High temperature rare earth permanent magnetic material and its preparation method
A rare earth permanent magnet, high temperature technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inorganic materials, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problem of difficult to meet the use temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
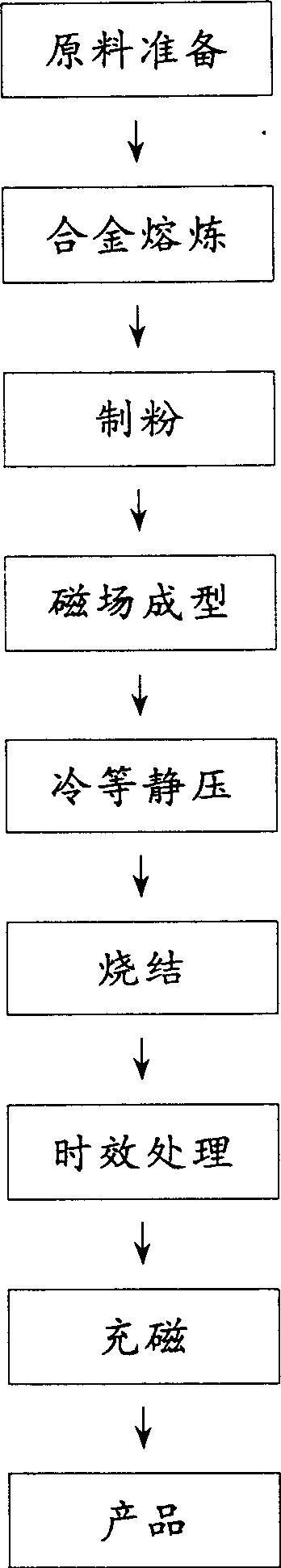
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] The ingredients are Sm: 24.5%, Co: 48.5%, Fe: 15%, Cu: 9%, Zr: 3%. The raw materials are smelted at 1325°C and then powdered, and then the magnetic field is 1194kA / m and the pressure is 300MPa. forming;
[0022] Sintering process: vacuum pre-sintering at 1190°C for 30 minutes, then sintering at 1210°C for 60 minutes under an argon protective atmosphere, then solid solution treatment at 1180°C for 120 minutes, and then air-cooled;
[0023] Aging treatment process: keep warm at 830°C for 20 hours, then cool to 370°C at a cooling rate of 0.5°C / min, keep warm for 15 hours, and then take out the furnace for air cooling. The magnetic properties of the obtained patterns are listed in Table 1, and the relationship between the irreversible rate of magnetic flux (η) and temperature is listed in Table 2.
[0024] test
[0025] temperature(°C)
Embodiment 2
[0027] The ingredients are Sm: 25%, Co: 48%, Fe: 16.5%, Cu: 8%, Zr: 2.5%. The raw materials are smelted at 1330°C and then powdered, and then the magnetic field is 1194kA / m and the pressure is 400MPa. forming;
[0028] Sintering process: vacuum pre-sintering at 1190°C for 30 minutes, then sintering at 1210°C for 60 minutes under an argon protective atmosphere, then solid solution treatment at 1180°C for 120 minutes, and then air-cooled;
[0029] Aging treatment process: keep warm at 830°C for 20 hours, then cool to 370°C at a cooling rate of 0.5°C / min, keep warm for 15 hours, and then take out the furnace for air cooling. The magnetic properties of the obtained patterns are listed in Table 3, and the relationship between the irreversible loss rate of magnetic flux (η) and temperature is listed in Table 4.
[0030] test
[0031] temperature(°C)
Embodiment 3
[0033] The ingredients are Sm: 25.5%, Co: 47.5%, Fe: 16%, Cu: 8%, Zr: 3%. The raw materials are smelted at 1335°C and then powdered, and then the magnetic field is 1592kA / m and the pressure is 600MPa. forming;
[0034] Sintering process: vacuum pre-sintering at 1190°C for 30 minutes, then sintering at 1210°C for 60 minutes under an argon protective atmosphere, then solid solution treatment at 1180°C for 120 minutes, and then air-cooled;
[0035] Aging treatment process: keep warm at 850°C for 20 hours, then cool to 370°C at a cooling rate of 0.5°C / min, keep warm for 15 hours, and then take out the furnace and air-cool. The magnetic properties of the obtained patterns are listed in Table 5, and the relationship between the irreversible loss rate of magnetic flux (η) and temperature is listed in Table 6.
[0036] test
[0037] temperature(°C)
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com