Method for producing granulated sorbents and installation for carrying out the method
A technology for manufacturing particles and sorbents, which is applied to the equipment for implementing the method, manufacturing particle sorbents, and the field of sorbents for obtaining lithium in salt liquids including natural salt liquids, which can solve the problems of burning hazards and low recovery rates of methyl chloride
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
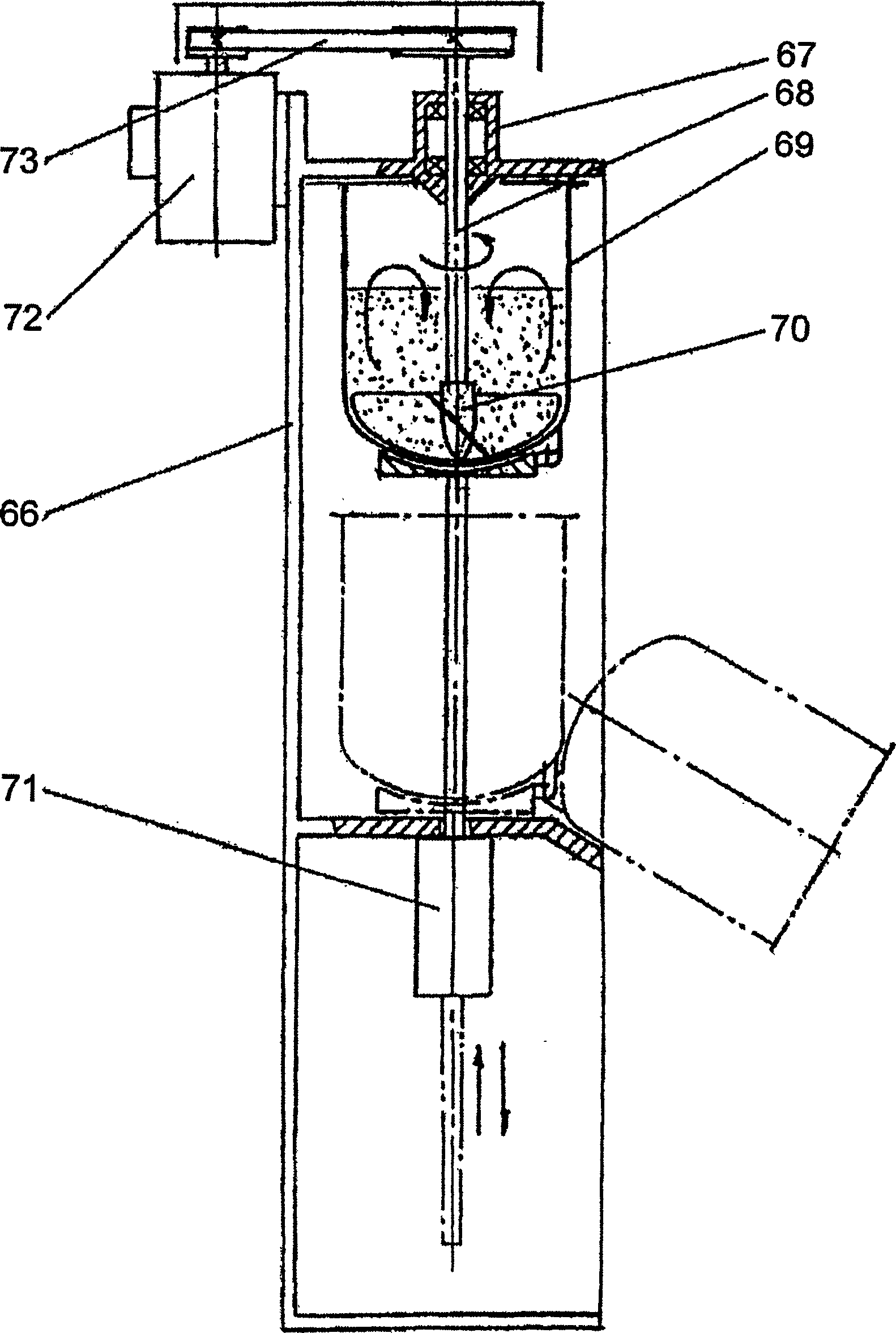
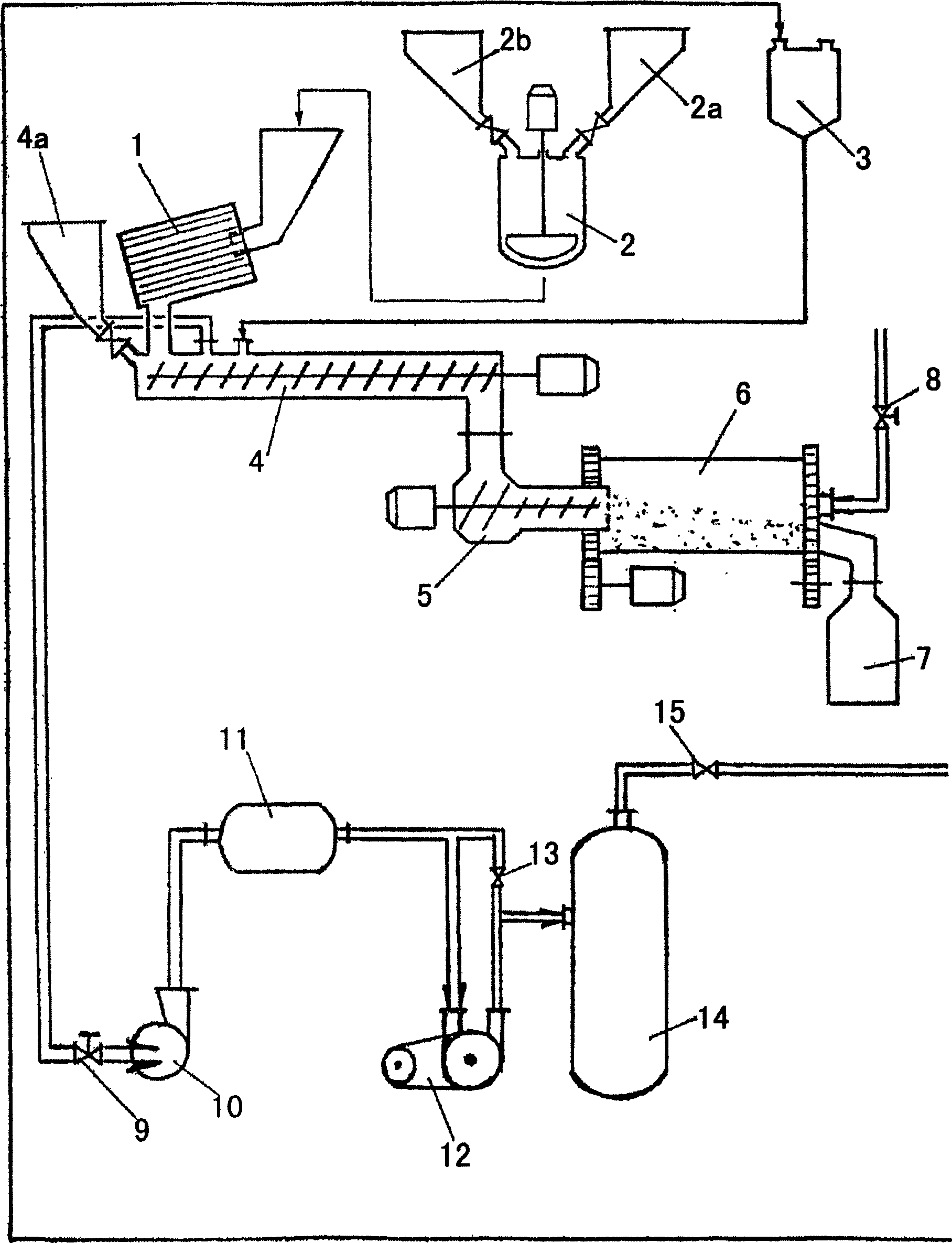
[0089] in such as figure 1 2.5 kg of finely divided gibbsite Al(OH) is fed into the mixer with a capacity of 10 liters as shown 3 (aluminum hydroxide) and 0.98kg lithium chloride monohydrate LiCl·H 2 O. The mixer container 4 is then raised as far as the stop, where the mixer slowly enters the charge. When the container reaches the top level, switch the mixer to full speed (about 450 rpm). After 15 minutes the mixer was turned off and the LiCl incorporation was 85%. The charge is filled in the container of the centrifugal