Injection mold and method for molding an optical element
A technology for injection molding and optical components, which is applied in optical components, household appliances, and other household appliances, etc. It can solve the problems of fine shape replication, severe heat dissipation of molten resin, etc., and achieve reduced heat dissipation, good heat preservation, and high replicability Improved effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] (Example 1, refer to figure 1 )
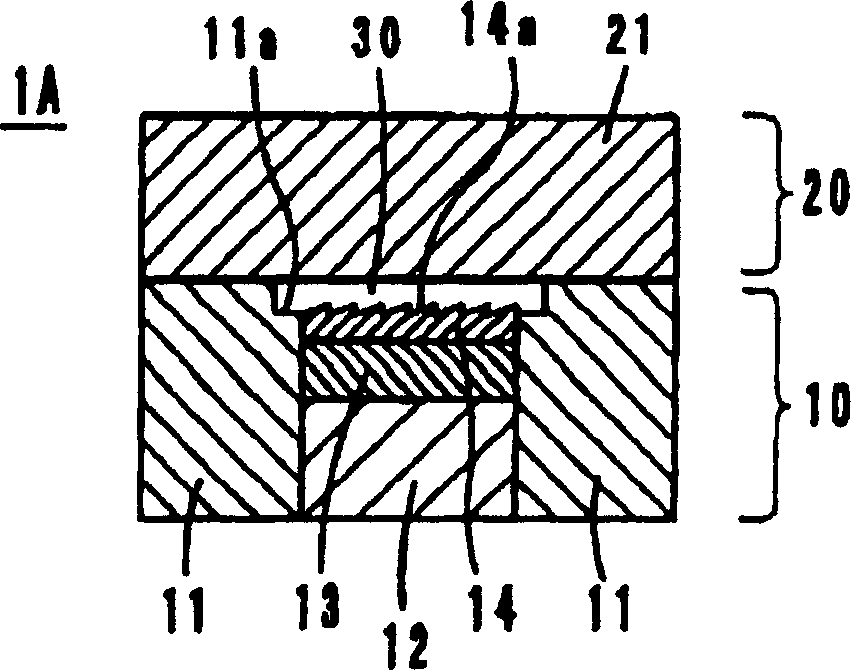
[0020] The mold 1A of embodiment 1 is as figure 1 As shown, it consists of a movable mold 10 and a fixed mold 2. The movable mold 10 is composed of base materials 11 and 12 , a heat insulating layer 13 and a surface processing layer 14 . The fixed mold 20 is composed of a base material 21 .
[0021] The surface processing layer 14 is finished according to the optical surface shape of molded products (optical elements) such as lenses, reflectors, prism plates, and light guide plates, and forms fine shapes 14a such as diffraction gratings, prism surfaces, and flashing surfaces. The cavity 30 is constituted by the surface-processed layer 14 , the base material 21 , and the inner peripheral upper edge of the base material 11 .
[0022] The base metals 12 and 21 are made of common mold base materials, such as metal materials such as carbon steel or stainless steel. The thermal conductivity of carbon steel is 50W / m·K, and the thermal c...
Embodiment 2
[0028] (Example 2, refer to figure 2 )
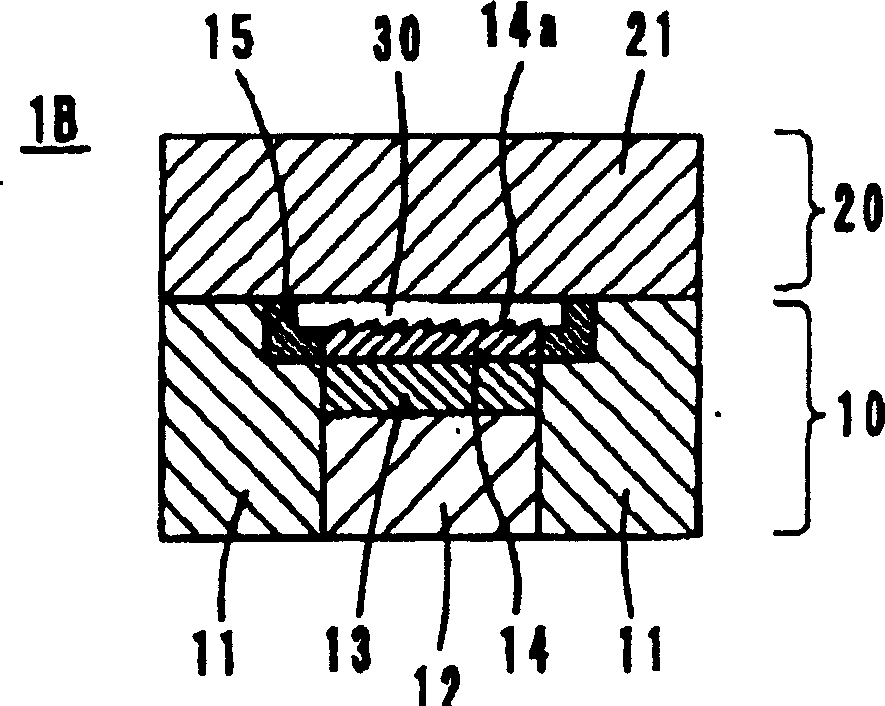
[0029] The mold 1B of embodiment 2 is as figure 2 As shown, the ring-shaped heat insulating material layer 15 is positioned on the upper edge of the inner periphery of the base material 11 constituting the movable mold 10, that is, a portion constituting a part of the cavity 30, in other words, between the base material 11 and the surface-processed layer 14. between.
