Hydrated acellular skin substitute material and manufacturing method thereof
A manufacturing method, cell-free technology, applied in skin transplantation, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve problems such as immune response, damage to the dermis, transplant rejection, etc., and achieve the effect of soft physical properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0081] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described more specifically by way of examples. However, the scope of the present invention is not limited to the following examples, and those skilled in the art should understand that various variations, modifications, or applications can be made within the scope of the technical idea derived from the contents of the claims.
Embodiment 1
[0083] Example 1. Manufacture of acellularized skin substitute material
[0084] (1) Skin pretreatment process
[0085] Skin tissue was prepared (collected from tissue banks, cadavers donated for non-profit purposes and used to treat patients).
[0086] Put the cleaned skin tissue on a sterile table, and use a scraper to remove fascial tissue, adipose tissue, and other foreign objects attached to the dermis until the dermis is partially visible. Use a sterile spatula to remove as much of the remaining fat as possible in the dermis, and use sterile scissors and forceps to remove the remaining unnecessary tissue. Wash several times with sterile distilled water.
[0087] (2) Fat removal process
[0088] The degreasing solution is made by mixing IPA and hexane at a mixing ratio of IPA:hexane of 2:8 to 8:2.
[0089] The degreasing solution and the pretreated skin tissue were put into a 4L jar, and stirred at room temperature at 150 rpm for 2 hours. Remove the skin tissue durin...
experiment example 1
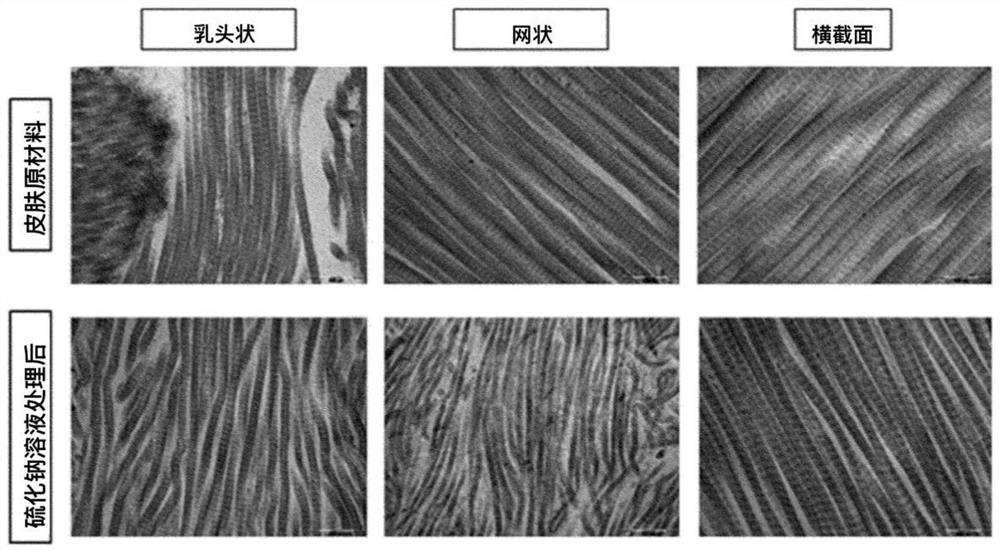
[0103] Experimental example 1. Confirm whether the collagen fibers in each step are damaged
[0104] After each step of Example 1, it was confirmed whether the collagen fibers of the skin tissue were damaged.