grinding-activator ZMA-06; when running through the centrifugal grinding-activating machine, the degree of component combination reaches 92%, and the molar ratio LiCl in the produced DHAL-Cl: Al(OH ) 3 is 0.46. When the material is treated with water, the molar ratio LiCl:Al(OH) in the product 3 It is equal to 0.33, which means that 28% of LiCl is taken out, and the amount of lithium (mg) relative to the mass (g) of the sorbent corresponds to a sorption...
example 2
[0094] Manufacture DHAL-Cl according to the method described in example 1, and molar ratio LiCl: Al (OH) 3 Equal to 0.46. The products are made into granules with different compositions by means of chlorinated polyvinyl chloride (PVC) as binder and methyl chloride (MCI) as solvent. The results are shown in Table 2:
[0095]
Show
example
Mixed ingredients for granulation, % max
Composition of dry granules, % max
exchange capacity
mg / g
DHAL-Cl
pvc
MCI
loading
h 2 O: LiCl
product
LiCl:AL(OH) 3
2-1
45.7
3.8
50.5
92.3
7.7
7.2
99.3
2-2
44.2
3.7
51.9
91.9
8.1
7.0
99.4
2-3
42.8
4.0
53.2
91.5
8.5
7.0
99.5
2-4
40.1
4.2
55.7
9...
