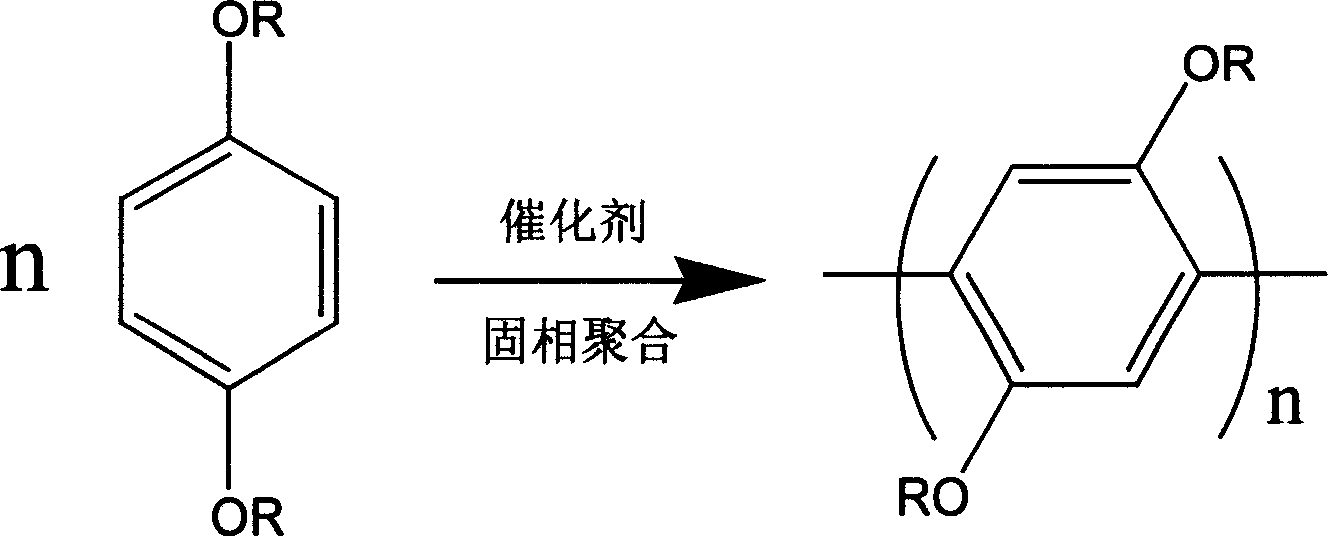
Preparation of poly(2,5-diakoxy-1,4-benzene)
A dialkoxybenzene and dialkoxy technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of poly(2,5-dialkoxy-1,4-benzene), can solve the problems affecting material properties, the effect of polydialkoxy on Problems such as poor regioregularity of benzene, to achieve the effect of shortening the reaction time, improving the preparation technology and product quality, and eliminating the reaction step
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1: 0.61 g of p-dibutoxybenzene and 1.00 g of anhydrous ferric chloride were weighed into a mortar and ground at room temperature. After milling for 30 minutes, the reaction was stopped. Wash the product in the mortar with ethanol or methanol, and separate the solid and liquid by centrifugation to remove ferric chloride and unreacted monomers. The separated solid was washed with ethanol or methanol, and then dried in a constant temperature oven (50° C.). After drying, dissolve the product completely with a small amount of chloroform, add methanol or ethanol four to five times the amount of chloroform to precipitate the polymer, centrifuge again to separate the solid from the liquid, and dry it in a constant temperature oven (50°C) to obtain the product Poly(2,5-dialkoxy-1,4-benzene) 0.44 g, yield 72%. The number average molecular weight of the polymer as determined by size exclusion chromatography was 30,000. After 300 M NMR analysis, the hydrogen spectrum res...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Example 2: Weigh 0.61 grams of p-dibutoxybenzene and 2.00 grams of mixed anhydrous rare earth chloride (Baotou industrial product, containing La27%, Ce51%, Nd15%, Pr5% in rare earth) and put it into a mortar medium grind. After grinding for 20 minutes, put it into a constant temperature oven (60° C.) for 0.5 hour. After continuing grinding for 10 minutes, the reaction was stopped. Wash the product in the mortar with water, and separate the solid and liquid by filtration to remove the rare earth. The solid was washed twice with ethanol or methanol, and then dried in a constant temperature oven (50° C.). After drying, wash the product with ethanol, then separate the solid from the liquid by centrifugation, pour off the supernatant, and leave the precipitate. Then the precipitate was dried in an oven to obtain the product poly(2,5-dialkoxy-1,4-benzene). After the product is completely dissolved by adding chloroform, blue fluorescence can be seen under the irradiation o...
Embodiment 3
[0023] Example 3: 0.61 g of p-dibutoxybenzene and 0.81 g of anhydrous copper chloride were weighed and ground in a mortar. After grinding for 10 minutes, put it into a constant temperature oven (50° C.) for 1 hour. After continuing grinding for 10 minutes, the reaction was stopped. Wash the product in the mortar with ethanol or methanol, and separate the solid and liquid by centrifugation to remove copper chloride and unreacted monomers. The solid was washed three times with ethanol or methanol, and then dried in a constant temperature oven (50° C.). After drying, the product poly(2,5-dialkoxy-1,4-benzene) was obtained. It is completely dissolved in chloroform, and blue fluorescence can be seen under the irradiation of ultraviolet light. The product has been analyzed by 300 M NMR and Fourier transform infrared spectrum, which proves that the linking mode of the benzene ring is 1, 4 linking, and the polymer has a good regioregular structure.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com