Process for preparation of hydrophilic pressure sensitive adhesives having optimized adhesive properties
A technology of hydrophilic polymers and adhesives, applied in the direction of amide/imide polymer adhesives, adhesive types, polyether adhesives, etc., can solve problems such as loss of adhesion
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1-16
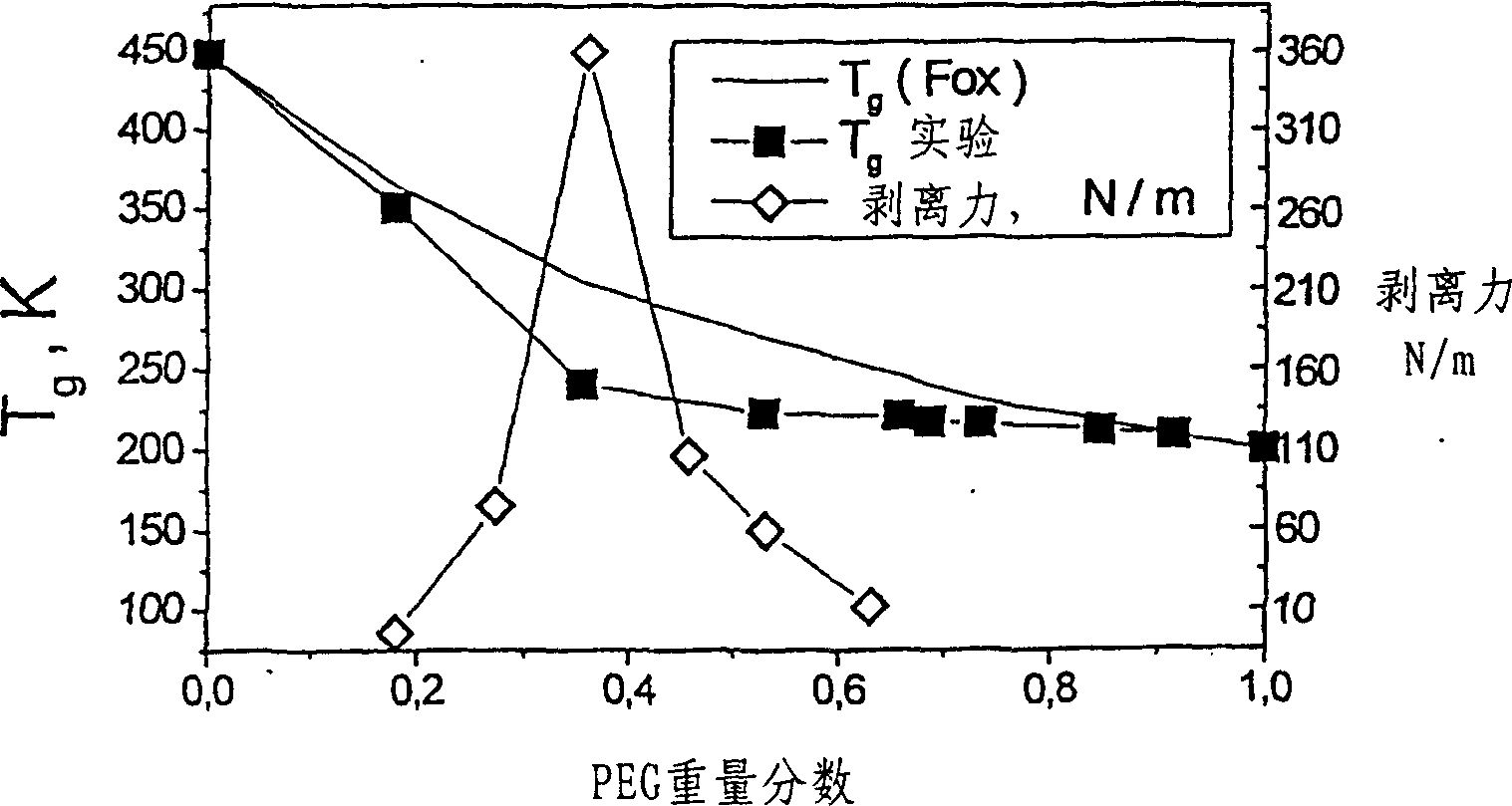
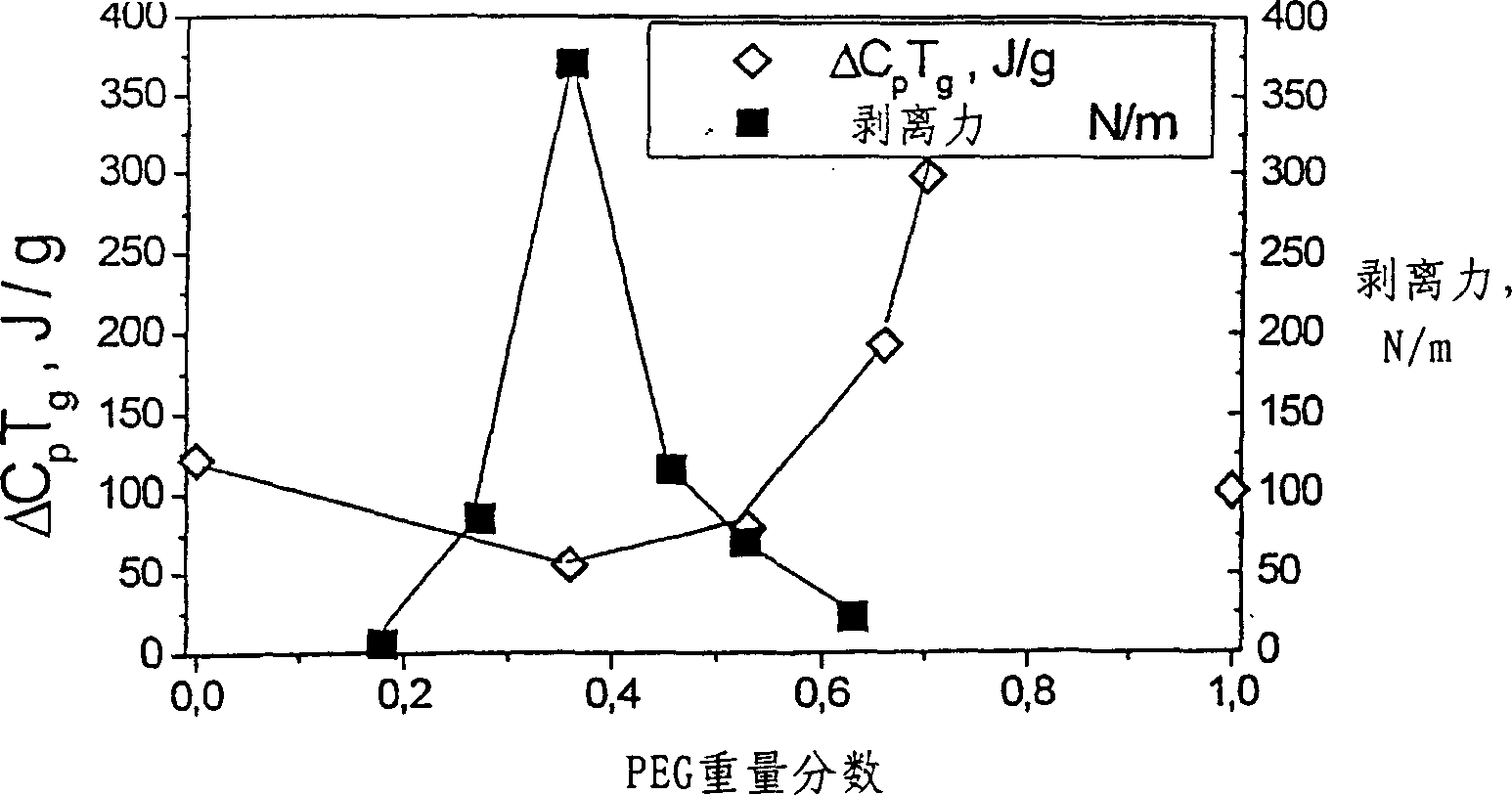
[0121] Preparation of PSA substrates by mixing PVP with PEG-400: effects on the composition, hydration and thickness of the adhesive layer
[0122] A bond coat with a thickness of 250-300 microns was prepared by dissolving a hydrophilic polymer and PEG (Mw=400) in a common solvent (ethanol), and casting the solution onto a backing sheet and drying. Unsupported PVP-PEG hydrogels were obtained by casting the respective solutions onto release liners followed by room temperature drying.
[0123] The bonding point strength of the adhesive hydrogel and a standard polyethylene (PE) sheet with a thickness of 100 m was evaluated by a 180° peel test using an Instron 1221 tensile strength tester at a peel rate of 10 mm / min. The crystallinity is 45%, the contact angle is 105°, and the surface energy is 28.5mJ / m 2 Low density PE is used as standard base material. The adhesive is saturated with water: control the water vapor pressure to 50% in a desiccator at room temperature, and equilib...
example 17-47
[0132] Preparation of PSA substrates by mixing PVP with different short-chain plasticizers
[0133] Component Action and Adhesion vs. Phase State
