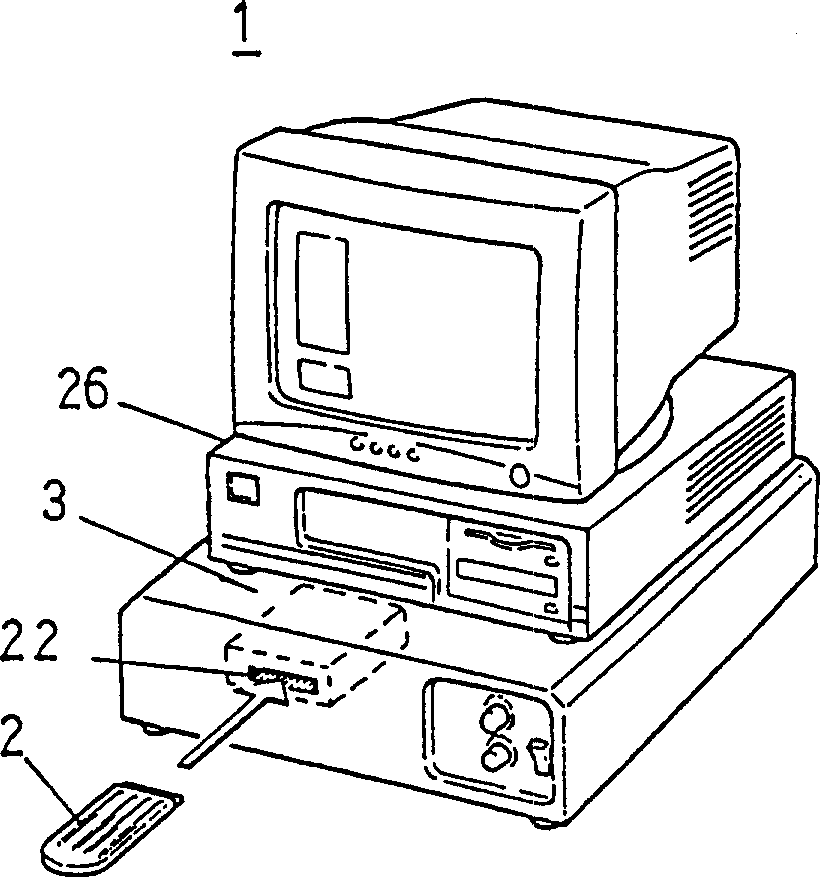
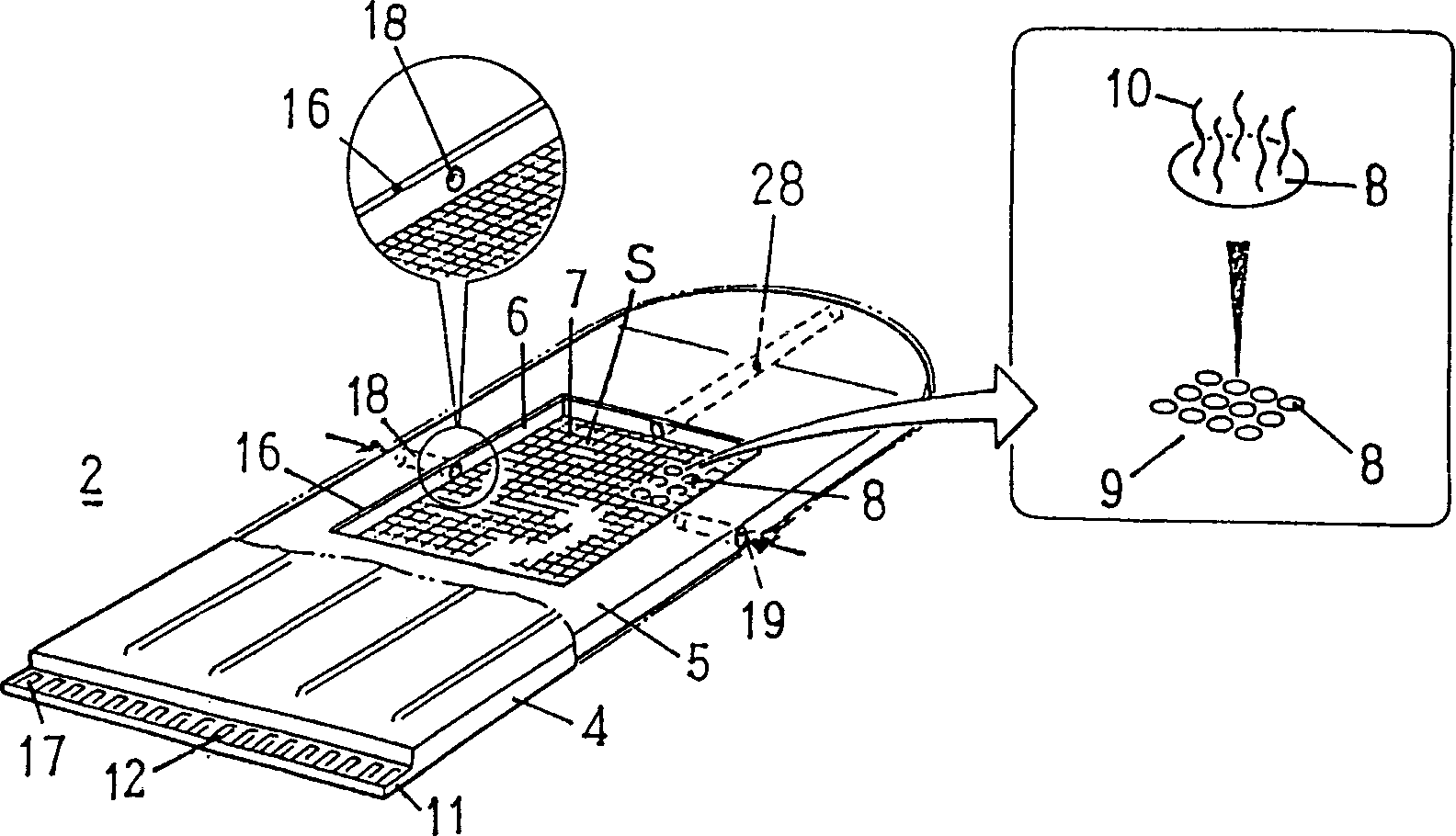
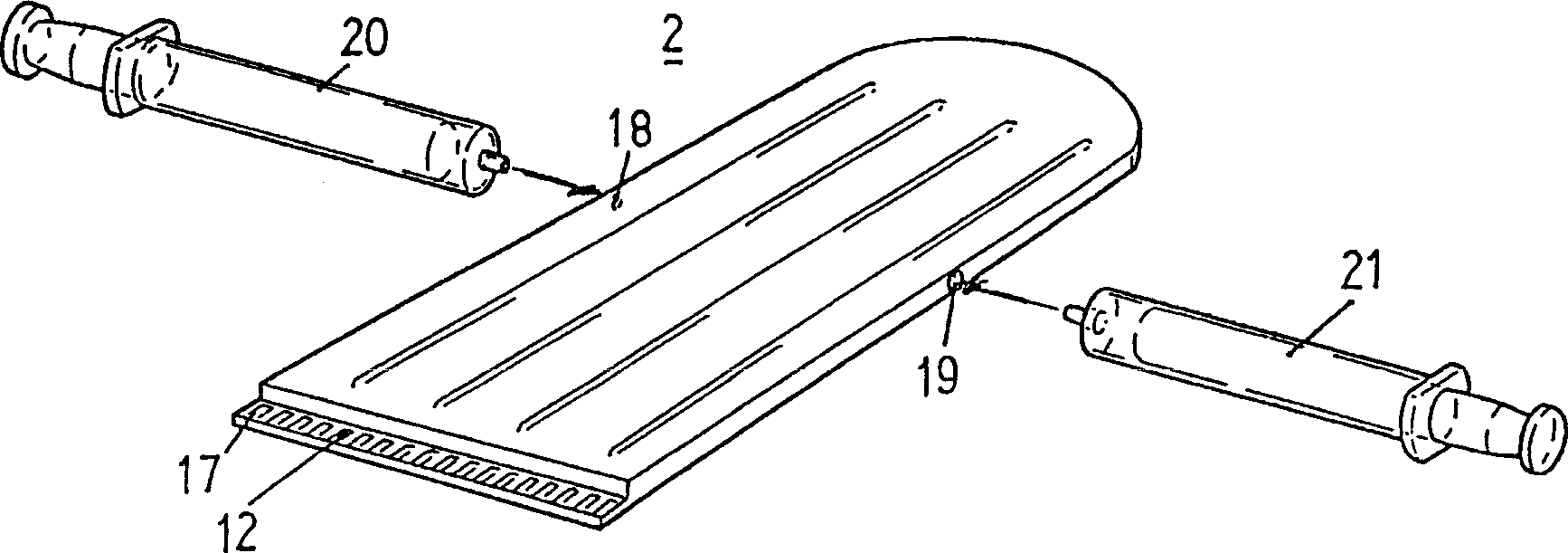
Method for detecting single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and point mutation in gene, detection apparatus and detection chip
A detection chip and detection device technology, which can be used in measurement devices, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., and can solve problems such as impracticability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] An example of detection of a base substitution SNP in codon 72 of the gene p53 is shown. The oligonucleotides had base sequences corresponding to the following two polymorphisms (genetic polymorphisms), and the oligonucleotides were immobilized at the points of the respective gold electrodes.
[0045] p53Pro (the 72nd position codon is Pro)
[0046] p53Arg (the 72nd position codon is Arg)
[0047] The 72nd codon of p53 is Pro, the DNA taken from the peripheral blood of normal people and the amplified PCR product are subjected to a hybridization reaction after high-temperature denaturation, and the PCR product is a fragment amplified from this DNA, which includes Codon 72 in p53 exon 4. Electrolyte solution with 0.1MAcOH-AcOK (pH5.6), 0.1M KCl, 0.05mM NFc, at 20 degrees to measure the change of current value before and after hybridization at 470mV (Ag / AgCl reference electrode standard).
[0048] DNA collected from peripheral blood
[0049] Current change (%) of p53Pr...
Embodiment 2
[0063] In this example, the measured current value is different due to the difference in the number of base substitutions, and thus the amount of matching errors can be measured. Seven oligonucleotides of dT20, dT10dAdT9, dT8dA4dT8, dAdT19, dT3dT17, dT19dA, dT17dA3 were immobilized on each point of the gold electrode respectively. The dA20 was subjected to a hybridization reaction.
[0064] Electrolyte solution with 0.1M AcOH-AcOK (pH5.6), 0.1M KCl, 0.05mM NFc, at 20 degrees, with 470mV (Ag / AgCl reference electrode standard) to measure the change of current value before and after hybridization. The measurement results are shown in Table 1.
[0065] dT20
[0066] The current change in Table 1 is almost dependent on the change in the amount of base matching errors. Especially when there is a mismatch at the end, a change larger than the Tm value is seen. Such detection cannot be carried out in the previous SSCP, and this method is the first time to figure it out. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com