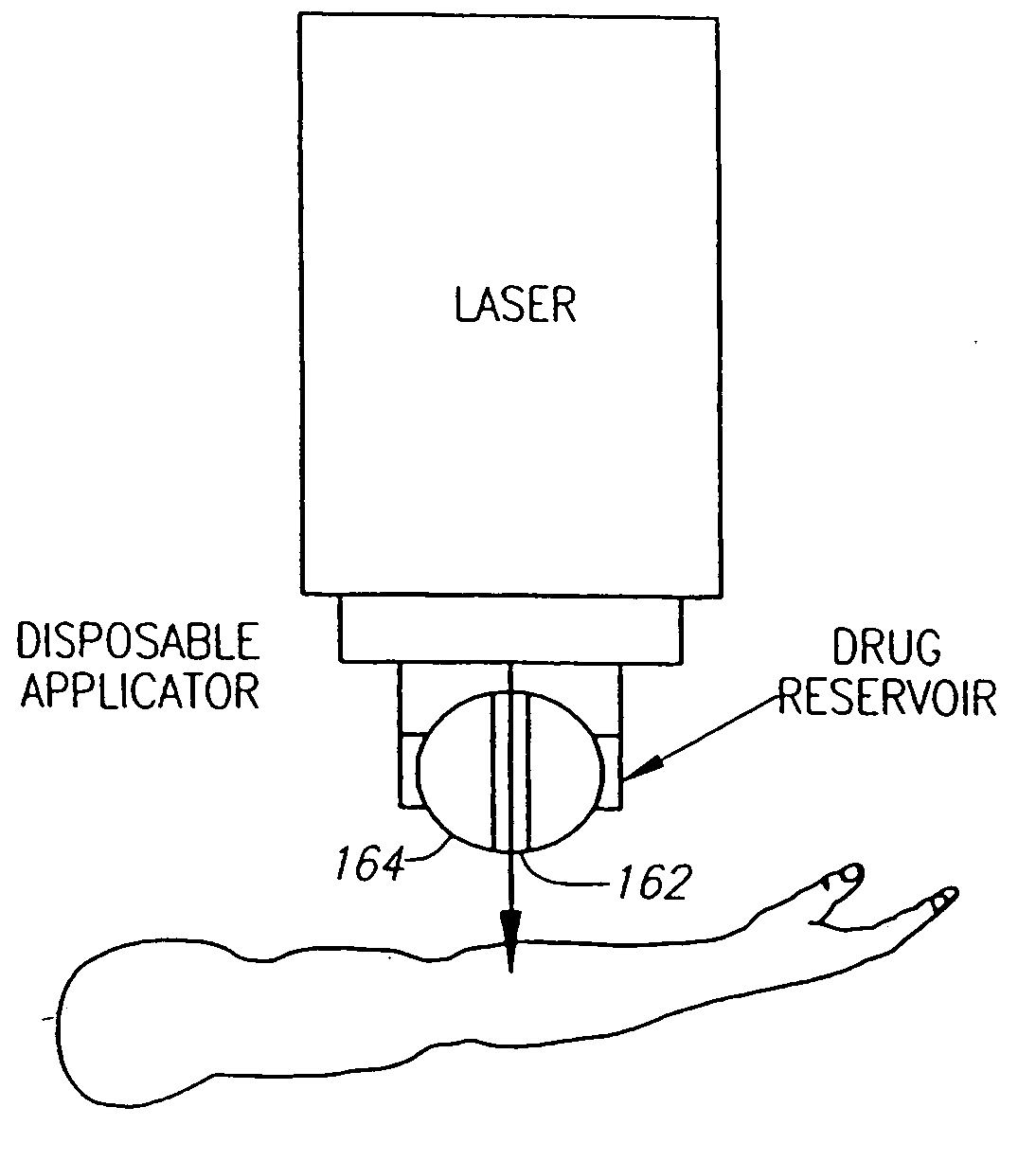
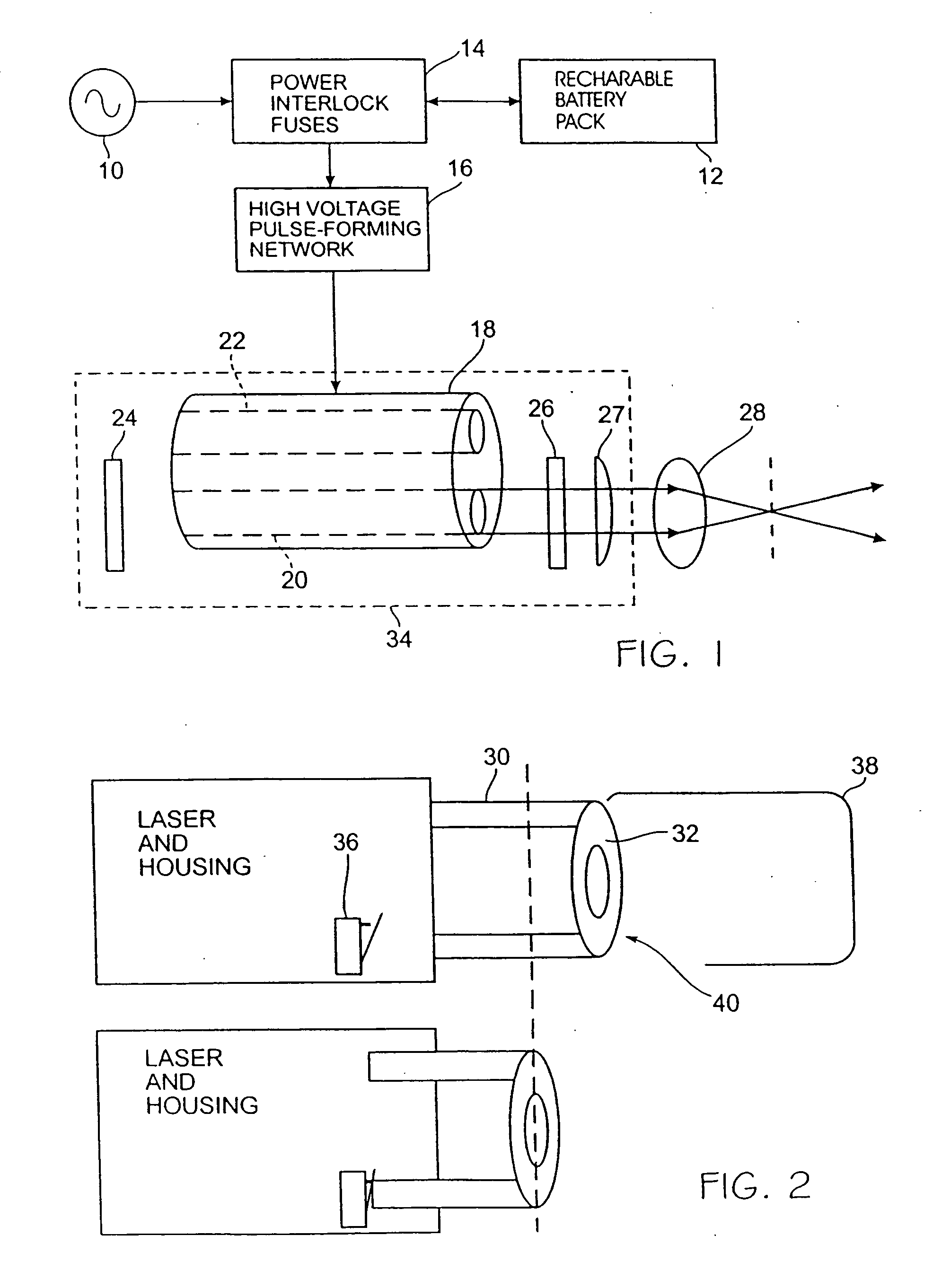
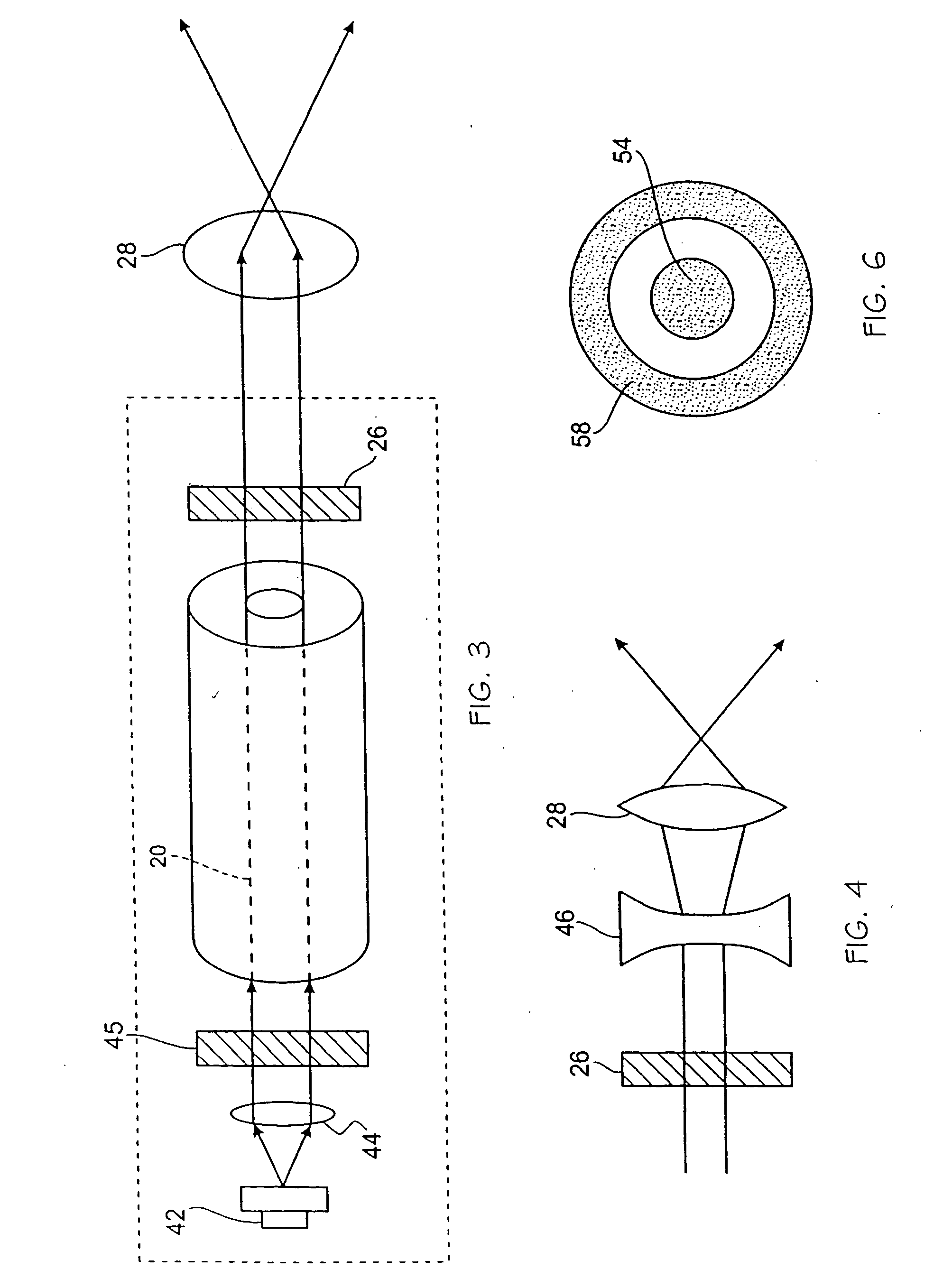
Removable tip for laser device with transparent lens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
The laser comprises a flashlamp (PSC Lamps, Webster, N.Y.), an Er:YAG crystal (Union Carbide Crystal Products, Washagoul, Wash.), optical-resonator mirrors (CVI Laser Corp., Albuquerque, N. Mex.), an infrared transmitting lens (Esco Products Inc., Oak Ridge, N.J.), as well as numerous standard electrical components such as capacitors, resistors, inductors, transistors, diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers, fuses and switches, which can be purchased from any electrical component supply firm, such as Newark Electronics, Little Rock, Ark.
example 2
An infrared laser radiation pulse was formed using a solid state, pulsed, Er:YAG laser consisting of two flat resonator mirrors, an Er:YAG crystal as an