Preparation method using bacterial lysate as inactivated vaccine adjuvant
A technology of inactivated vaccines and lysates, which is applied in the field of preparation of bacterial lysates as inactivated vaccine adjuvants, which can solve the problems of limited use of vaccine adjuvants, poor immune enhancement effect, local irritation, etc., and achieve improved vaccine immunity , The production method is simple and the cost is low
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Adjuvant preparation:
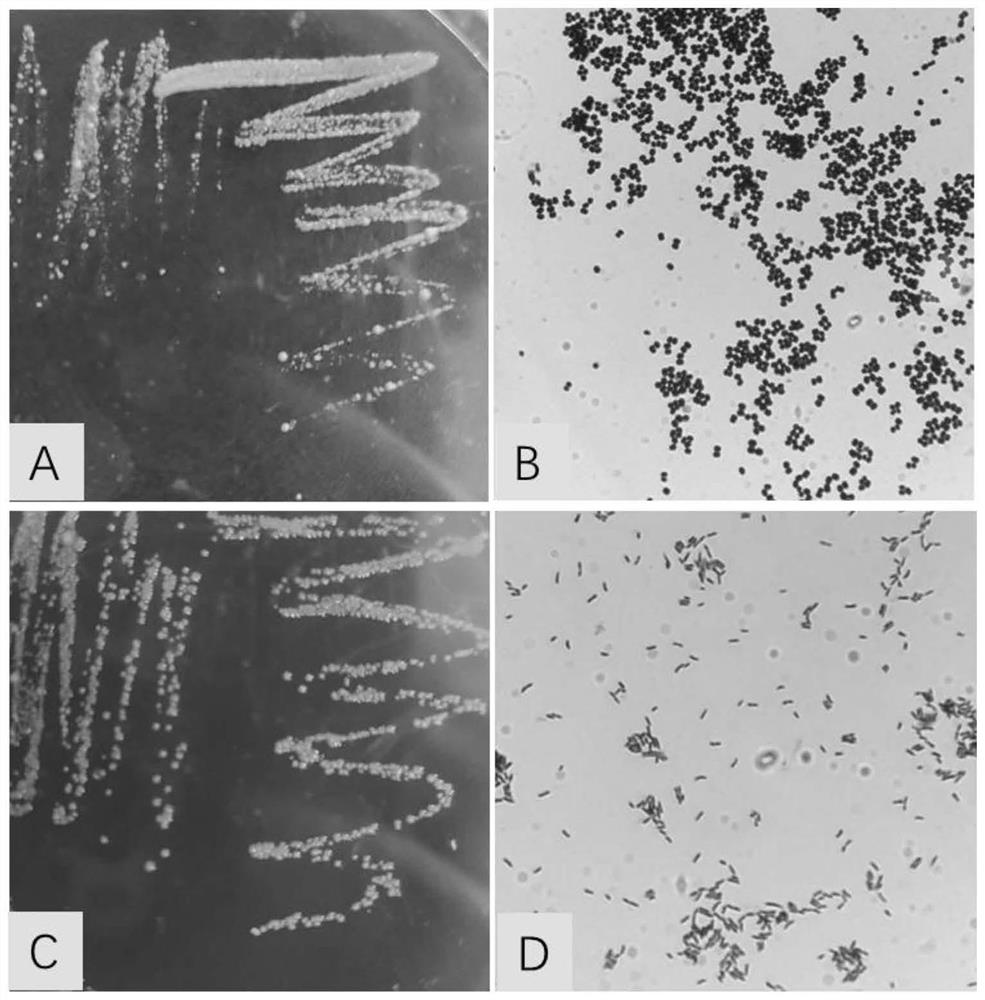
[0044] Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis and Rhodococcus equi were inoculated in LB solid medium at 37°C for 14 hours, picked a single colony, inoculated in 3ml LB liquid medium on a shaker (220rpm) at 37°C for 12h, and inoculated with 600ml LB at a ratio of 3‰ Liquid culture medium, cultivated at 37°C for 12h-16h, measured OD600 reached about 1.0, centrifuged to collect bacteria, diluted with sterilized normal saline to make the concentration of bacteria reached 8.0×109cfu / mL, directly passed through a high-pressure homogenizer, crushed bacteria, Or after 1:1 mixing, the high-pressure homogenizer continuously crushes three times to obtain the vaccine adjuvant mixed with Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis, Rhodococcus equi and the two, mix with inactivated Pasteurella 1:1, and obtain the vaccine adjuvant added with Inactivated vaccines for Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis, Rhodococcus equi and a mixture of both. The morphology of Corynebacter...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Safety evaluation of lysates of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis and Rhodococcus equi:
