Method for stratifying diabetic patients
A technology for type 1 diabetes and patients, applied in chemical instruments and methods, metabolic diseases, pharmaceutical formulations, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
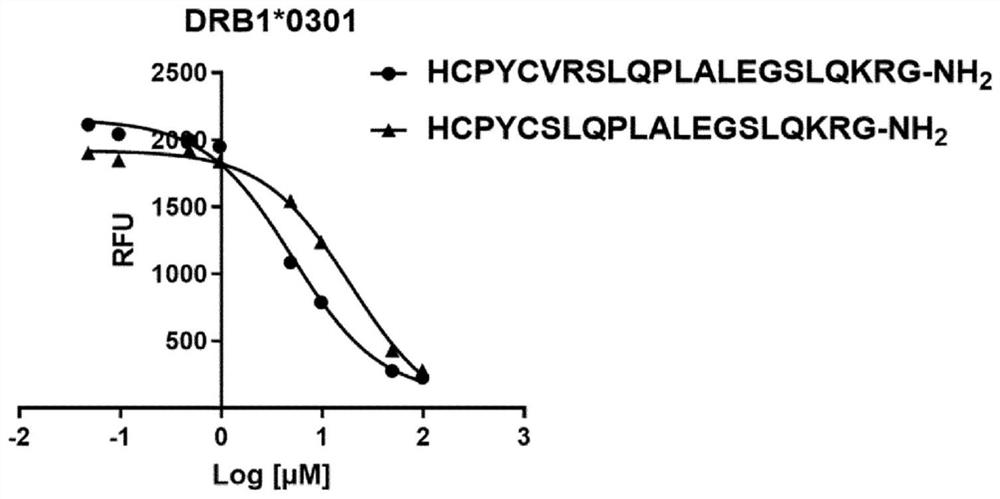
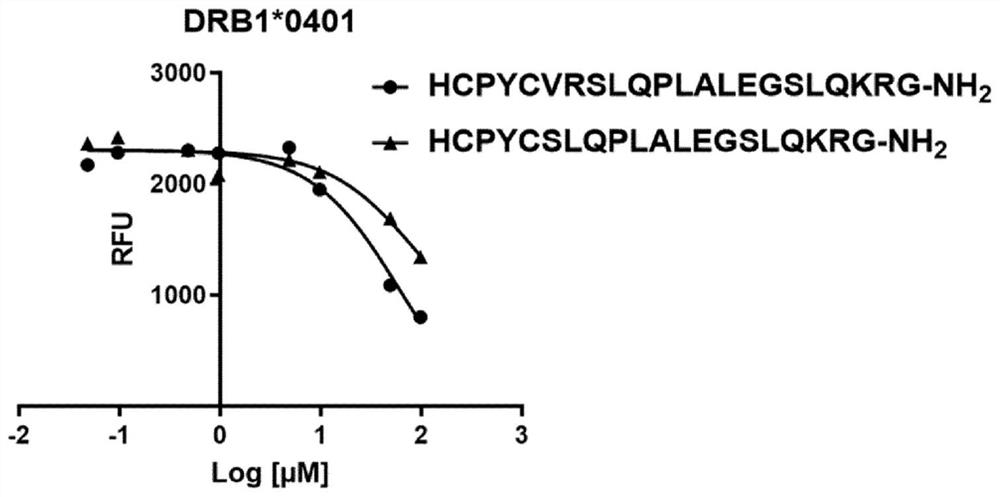
[0269] Example 1: Binding of immunogenic peptides comprising insulin MHCII T cell epitopes and oxidoreductase motifs to soluble DRB1*0301 or DRB1*0401 recombinant MHC II proteins.
[0270] To test the binding of peptides comprising MHC class II T-cell epitopes and oxidoreductase motifs from the proinsulin region C20_A1, a soluble phase competition assay was performed with increasing concentrations of HCPYCVRSLQPLALEGSLQKRG (SEQ ID. NO: 25) The peptide with HCPYCSLQPLALEGSLQKRG (SEQ ID. NO. 26) competed with the labeled control peptide (high affinity binder; biotinylated) for binding to soluble DRBI*0301 or DRB1*0401 recombinant human MHC II protein. As the binding approaches equilibrium (18 hours), the peptide-MHC II complex is captured and separated from the unbound reagent. The captured peptide-MHCII complex was detected by time-resolved fluorescence (Eu 3+ Streptavidin) was quantified, and the data were processed and plotted to determine the dose-dependent binding properti...
