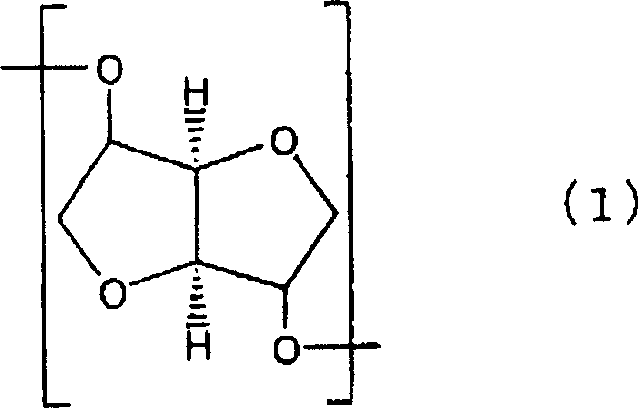
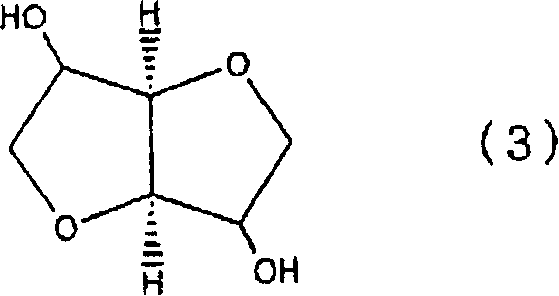
Polycarbonate and process for producing the same
A technology of polycarbonate and diester carbonate, which is applied in the field of polycarbonate and its preparation, can solve the problems of lack of heat resistance and achieve the effect of excellent heat resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0078] 29.23 parts by weight of isosorbide, 1.51 parts by weight of ethylene glycol and 49.48 parts by weight of diphenyl carbonate were added to the reactor, and 2×10 -3 Parts by weight polymerization catalyst tetramethylammonium hydroxide (relative to 1 mole of diol component is 1 * 10 -4 Mole) and 30×10 -4 Parts by weight 2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane disodium salt (relative to 1 mole of diol component is 0.5×10 -6 mol), melted at 180°C in a nitrogen atmosphere.
[0079] Under stirring, the pressure in the reaction tank was reduced to 13.3×10 -3 MPa, reacted for 20 minutes while distilling off the produced phenol. Then, after raising the temperature to 200°C, the pressure was reduced slowly, and the phenol was distilled off at 4.00×10 -3 The reaction was carried out at MPa for 25 minutes, and then the temperature was raised to 215° C. for 10 minutes.
[0080] Next, depressurize slowly, then at 2.67×10 -3 Reaction under MPa for 10 minutes, at 1.33×10 -3 The reaction...
Embodiment 2~5
[0083] The isosorbide, ethylene glycol and diphenyl carbonate of amount shown in table 1 are joined in the reactor, add polymerization catalyst tetramethyl ammonium hydroxide and 2,2-bis(4 -Hydroxyphenyl)propane disodium salt was melted at 180° C. under a nitrogen atmosphere, and polymerized in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain a polymer. The reduced viscosity and glass transition temperature are listed in Table 1.
Embodiment 6~8
[0085] Isosorbide, 1,3-propylene glycol and diphenyl carbonate of amount shown in table 1 are joined in the reactor, add polymerization catalyst tetramethylammonium hydroxide and 2,2- with the same concentration ratio of Example 1 Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)propane disodium salt was melted at 180°C under a nitrogen atmosphere.
[0086] This was polymerized in the same manner as in Example 1 to obtain a polymer. The reduced viscosity and glass transition temperature are listed in the table.
[0087] The polymer obtained in Example 6 was formed into a dumbbell-shaped molded sheet and a 120 mm×12 mm×3 mm plate-shaped molded sheet, and the formability thereof was evaluated. The results are listed in Table 3.
[0088] A film prepared from the polymer prepared in Example 6 was evaluated for biodegradability, and the weight loss rate was 15.9%.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com