Topical anti-infective formulations
An anti-infection, topical technology, applied in biocides, antibacterials, animal repellents, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
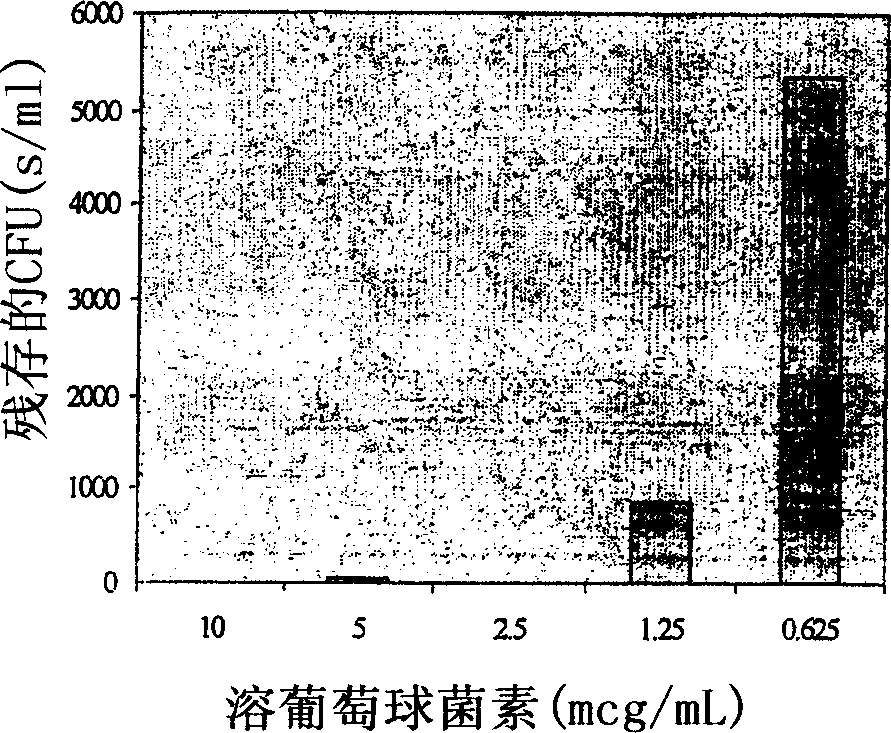
[0093] Example 1 - In Vivo Efficacy of Lysostaphin Topical Cream
[0094] Lysostaphin was formulated as a topical cream to examine its efficacy against Staphylococcus aureus in a mouse skin infection model ( figure 2 ). Application of six doses of 0.5% w / w lysostaphin cream over two days eradicated the infection in three out of four mice, leaving only few colonies in the remaining mice. 0.25% w / w lysostaphin cream also showed considerable activity, clearing the infection in one of three mice and reducing the infectious titer in two of them by more than 3 logs, but it was more effective than 0.5% w / w lysostaphin cream was more than ten-fold lower, indicating an exponential dose response for this therapy. Surprisingly, the placebo cream also had considerable staphylococcal killing activity, reducing bacterial titers in the skin by approximately 100-fold. The activity of the lysostaphin cream was apparently a combined or synergistic killing effect of both lysostaphin and th...
Embodiment 2
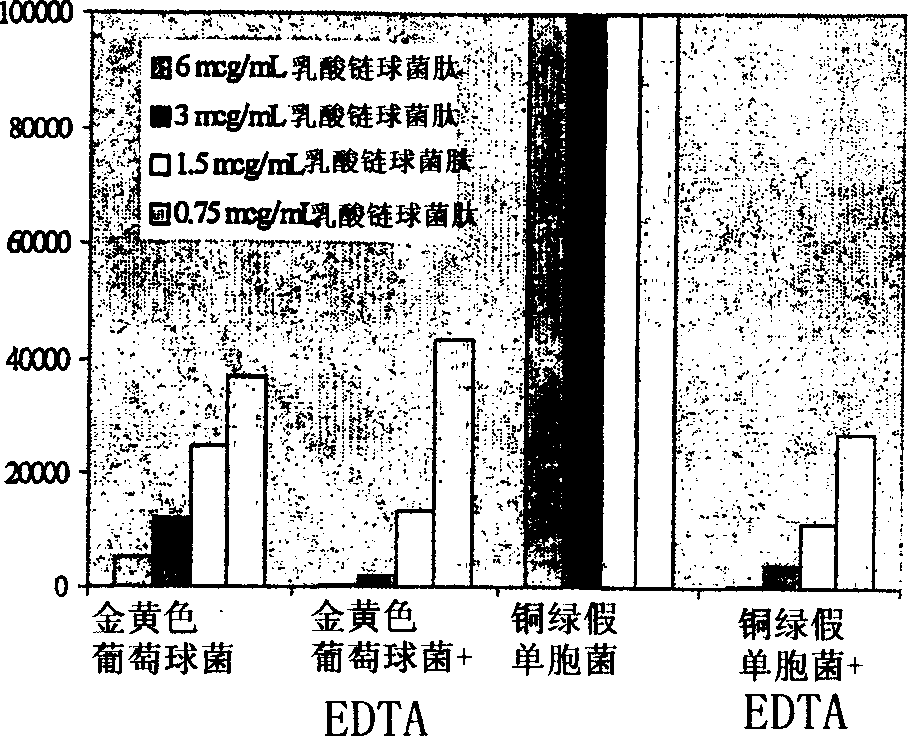
[0096] Example 2 - In Vivo Efficacy of Nisin Topical Cream
[0097] Nisin was formulated as a topical cream to test its efficacy against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa in a mouse skin infection model ( Figure 4 and 5 ), which helps prevent the emergence of lysostaphin-resistant organisms. In combination with EDTA, the bactericidal activity of nisin extends to Gram-negative bacteria, which are also important causes of infectious skin diseases. Although nisin cream is not as effective as lysostaphin cream ( figure 2 and 4 ), but nisin still had considerable activity against S. aureus after two days of treatment. Nisin cream at 0.5% w / w did not eradicate infection in any of the animals, but did reduce bacterial titers by approximately 3.5 logs. More importantly, when small doses (0.1% w / w each) of lysostaphin and nisin were combined in a single cream formulation, skin infections were completely eradicated in all animals tested. Neither 0.1% w / w lysosta...