active medium, a power supply, and a means of focusing the laser beam. The wavelength of the laser beam was 2.94 microns. Single pulses were used.
The operating parameters were as follows: The energy per pulse was 40, 80 or 120 mJ, with the size of the beam at the focal point being 2 mm, creating an energy fluence of 1.27,2.55 or 3.82 J / cm2. The pulse temporal width was 300 μs, creating an energy fluence rate of 0.42, 0.85 or 1.27×104 W / cm2.
Transepidermal water loss (TEWL) measurements were taken of the volar aspect of the forearms of human volunteers. Subsequently the forearms were positioned at the focal point of the laser, and the laser was discharged. Subsequent TEWL measurements were collected from the irradiation sites, and from these the measurements of unirradiated controls were subtracted. The results (shown in FIG. 27)...
example 3
An infrared laser radiation pulse was formed using a solid state, pulsed, Er:YAG laser consisting of two flat resonator mirrors, an Er:YAG crystal as an active medium, a power supply, and a means of focusing the laser beam. The wavelength of the laser beam was 2.94 microns. A single pulse was used.
The operating parameters were as follows: The energy per pulse was 60 mJ, with the size of the beam at the focal point being 2 mm, creating an energy fluence of 1.91 J / cm2. The pulse temporal width was 300 μs, creating an energy fluence rate of 0.64×104 W / cm2.
The volar aspect of the forearm of a volunteer was placed at the focal point of the laser, and the laser was discharged. After discharge of the laser, the ablated site was topically administered a 30% liquid lidocaine solution for two minutes. A 26G-0.5 needle was subsequently inserted into the laser ablated site with no observable pain. Additionally, after a 6-minute anesthetic treatment, a 22G-1 needle was fully inserted into t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com