Method for enhancing utilization of acetic acid and improving L-arginine produced by escherichia coli fermentation
A technology of Escherichia coli and recombinant Escherichia coli, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of reduced yield of target products, loss of carbon atoms, etc., and achieve the effects of reducing growth toxicity, reducing toxicity, and high application value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Screening of acetyl-CoA synthase
[0045] Specific steps are as follows:
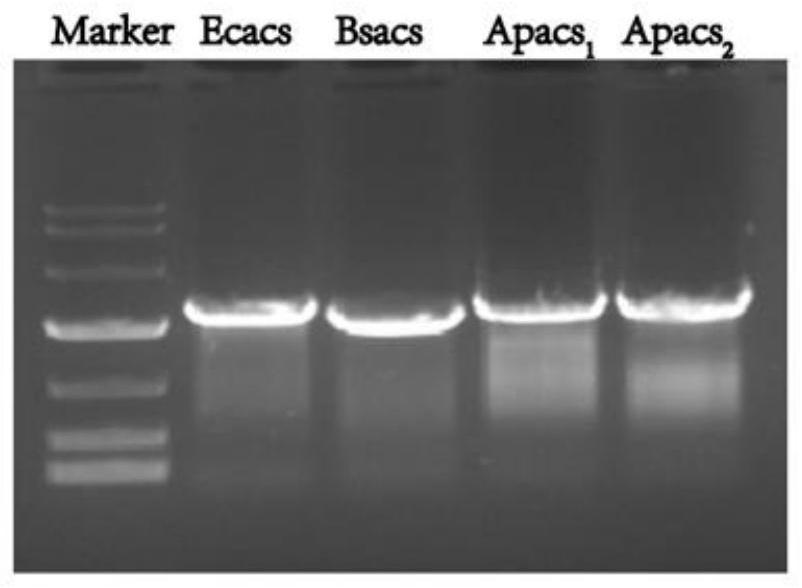
[0046] (1) Take the genomic DNA of Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis, and Acetobacter pasteurianus as templates respectively, and use F and R as primers to carry out PCR amplification to obtain nucleotide sequences as shown in SEQ ID No.1 to SEQ ID No.4 respectively. The encoding acetyl-CoA synthase genes acs1~acs4; wherein, PCR amplification primers are shown in Table 1:
[0047] Table 1: PCR primers
[0048]
[0049]
[0050] PCR amplification conditions were: 95°C pre-denaturation, 3 min; 95°C denaturation, 30s, 58°C annealing, 30s, 72°C extension, 90s, 30 cycles; 72°C final extension for 10 min.
[0051] The PCR amplification system was: template 0.5 μL, upstream and downstream primers 0.5 μL each, sterilized double-distilled water 23.5 μL, PrimerStar DNA polymerase 25 μL.
[0052] (2) The genes acs 1 to acs 4 (amplification results as shown in figure 1 shown) and the p...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2: Construction of Acetyl-CoA synthase expression vector
[0054] Specific steps are as follows:
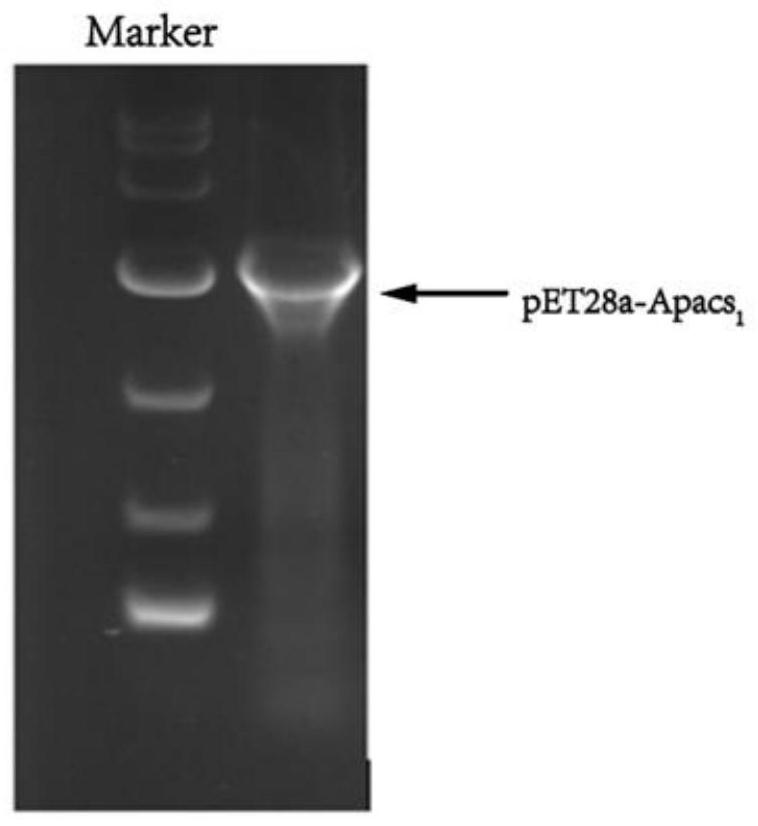
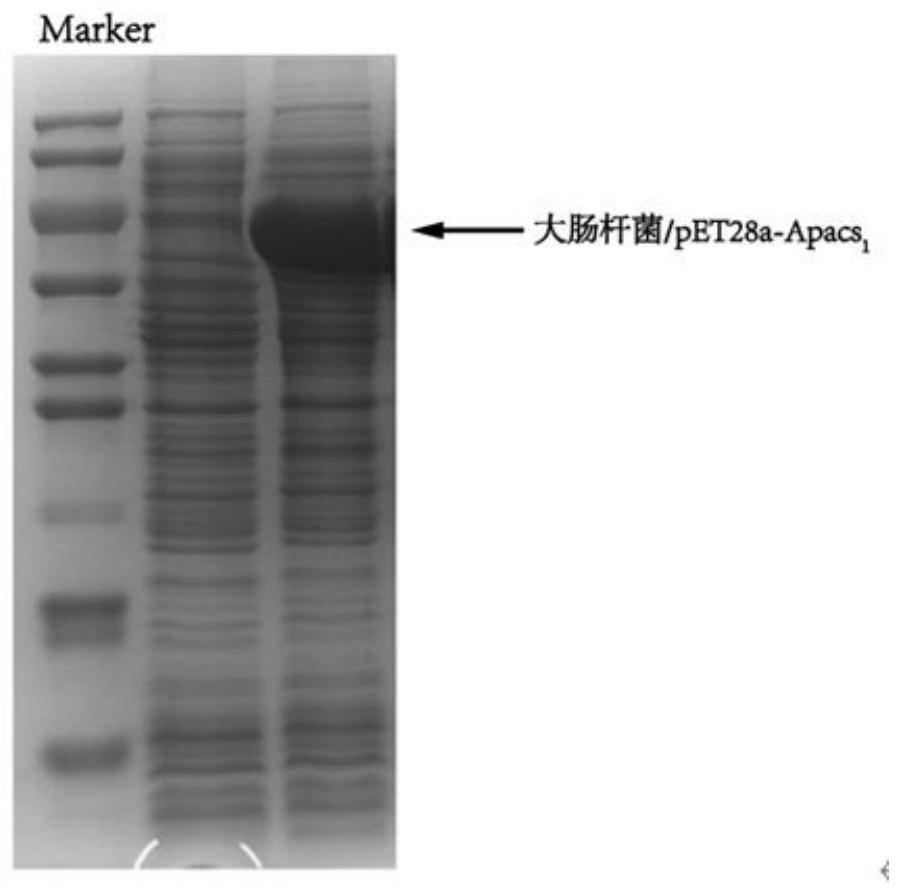