example 3
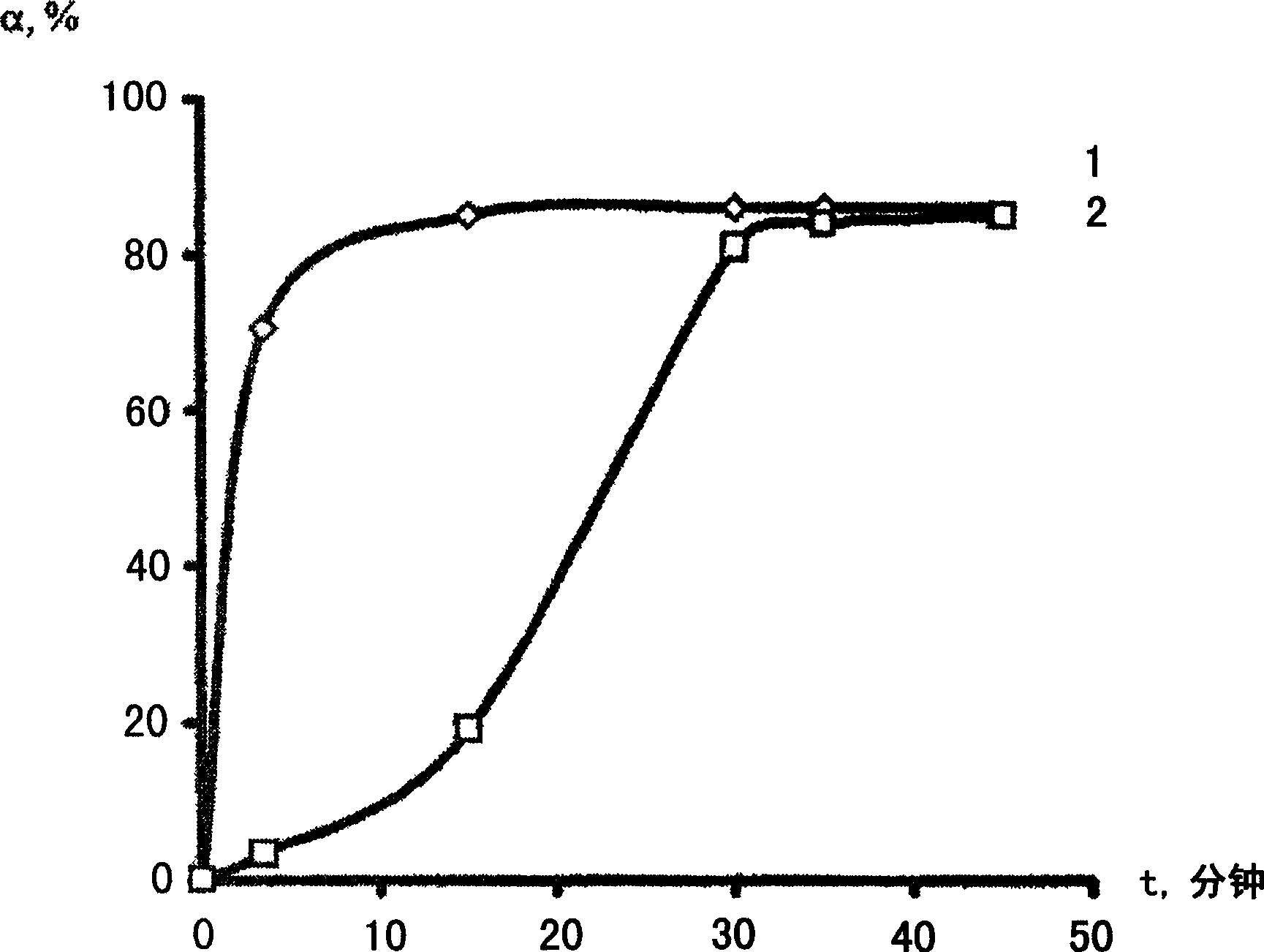
[0103] With the help of a special laboratory apparatus, a drying chamber with inlet and outlet fittings, the process of separating methyl chloride from a paste obtained by dissolving PVC and DHAL-Cl sorbent in methyl chloride under stirring was studied . A possible method for separating methyl chloride is paste drying under air flow (draft gas) and low pressure. The low pressure in the drying chamber and the supply of air thereto are ensured by means of a gas blower and shut-off control solenoid valves arranged on the inlet and outlet of the drying chamber. Air consumption is measured with a rotameter, while low pressure is measured with a U-shaped manometer. Sampling of the gaseous phase exiting the drying chamber was performed with a 100 ml gas syringe at the outlet of the drying chamber. The control for the separation of methyl chloride was carried out according to the gas chromatography method with respect to the methyl chloride during the sampling of the gas phase at th...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com