Embodiment 2
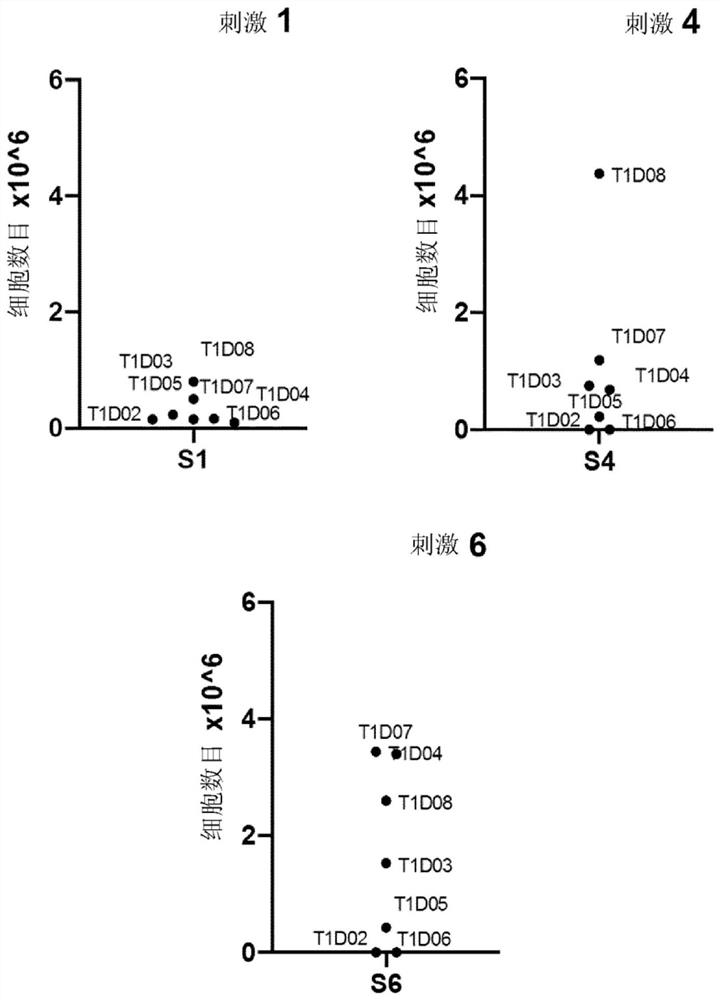
[0271] Example 2: Ability of immunogenic peptides comprising insulin MHCII T cell epitopes and oxidoreductase motifs to prime and expand CD4+ T cells from various insulin-dependent diabetic patients.
[0272] Naive CD4+ T cells from different type 1 diabetes (T1D) patients were tested for reactivity to the peptide defined by the sequence HCPYCVRSLQPLALEGSLQKRG. T1D patients were first tested for HLA DRB1 typing (see Table 1).
[0273] Table 1: HLA DRB1 typing of T1D patients tested.
[0274]
[0275] HLA typing is performed using methods known in the art, eg as reported in Mack et al., 2009, Tissue Antigens. 2009 Jan;73(1):17-32.
[0276] Blood samples were then processed and naive CD4+ T cells were purified by magnetic separation techniques. Peptide priming and amplification of these were tested using peptide-preloaded autologous dendritic cells (monocyte-derived DCs differentiated in the presence of GM-CSF and IL-4 followed by maturation with TNF-α) as antigen-presentin...
Embodiment 3
[0278] Example 3: Phase Ib clinical trial with an immunogenic peptide with the sequence HCPYCSLQPLALEGSLQKRG in T1D patients.
[0279] The safety, clinical efficacy, and induction of immune responses of an immunogenic peptide with the sequence HCPYCSLQPLALEGSLQKRG were evaluated in a Phase Ib clinical trial in recent-onset (≤6 months) adult T1D patients. In this dose-escalation, placebo-controlled study, patients received four biweekly subcutaneous injections of one of the three tested doses or matching placebo. The peptides were injected with alum as an adjuvant. Patients were followed for 6 months to evaluate the safety of the peptides and the induction of immune responses.
[0280] The main inclusion criteria are:
[0281] -BMI 1728kg / m 2 of men and women between the ages of 18 and 30;
[0282] - Preliminary diagnosis of type 1 diabetes according to ADA / WHO criteria within the past 6 months;
[0283] - Insulin requirements determined by the investigator;
[0284] - HL...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com