Method for producing human cloned embryos by employing inter-species nuclear transplantation technique
A technology for cloning embryos and humans, applied in the production of human cloned embryos by internuclear transfer technology, in the field of human cloned embryos, which can solve the problems of unsatisfactory human tissues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] The present invention is now further illustrated by the following examples, which should not be construed as limiting the scope of the present invention. Example 1: Preparation of Donor Cells and Recipient Oocytes
[0033] To prepare donor cells, tissues collected from human skin were washed with PBS (phosphate-buffered saline, Gibco's BRL, Life Technology, USA), and then crushed to 100 mesh. Then at 39°C, 5% CO 2 Incubate the tissue in PBS containing 0.25% trypsin, 1 mM EDTA, and 1 mg / ml collagenase type II for 1 hour at ambient temperature. After the tissue is enzymatically digested, centrifuge at 1500 rpm for two minutes and suspend In DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium, Gibco's BRL, Life Technology USA) supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% NEAA (non-essential amino acids), and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. Transfer the suspension into a cell culture dish and incubate at 39 °C, 5% CO 2 environment to obtain somatic cell lines. Thereafter, the cells were treated with...
Embodiment 3
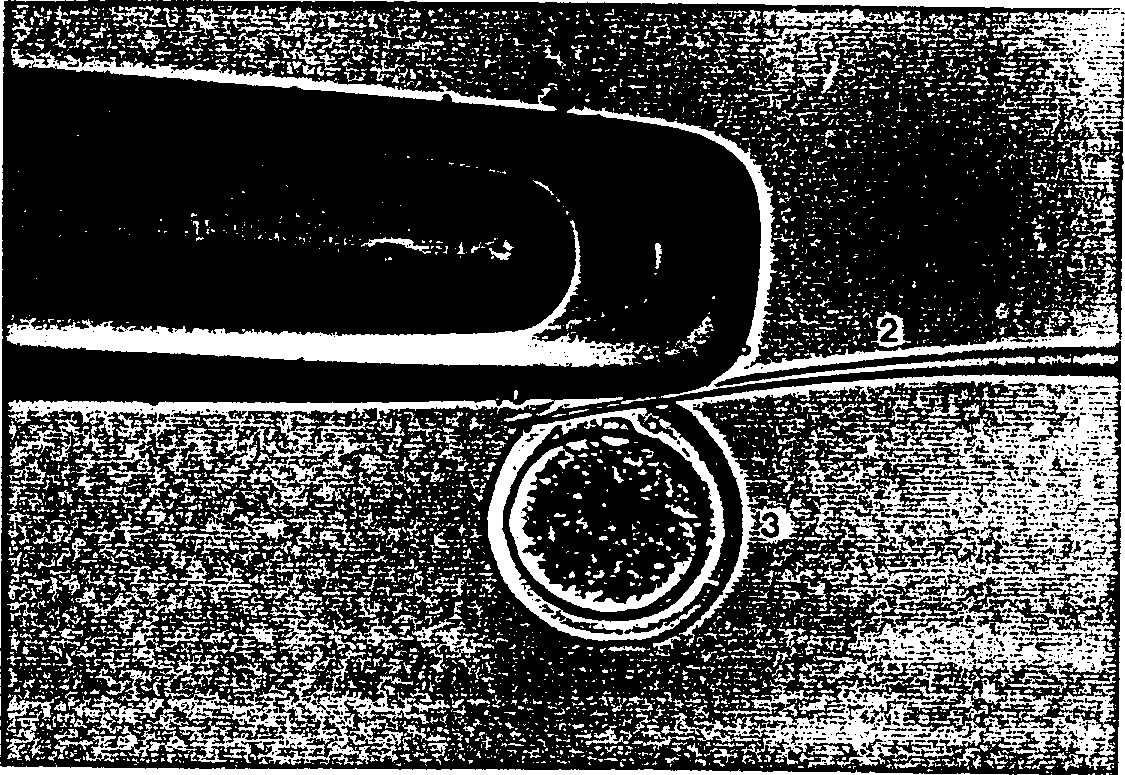
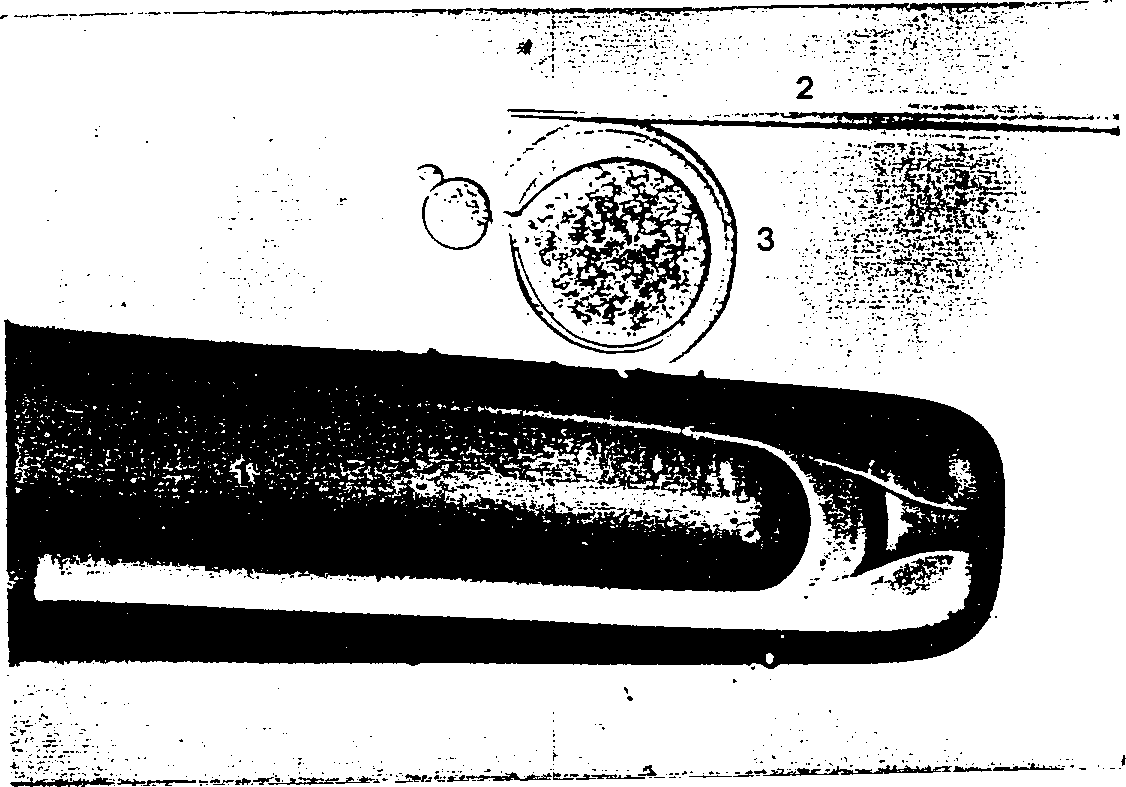