[0134] Using the preparation method and evaluation test method described in Example 1, samples of PVP K-90 mixed with various plasticizers were obtained and tested at 50% RH and room temperature. The results are shown in Table 3. Viscous mixtures can be obtained by mixing PVP with hydroxyl-terminated (Examples 17-41 ) or carboxy-terminated (Examples 42-47) short-chain plasticizers. Short-chain plasticizers include: ethylene glycol (Examples 17-19) and its polymers (PEG) in the molecular weight range of 200-600 g / mol (Examples 20-23); low molecular weight 1,3- and 1,2- Propylene glycol (PG) (Examples 24, 25), and alkanediols, from Propylene Glycol to Pentylene Glycol (PD) and Hexylene Glycol (HD) (Examples 27-39). Polypropylene glycol (PPG) was found to be a good plasticizer for PVP, but did not develop any tack or adhesion (Exam...
example 48-64
[0136] Preparation of PSA compositions by mixing different hydrophilic polymers with complementary short-chain plasticizers
[0137] These examples illustrate that not only PVP but also a collection of different hydrophilic polymers become sticky once mixed with short chain plasticizers having complementary reactive groups at the chain ends. Suitable hydrophilic polymers include poly(N-vinylamides) such as, PVP (Examples 1-47), poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) (PVCap) (Examples 48-52) and poly(N-vinyl Acetamide) (PVAA, Example 53), poly(N-alkylacrylamide), examples are poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM, Example 54), polymethacrylic acid and polyacrylic acid (PMA, PAA , Examples 55-60) and their copolymers, examples are shown in Table 4 (Luviscols VAP(R), available from BASF, Examples 61-64). Luviscol VAP37 is a copolymer of vinylpyrrolidone (VP, 30%) and 70% vinyl acetate (VA). Luviscol VAP 73 contains 70% VP and 30% VA.
[0138] Among the polymers shown in Table 4, it was found ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com