Embodiment 3
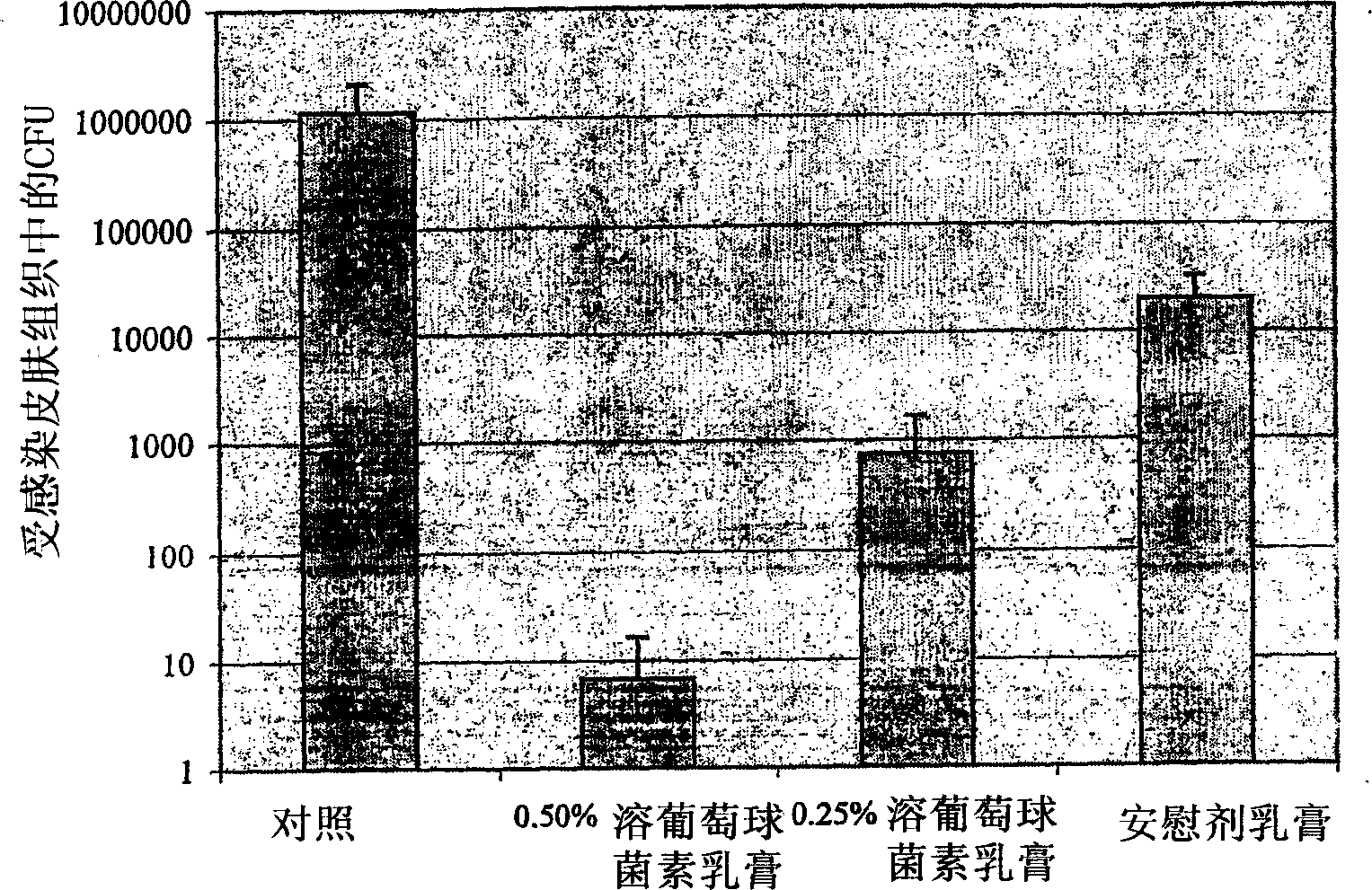
[0099] Example 3 - In vivo efficacy of topical creams without anti-infective agents
[0100] The in vivo efficacy of the cream formulation was demonstrated in a skin graft model. S. aureus was colonized into the skin of hairless mice by swabbing the bacteria on the skin surface (no wound or suture). The grafted skin was treated with the topical cream base prepared in Example 1 or the topical cream prepared in Example 1 plus 1% w / w DMSO for two days, three times a day. Lysostaphin in a topical cream only reduced skin colonization by about half, while the addition of the absorption enhancer DMSO to a cream containing no lysostaphin or any other anti-infective agent resulted in virtually clear completely ( Figure 6 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com