Method for establishing anti-hepatitis C virus drug screening experimental animal model
A hepatitis C virus and drug technology, applied in the field of establishing anti-hepatitis C virus drug screening, can solve the problems of low model success rate, simple genotype, and low virus concentration, and achieve the effect of high model success rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Embodiment 1, artificial synthesis and quantification of hepatitis C virus
[0033] ①Synthesis of hepatitis C virus
[0034] Take the carrier pHCV-2 (CCTCC M201013) obtained in patent 200311111111, take 1 μg of ScaI enzyme-digested pHCV-2 and add it to 100 μl of OPTI-MEM, take 1 μg of pHCV-2 and add it to 100 μl of OPTI-MEM and let it stand at room temperature for 15 minutes; And take 5 microliters of LF2000 and add 95 microliters of OPTI-MEM to mix at room temperature for 15 minutes, mix the carrier and LF2000, and transfect for 10 5 Hela cells, and two control groups without carrier and without LF2000, after 6 hours of transfection, remove the transfection medium and replace it with DMEM containing 2.5% fetal bovine serum, DMEM medium contains 10 7 pfu vTF7-3 (ATCC N0 VR-2153) recombinant poxvirus, and added rifampicin 10 mg / ml. After 2 hours of inoculation, the inoculum was removed and the cells were cultured in DMEM containing 2.5% fetal bovine serum. After 48-72...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Embodiment 2, establishment and confirmation of animal model:
[0042] Animal blood is drawn, and the hepatitis C virus in the animal is detected by PCR method, and the hepatitis C of the animal is screened. All experimental animals were negative in PCR test before being inoculated with artificially synthesized hepatitis C virus. The artificially synthesized virus was inoculated with 0.8ml from the tail vein, and 0.6ml was injected intraperitoneally on the second day and the third day respectively, the inoculation volume was 2ml, and the viral load of each animal was 10 5 C and above, divided into 7 groups. The success rate of the positive model after vaccination varies with the viral load, and the viral load of each animal is inoculated at 104c including 10 4 c, The success rate of establishing the animal model of hepatitis C virus is below 34%. Each animal was inoculated with a viral load of 10 9 c includes 10 9 c. The success rate of establishing the animal mode...
Embodiment 3
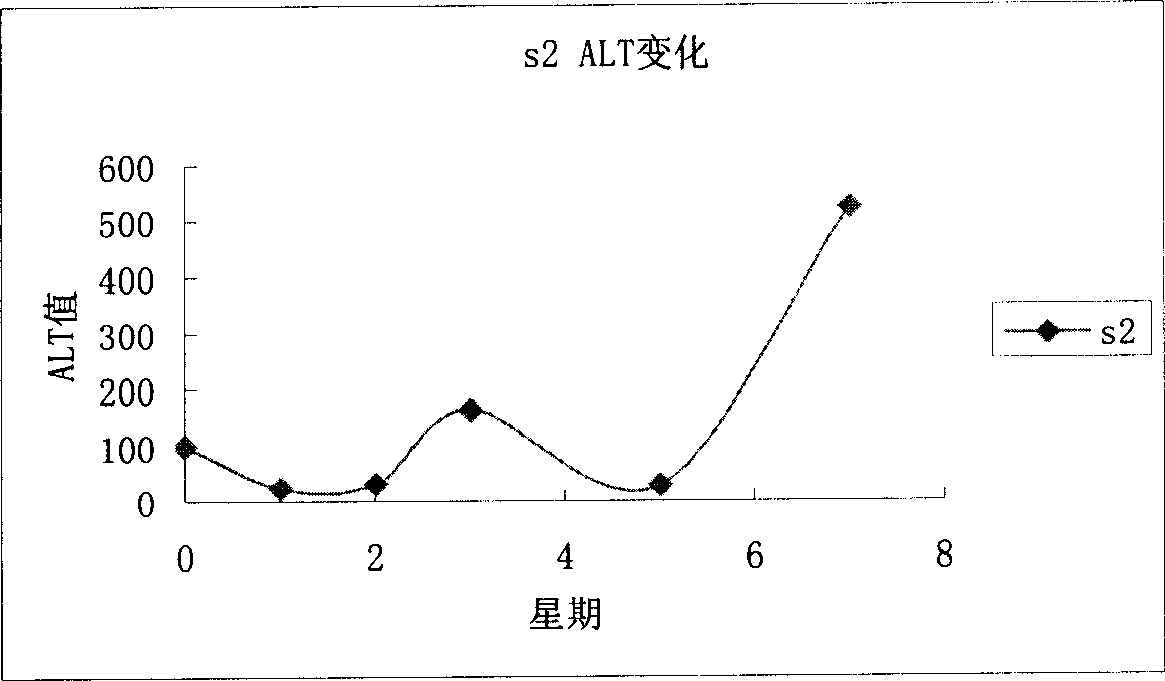
[0072] Example 3, Hepatitis C virus positive tree shrew model screening anti-hepatitis C virus drug selection.
[0073] Select 40 successfully infected animals (RT-PCR, positive immunohistochemistry) and randomly divide them into two groups, A and B, and draw blood from 10 animals in each group to detect HCV viral load with placebo (normal saline), PEG IFN-α- 2a (Roche), PEG IFN-α-2bRoche), ribavirin ribavirin, RBV Roche) administration, dose according to PEG IFN-α-2a 1.5μg / kgSQ (subcutaneous injection) once a week PEG IFN-α-2bRoche ) 1.0μg / kg SQ (subcutaneous injection) RBV once a week, body weight less than 150g 2mg orally twice a day, body weight greater than 150g 3mg orally twice a day after oral administration, draw blood at 1, 2, 4, and 8 weeks for HCV viral load quantity.
[0074] 1 week
[0075] 1 week
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com