Iron-based magnetically soft alloy, method for manufacturing same, and magnetic component comprising same
A technology of soft magnetic alloy and manufacturing method, applied in the direction of inductance/transformer/magnet manufacturing, magnetic objects, magnetic materials, etc. Low magnetic loss characteristics, low coercive force, and easy design of process conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0102] Weigh the raw materials of Fe, B, C, Nb and Cu to produce Fe by the experimental formula 80.3B 16.8 C 1.0 Cu 0.9 Nb 1.0 The Fe master alloy indicated, and the Fe master alloy was fabricated by the arc melting method. After that, after melting the produced Fe master alloy, in an Ar atmosphere, it was melt-spun at a rate of 60 m / s for 10 6 Rapid cooling at a rate of K / sec produced a ribbon-shaped iron-based soft magnetic initial alloy with a thickness of about 20 μm and a width of about 20 mm.
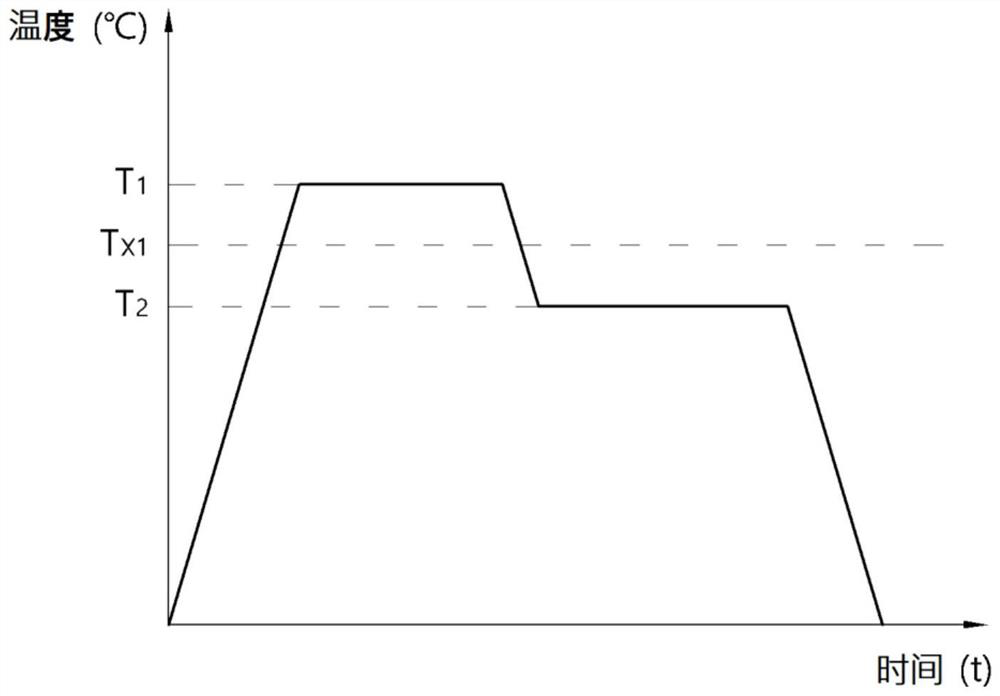
[0103] Then, the produced ribbon-shaped iron-based soft magnetic initial alloy was wound so that the outer diameter was 20 mm and the inner diameter was 10 mm, and the core-shaped initial alloy or ribbon was heated at a heating rate of 80°C / min under normal temperature conditions. The shaped initial alloy was heat-treated and kept at a temperature of 470° C. for 10 minutes, thereby producing an iron-based soft magnetic alloy as shown in Table 1 below.
Embodiment 2~ Embodiment 16
[0105] Production was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1, and the composition and / or the heat treatment temperature were changed as shown in Table 2 or Table 3 below, thereby producing the iron-based soft magnetic alloy shown in Table 2 or Table 3 below.
experiment example 1
[0109] The following physical properties were evaluated for the initial alloys produced in Examples 1 to 16 and Comparative Examples 1 to 5 and the alloys after heat treatment, respectively, and are shown in Tables 1 to 3.