[0041] Replace the cutting tube mounted on the micromanipulator with an injection tube. Enucleated oocytes were washed three times with TCM199 wash medium and then pipetted into injection droplets. The donor cells are drawn into the syringe and then transferred into the injection droplet. Figure 4 Indicates the process of transferring a somatic cell into an enucleated oocyte. Such as Figure 4 As shown, enucleated oocytes were placed with their cleft orientation at 1 o'clock, held with a holding tube, and then injected into donor cells through the cleft using a syringe and hydraulic pressure to obtain a reconstructed embryo. Embryos were washed three times with TCM199 wash medium and then incubated in TCM199 wash medium. Example 3: Electrofusion and activation
[0042] The reconstructed embryos were electrofused using an electrocytomanipulator (USA, BTX, ECM2001), and then reactivated. Add 15 microliters of 0.28M mannitol, 0.5mM HEPES (pH7.2), 0.1mM MgSO to the TCM199 cu...
Embodiment 4
[0043] To activate electrofused embryos, embryos were incubated for 4 minutes in the dark in a solution of ionomycin (Sigma Chemical Co., USA), a TCM199 wash containing 5 [mu]M ionomycin and 1% BSA. The ionomycin stock solution was prepared by dissolving 1 mg of ionomycin in 1.34 ml of DMSO. Activated embryos were incubated for 5 minutes in 35 mm dishes containing TCM199 wash medium supplemented with 10% FBS to wash ionomycin from the embryos. Example 4: Post-activation and in vitro culture of electrofused embryos
[0044] The activated embryos were activated for 4 hours in 25 microliters of cycloheximide (Sigma Chemical Co., U.S.) solution, and the cycloheximide solution was added to the in vitro culture medium mTALP by adding cycloheximide stock solution ( 10 mg / ml in ethanol), to a final concentration of 10 μg / ml to prepare. Embryos were then screened, and the selected embryos were placed at a temperature of 39 °C, 5% CO 2 Incubate for 7 days under ambient conditions. E...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com