[0048] The three batches of adjuvant prepared in Example 1 were injected into 3 healthy mice in a single dose, 5 times the dose and 10 times the dose, and inoculated into the inner muscle of the hind limb. After 14 days of observation, the body temperature and appetite of the inoculated mice were normal, there was no swelling and inflammation at the inoculation site, and no local and systemic reactions occurred; 14 days later, the mice were killed, and the skin of the injection site was cut to observe the pathological changes of the injection site. There was no abnormality in the subcutaneous area of the injection site Muscle tissue at the inoculation site of the inner muscle of the hind limb was normal, and no inflammatory reaction was seen at the injection site. It shows that it has better safety for mice.
example 3
[0050] The promotion effect of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis and Rhodococcus equi lysates on mice immunized with Pasteurella inactivated vaccine:
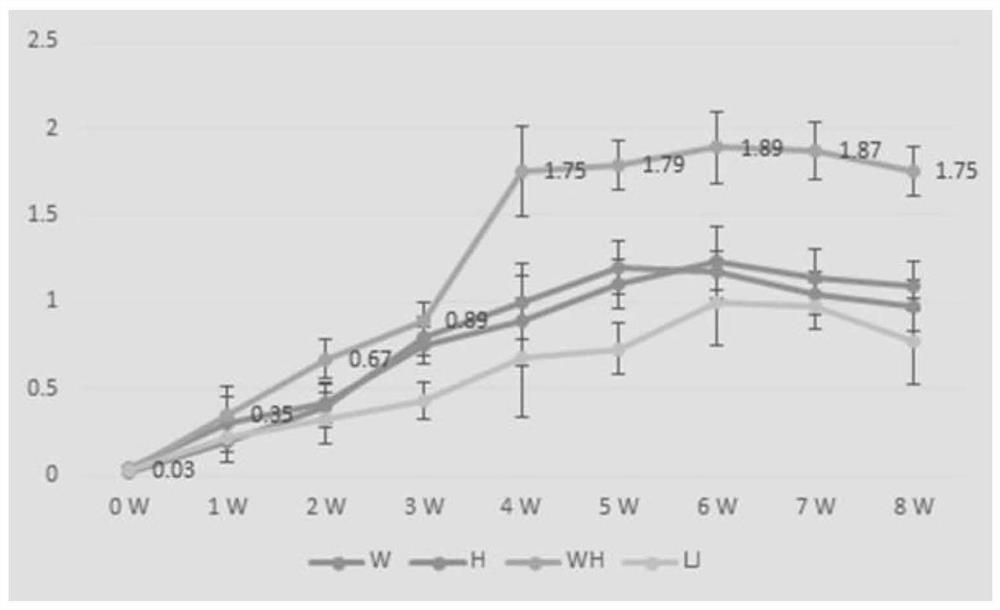
[0051] The lysate of Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis, Rhodococcus lysate and the lysate of the two mixtures, and 20% aluminum gel adjuvant were mixed with Pasteurella inactivated vaccine at a ratio of 1:9, and then immunized 4-6 weeks old Kunming 5 mice of each strain, 1ml / mouse. After immunization, the indirect ELISA method established in the laboratory was used to continuously detect the antibody level for 8 weeks, and draw the growth and decline rules of the antibody, as shown in figure 2 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com