[0110] 1. Crystal structure analysis
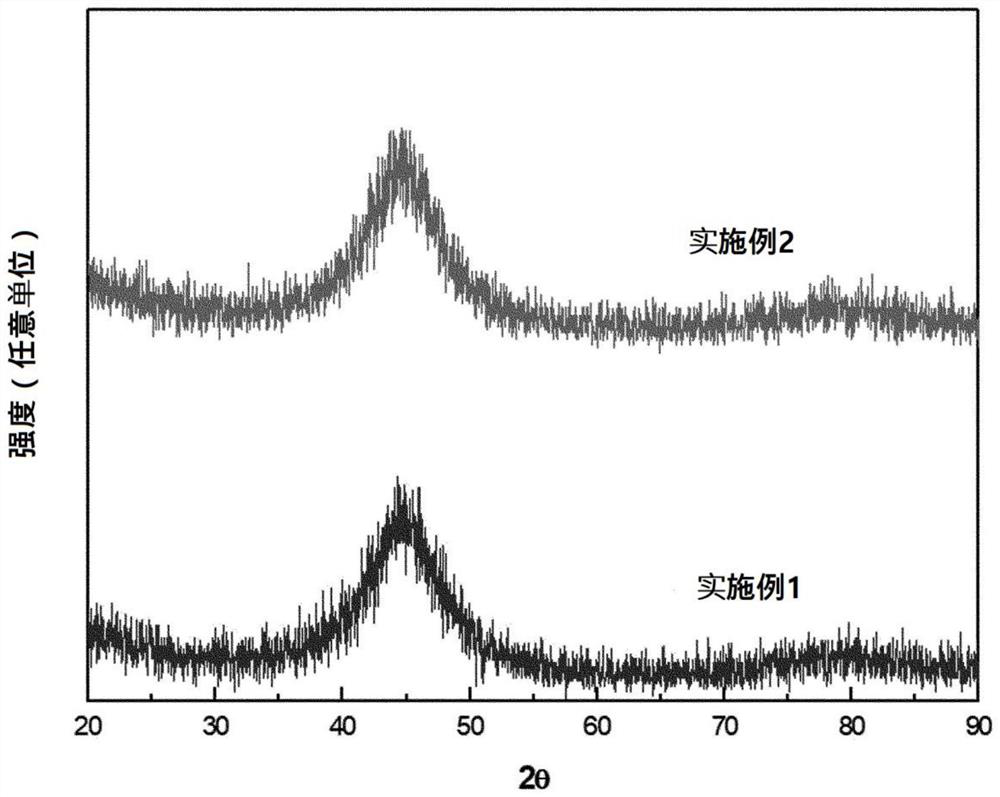
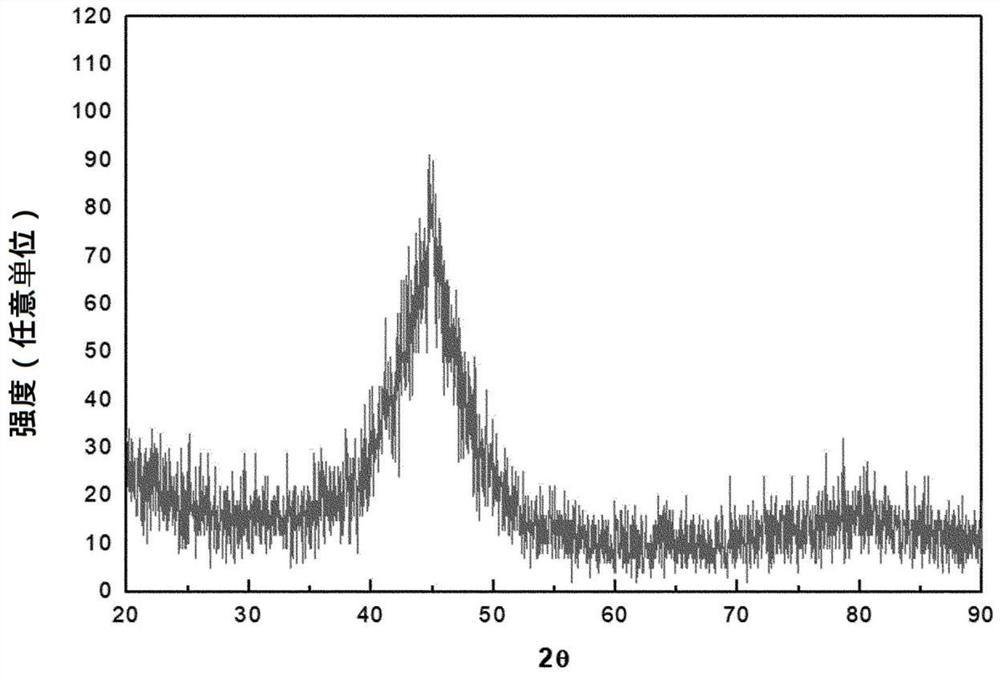
[0111] In order to confirm the crystal phase of the produced initial alloy and the alloy after the heat treatment, and the average particle size of the generated crystal, the X-ray diffraction pattern and the transmission electron microscope were analyzed. In this case, in figure 2 The X-ray diffraction patterns of the iron-based soft magnetic alloys before the heat treatment of Examples 1 and 2 are shown in the analysis results. and, in image 3 and Figure 4 The X-ray diffraction pattern and transmission electron microscope image of Example 1 after heat treatment are shown, respectively. Figure 5 and Image 6 The X-ray diffraction pattern and the transmission electron microscope image of Example 2 after the h...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| saturation flux density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com