[0105] (1) Confirm whether the collagen fibers are damaged after the fat removal process
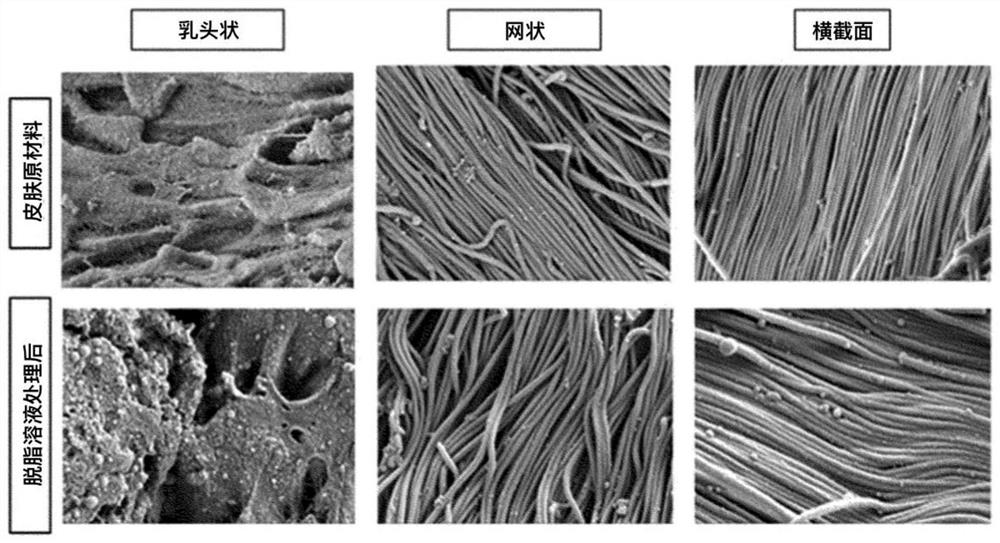
[0106] After performing the (2) fat removal process of Example 1, the skin tissue was photographed using a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
[0107] figure 1 It shows the result of photographing with a scanning electron microscope (SEM) to confirm whether the collagen fibers are damaged after the treatment of the degreasing solution.
[0108] Such as figure 1 As shown, it was confirmed that no tissue deformation or collagen fiber damage was observed in the skin (IPA / hexane) from which fat was removed using a degreasing solution, as in the raw skin material (raw skin).
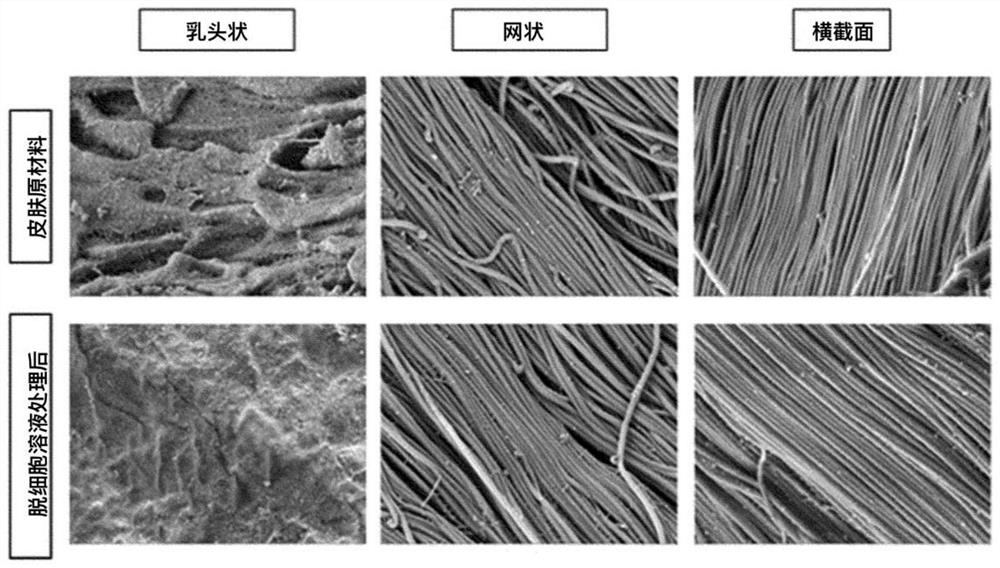
[0109] (2) Confirm whether the collagen fibers are damaged after the cell removal process
[0110] After...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com