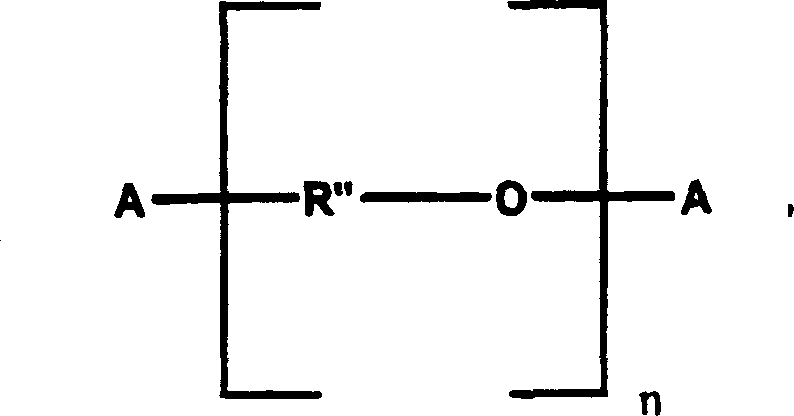
Thermoplastic elastomer based on polycondensates
A technology of thermoplastic elastomers and polycondensates, which is applied in the field of new thermoplastic elastomers to achieve good UV stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1: Preparation of PA12 prepolymer with OH end groups
[0036] Add 25.00 g of high molecular weight PA12 to a 250 ml three-necked flask by weighing, and flush with extremely pure nitrogen. After adding 0.5 g of dimethyl adipate to block the amino end groups, the particles were melted at a metal bath temperature of 250° C. under a nitrogen atmosphere. 4.274 g of adipic acid (29.27 mmol) as a splitting agent was added to the melt with stirring and stirred for 15 minutes. The obtained number group terminated prepolymer (number average molecular weight M n 1000; 29.3 mmol) was immediately further processed in the molten state.
[0037] After cooling the melt to 180 °C, a micro-distillation column was attached to the flask. A solution of 8.80 g of glycidylphenyl ether (58.6 mmol) dissolved in 10 ml of dried N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) was then rapidly added to the melt under stirring. The batch was stirred for an additional 2 hours, the supply of ultra pure nitrogen...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Preparation of isocyanate-terminated PTHF prepolymer
[0039] 29.00 g (29 mmol) of dried PTHF-1000 with OH end groups were melted at 80° C. and degassed alternately by evacuation and nitrogen. Then 8.780 g of 1,6-hexamethylene diisocyanate (52.2 mmol) was rapidly added to the material while stirring at 80° C. and the reaction mixture was mixed uniformly. The temperature was then increased to 120°C. The theoretically calculated NCO concentration is reached after about 150 minutes at 120° C. under these conditions. The reaction was terminated after 3 hours; the melt of the prepolymer was used directly in Example 3.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Example 3: Kneader reaction (reaction coupling)
[0041] The chamber of the Haake laboratory kneader was heated to 200°C and the rotation speed was adjusted to 90 revolutions per minute. The melt of Example 1 and the melt of Example 2 were added successively to the kneader. Five minutes after the feed addition was complete, the chamber temperature was lowered to 150°C, the chamber was opened and the product was removed. After hardening an elastic material with thread-forming properties is obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com