[0055] The recombinant plasmids pET28a-acs 1 to pET28a-acs 4 obtained in Example 1 were chemically transformed into Escherichia coli E.coli BL21 (DE3) to obtain transformed products; the transformed products were spread on LB solid medium (containing 10 μg·mL -1 Kanamycin), incubate at 37°C upside down for 12 hours to obtain transformants; colony PCR verification, pick and verify correct transformants and inoculate into LB liquid medium (containing 10 μg·mL -1 kanamycin), in a constant temperature incubator at 37°C, under the conditions of 120-180rpm shake flask culture for 12h, extract the plasmid for PCR verification and sequencing verification, if the verification is correct, the recombinant Escherichia coli E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a-acs 1~E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a-acs 4; The recombinant plasmids pET28a-acs 1~pET28a-acs 4 of four acetyl-CoA synthases from differen...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3: Construction of host cells
[0060] Specific steps are as follows:
[0061] (1) Using the genome of Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) as the DNA template, using the primers in Table 3 to amplify the homology arm fusion fragments (adiA, speA, speC, and speF genes of adiA, speA, speC, and speF gene amplification results are as follows: Figure 4 shown).
[0062] Table 3 Primers
[0063]
[0064] PCR amplification conditions were: 95°C pre-denaturation, 3 min; 95°C denaturation, 30s, 58°C annealing, 30s, 72°C extension, 90s, 30 cycles; 72°C final extension for 10 min.
[0065] The PCR amplification system was: template 0.5 μL, upstream and downstream primers 0.5 μL each, sterilized double-distilled water 23.5 μL, PrimerStar DNA polymerase 25 μL.
[0066] (2) Inoculate Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) in LB liquid medium, cultivate overnight at 37°C, introduce pCas9 plasmid into BL21 by electroporation, spread the plate, pick positive transformants and inoculate in LB...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com