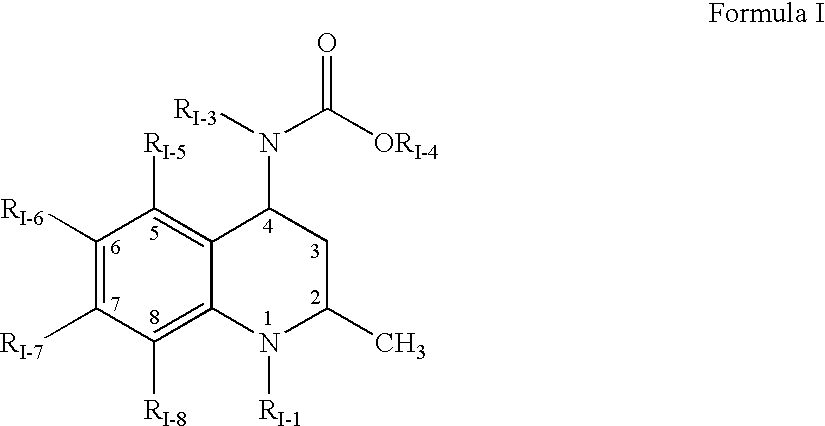
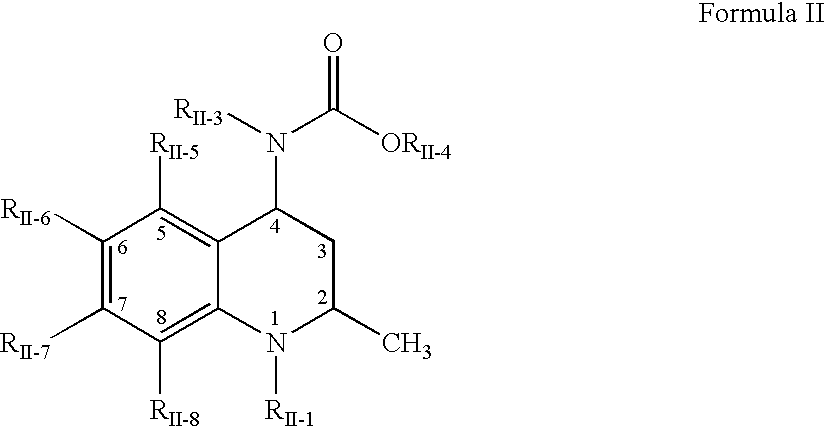
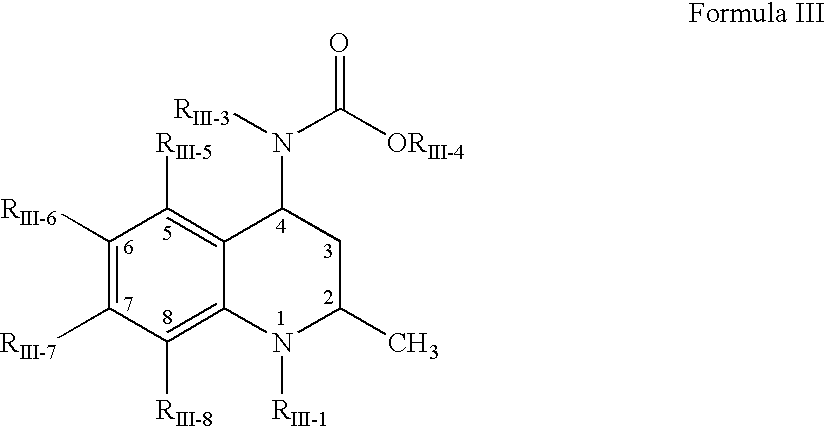
Pharmaceutical compositions of dispersions of drugs and neutral polymers
a technology of neutral polymer and pharmaceutical composition, which is applied in the direction of powder delivery, amide active ingredients, macromolecular non-active ingredients, etc., can solve the problems of drug degradation within the dispersion, loss of potency of the composition, and inability to chemically stable drugs in the dispersion, so as to improve the chemical stability of acid-sensitive drugs, enhance aqueous concentration and bioavailability, and minimize the loss of potency and generation of impurities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-2
[1313] This example discloses solid amorphous dispersions of an acid-sensitive, low-solubility drug and neutral polymer. For Example 1, a dispersion of quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid [4(R)-carbamoyl-1(S)-3-fluoro-benzyl)-2(S),7-dihydroxy-7-methyl-octyl] amide (Drug 1) and the neutral polymer hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC E3 Prem) was made by preparing a solution containing 0.125 wt % Drug 1 and 0.375 wt % HPMC in methanol, and spraying the solution into a drying chamber using an atomizing spray nozzle as described below. For Example 2, a dispersion of Drug 1 with the neutral polymer polyvinyl pyrollidone (PVP-Plasdone K-29 / 32 available from ISP Technologies Inc., Wayne, N.J.) was made by preparing a solution containing 0.33 wt % Drug 1 and 1.0 wt % PVP in acetone / methanol (9 / 1, wt / wt), and spray-drying the solution as described below.
[1314] For Control C1, a dispersion of Drug 1 with hydroxy propyl methyl cellulose acetate succinate, LF-grade (HPMCAS-LF) (with about 14-18 wt %...
example 3
[1316] In this example the chemical stability of the dispersions of Examples 1 and 2 was assessed by monitoring the potency of the drug before and after exposure to increased temperatures and relative humidity (RH) in accelerated-aging studies. Dispersions of Examples 1 and 2, and Control C1, were placed in two controlled atmosphere chambers: one chamber maintained at 70.degree. C. (no RH control); the second chamber maintained at 40.degree. C. and 75% RH. Potencies of the dispersions before and after storage were determined using HPLC. A Kromasil C.sub.4HPLC column was used with a mobile phase of 45 vol % of 0.2 vol % H.sub.3PO.sub.4, and 55 vol % acetonitrile. UV detection was measured at 245 nm. Drug 1 potency was the percent of the total HPLC peak area corresponding to the theoretical amount of drug originally present in the dispersion prior to storage based on the amount of drug present in the initial solutions before spray-drying. The results are shown in Table 2 below.
2TABLE ...
example 4
[1318] In this example the dispersions of Examples 1 and 2 were tested to show that the dispersions provided concentration-enhancement of the drug in aqueous solution. For Control C2, the crystalline form of the drug alone was used without further processing. For this test, 7.2 mg of the dispersions of Examples 1 and 2, and 3.6 mg of Control C2, was added to respective microcentrifuge tubes. The tubes were placed in a 37.degree. C. temperature-controlled bath, and 1.8 mL phosphate buffered saline (PBS) at pH 6.5 and 290 mOsm / kg was added to each. The samples were quickly mixed using a vortex mixer for about 60 seconds. The samples were centrifuged at 13,000 G at 37.degree. C. for 1 minute. The resulting supernatant solutions were then sampled and diluted 1:6 (by volume) with methanol and then analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The contents of the tubes were mixed on the vortex mixer and allowed to stand undisturbed at 37.degree. C. until the next sample was t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| solubility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| solubility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wt % | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com