Trichoderma asperellum and application thereof
A technology of Trichoderma aculeatus and fungi, applied in the field of Trichoderma aculeatus, can solve the problems of pesticide residues, rampant pathogens, enhanced drug resistance of pathogens, etc., and achieve the effect of high safety
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
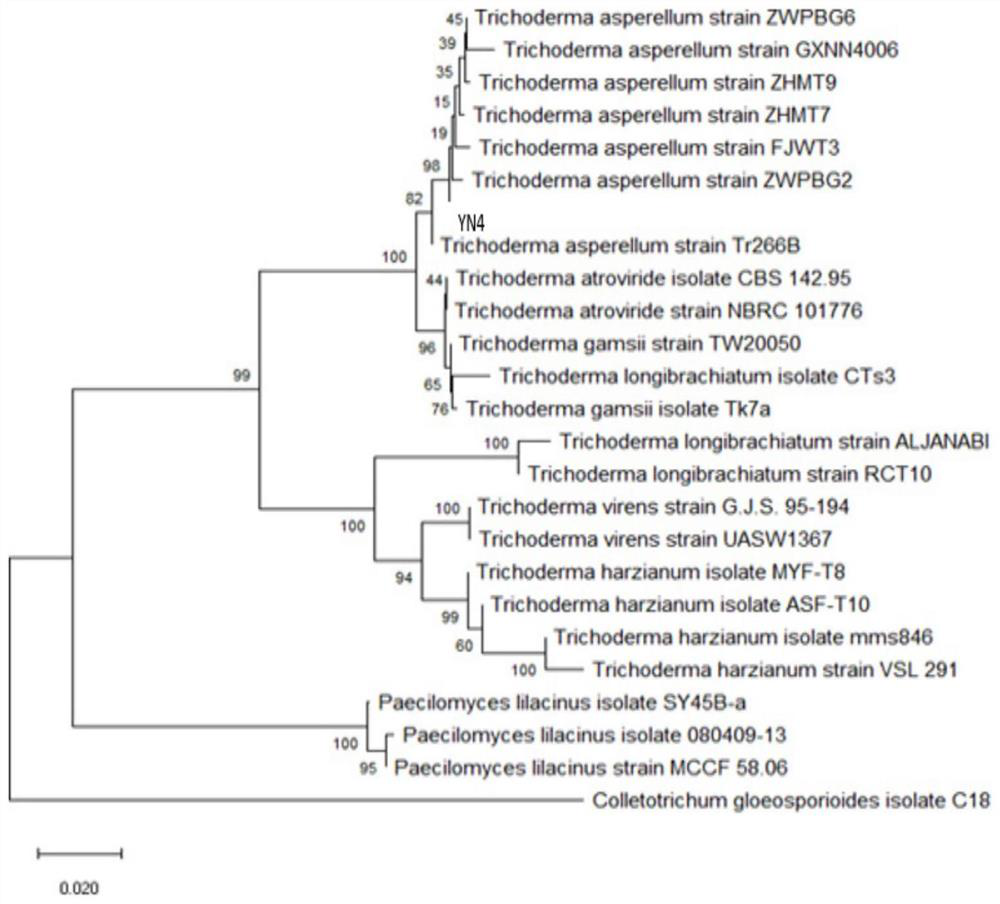
[0067] Example 1 Isolation and identification of Trichoderma strain YN4
[0068] 1. Sample collection
[0069] Tea leaves were collected from Honghe Prefecture, Yunnan, and returned to the laboratory for tissue isolation. First, clean the surface of the leaves, and select intact leaves without disease spots for separation. For the method of tissue isolation, please refer to "Plant Pathology Research Methods".
[0070] 2. Morphological identification
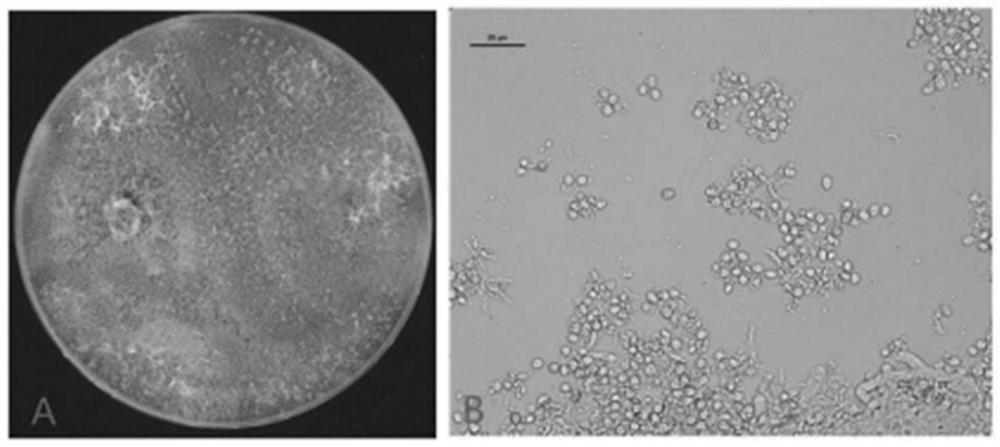
[0071] From the colonies isolated from the tea tree leaf tissue, the newly grown colonies were picked with sterile toothpicks and cultured on a new PDA plate, and cultured in a 28°C incubator for 2-3 days. Observe the colony morphology and color of the strain. Take an appropriate amount of bacteria with a sterile dissecting needle and observe it under an optical microscope, and take pictures of hyphae, conidia, etc. According to the morphological characteristics of the strain, it was preliminarily identified as Trichoderma, ...
Embodiment 2
[0080] Example 2 Inhibitory effect of Trichoderma strain YN4 on various pathogenic bacteria
[0081] 1. Experimental method
[0082] The antagonistic effect of the strain T. asperellum YN4 identified in Example 1 against 12 phytopathogenic fungi was determined by the confrontation method.
[0083] Tested phytopathogenic fungi: F. oxysporum f. sp. glycines, F. oxysporum f. sp. cube, F. oxysporum f. sp. .solani), F. falciforme, C. siamense, C. gloeosporioides, C. truncatum, S. sclerotiorum rolfsii), N. sphaerica, R. solani, P. oryzae, and B. cinerea. The above plant pathogenic fungal strains are all preserved by our laboratory.
[0084] Specific practices: the strains T. asperellum YN4 and the test plant pathogenic fungi identified in Example 1 were grown in PDA plates for 3 to 5 days, respectively, using a hole punch with a diameter of 5 mm to punch holes at the edge of the colony to obtain bacteria. cake. In a PDA plate with a diameter of about 9cm, two places in diameter 2...
Embodiment 3
[0095] The antibacterial effect of embodiment 3 Trichoderma strain YN4 volatile organic matter
[0096] 1. Antibacterial effect of volatile organic compounds of Trichoderma strains
[0097] 1. Experimental method
[0098] Use a sterilized hole puncher with a diameter of 5mm in a constant temperature incubator at 28°C for 2 to 3 days to cultivate the bacterial colony edge of the strain Trichoderma asperellum (T. asperellum) YN4 identified in Example 1. The center of the petri dish with a 9 cm medium containing PDA was cultured at 28° C. until the colony diameter reached 5 cm, and a sterilized double cellophane with a diameter of 10 cm was covered above. Four kinds of plant pathogenic fungi (Siamese anthracnose, Fusarium spp., Fusarium oxysporum Cuban-specialized type and Fusarium rot) were made into 5 mm diameter cakes and inoculated into petri dishes containing PDA medium middle. The petri dish inoculated with the strain T. asperellum (T. asperellum) YN4 (covered with steri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com