[0030] In this mold 1B, the base material 11 is made of a common mold base material. The heat insulating material layer 15 is formed of various stainless steels, titanium alloys, and nickel alloys shown in Example 1 that have low thermal conductivity. Or it can also be used as silicon nitride (Si 3 N 4 , 20W / m·K) or aluminum titanate (Al 2 o 3 ·TiO 2 , 1.2W / m·K) and so on. It can also be formed with a heat-resistant polymer such as polyimide resin (thermal conductivity: 0.28 W / m·K). Of course, materials other than those mentioned above can also be used, and ce...
Embodiment 3
[0033] (Example 3, refer to image 3 )
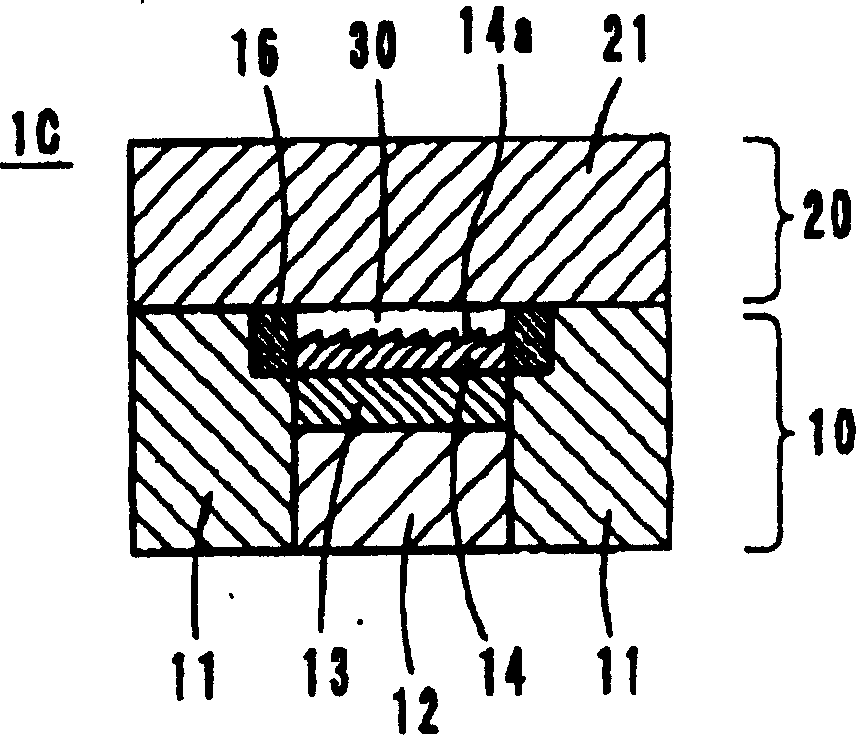
[0034] The mold 1C of embodiment 3 is as image 3 As shown, a heat-insulating material layer 16 is provided instead of the heat-insulating material layer 15 in the mold 1B of Embodiment 2 described above. The material of the heat insulating material layer 16 is the same as that of the heat insulating material layer 15, and the other configurations and materials are the same as those of the second embodiment. Therefore, its function and effect are also the same as in Example 2.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal conductivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com