Mold type semiconductor laser
A technology for molding semiconductors and lasers, which is applied to semiconductor lasers, structural details of semiconductor lasers, semiconductor devices, etc., and can solve problems such as high price, high difficulty, and increased cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
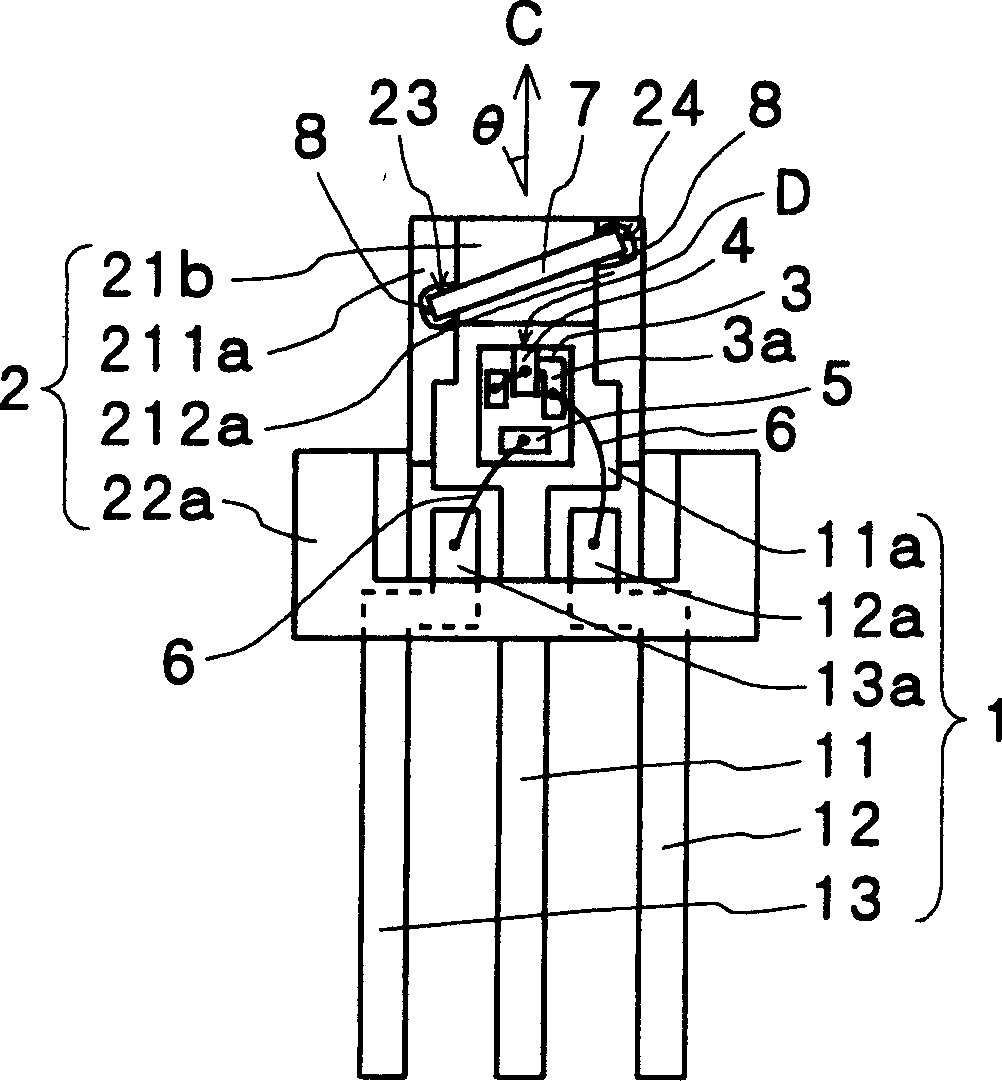
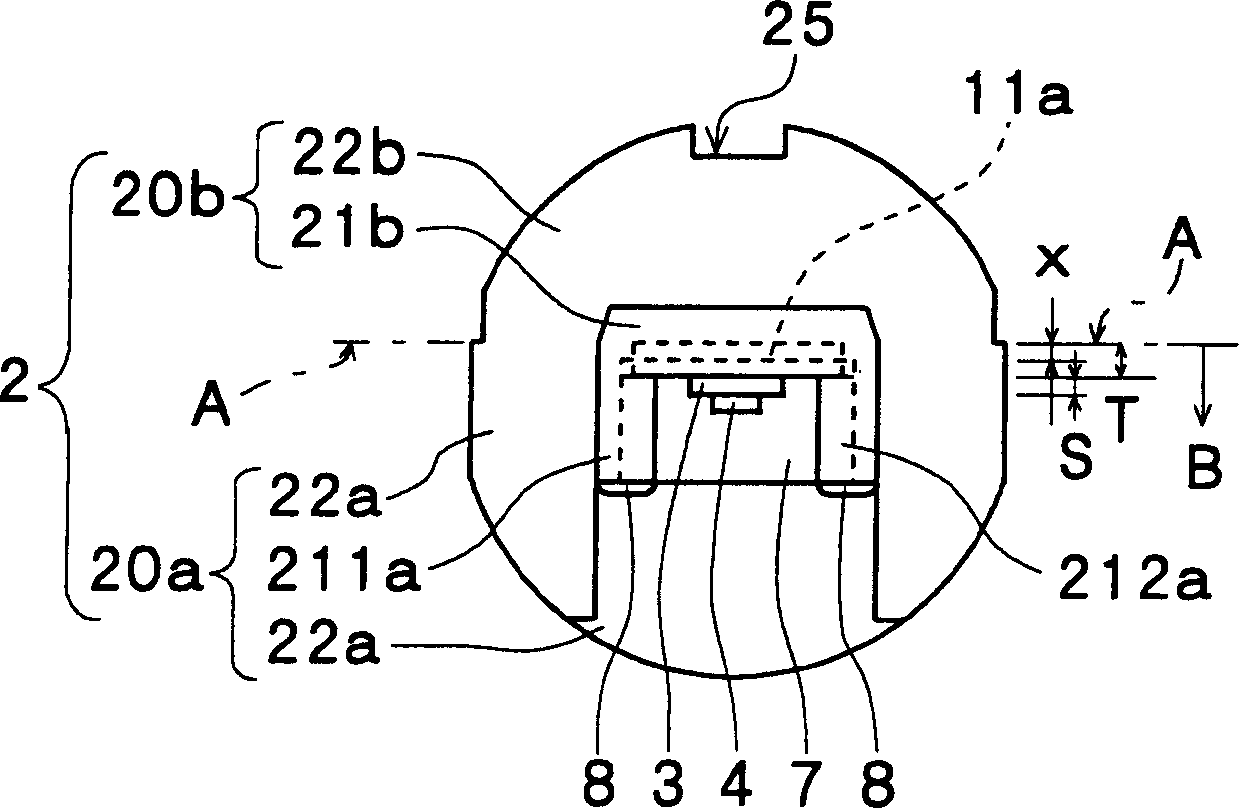
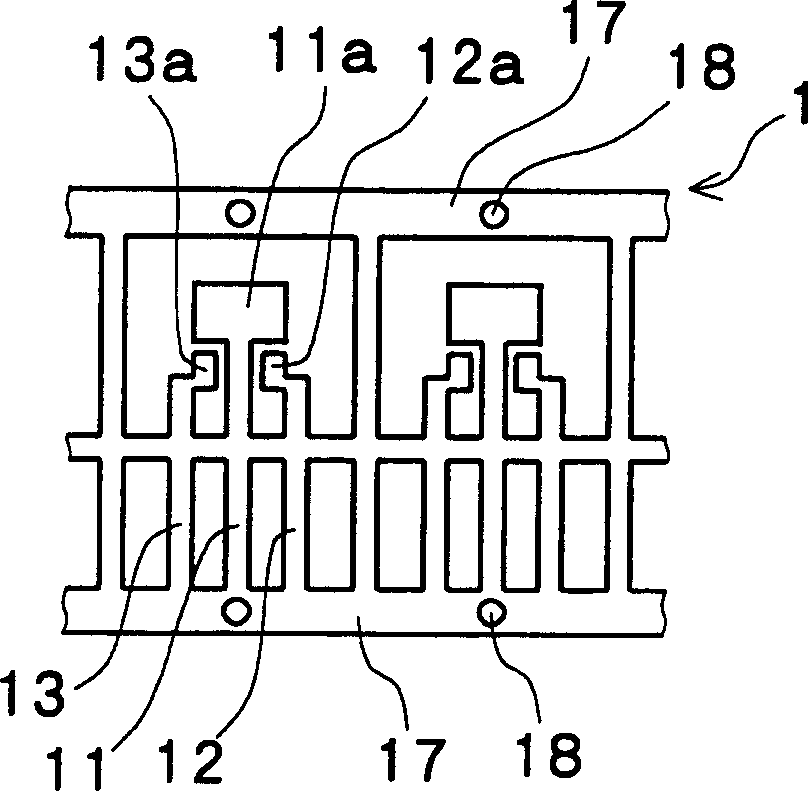
[0021] Embodiments of the molded semiconductor laser of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. An explanatory diagram of a front view and a top view of an embodiment of the molded semiconductor laser of the present invention is shown in Figure 1A-1B . As shown in the drawing, a die pad 11a formed of a plate-shaped lead frame body 1 and a plurality of leads 11 to 13 are integrally held in a package 2 made of molded resin. The laser chip 4 is mounted on the die pad 11 a through the sub-mount 3 . Further, slits 23 and 24 for forming parallel transparent plate 7 in package 2 at a predetermined angle θ for correcting astigmatism, which are not perpendicular to laser beam emission direction C, are fixed in front of emission surface D of laser chip 4 . In addition, θ is the angle formed by the parallel transparent plate 7 with respect to the plane perpendicular to the emission direction C of the laser beam, that is, the angle formed by the no...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com