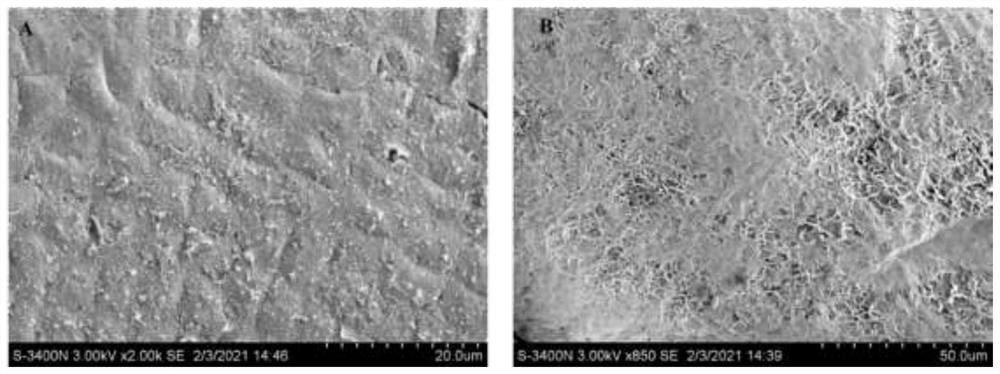
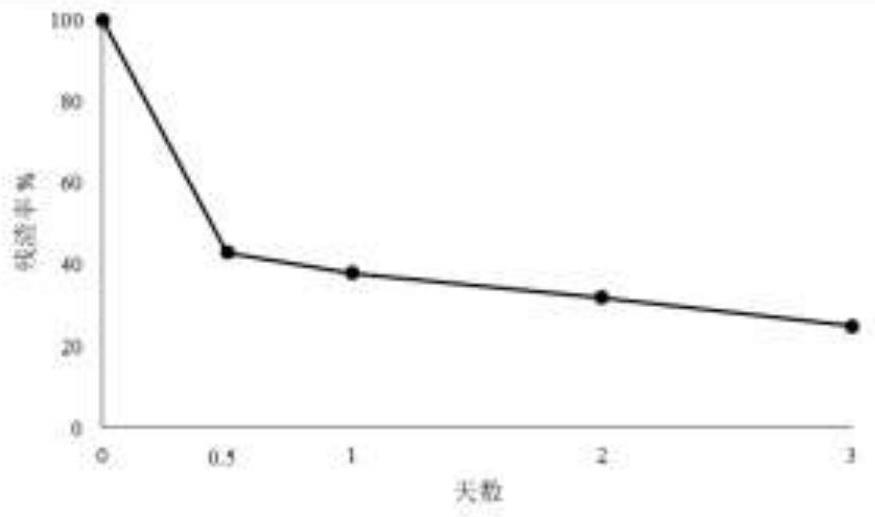
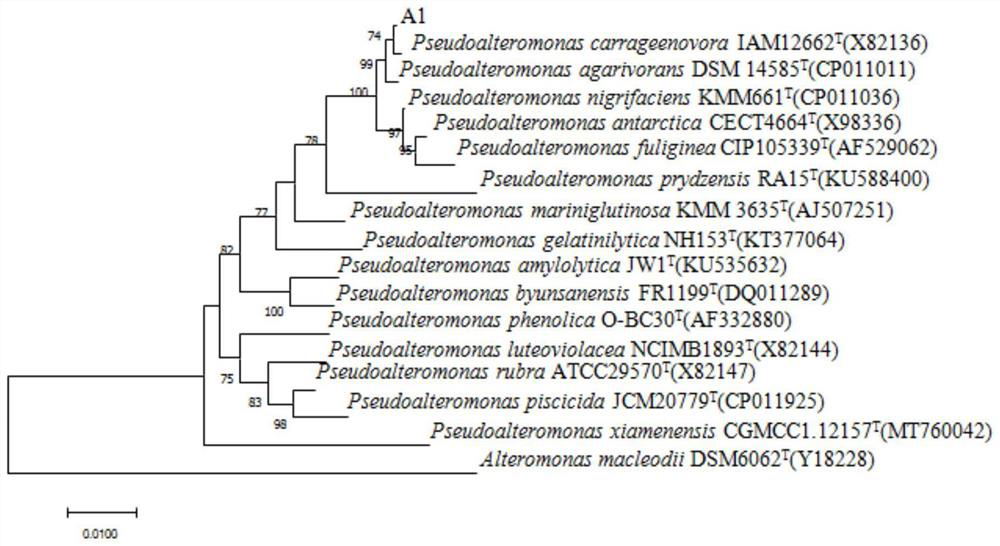
Strain capable of decomposing kelp
A technology of strains and kelp, applied in the direction of bacteria, biological organic part treatment, microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve the problems of destroying seaweed cell walls and high cost investment.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Collection of Carrageenan Pseudoalteromonas carrageenovora:
[0020] Cut 20 grams of fresh kelp samples into small pieces with sterile scissors, add them to an Erlenmeyer flask filled with 30 mL of sterilized physiological saline (0.9%, NaCl), and shake at 25°C and 150 r / min for 3 Hours. Draw 1 ml of the solution from the Erlenmeyer flask, add it to a 9 ml sterile saline test tube, perform 10-fold serial dilutions, and spread it on 2216E solid medium (peptone 5g / L, yeast powder 1g / L, agar Powder 20g / L, prepared by filtering seawater, pH 7.6-7.8.), cultured at 25°C for 7 days, picked different single colonies into 2216E solid medium according to the characteristics of colony shape, color, etc., streaked and purified until a single pure colony. Inoculate all the isolated strains on the alginate lyase screening medium (sodium alginate 20g / L, peptone 5g / L, yeast powder 1g / L, agar powder 20g / L, prepared by filtering seawater, pH 7.0.) plate Cultured for 3 days. Add 10% c...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Identification of Carrageenan Pseudoalteromonas carrageenovora:
[0023] The DNA of strain A1 was extracted using a bacterial genomic DNA extraction kit (Takara), and the 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR using 27F (5'-AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG-3') and 1541R (5'-AAGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCA-3') as primers. The PCR reaction system is 40 μL, which contains 1 μL 27F, 1 μL 1541R, 2×Mix 20 μL, ddH 2 O16 μL. The reaction conditions were 5 minutes of pre-denaturation at 94°C, followed by 30 cycles of 1 minute at 94°C, 1 minute at 55°C, 1.5 minutes at 72°C, extension at 72°C for 1.5 minutes, and cooling to 8°C. The PCR product was sent to Beijing Qingke Biological Co., Ltd. for 16S rRNA gene sequencing. After comparing the sequence with the NCBI database, the strain A1 belonged to the genus Pseudoalteromonas, which had the highest similarity (99.9%) with the published species Pseudoalteromonas carrageenovora, so the The strain is Pseudoalteromonas carrageenovora, named Pseudoalteromonas ...
Embodiment 3
[0026] The application of strain decomposing kelp, the specific steps are as follows:
[0027] Medium preparation:
[0028] 2216E liquid medium (5g / L peptone, 1g / L yeast powder, prepared by filtering seawater, pH 7.6-7.8.)
[0029] Preparation of seed solution: inoculate the A1 strain from a slant, put it into a 20 ml Erlenmeyer flask (100 ml) filled with 2216E liquid medium, and cultivate it for 2 days at 25° C. and 150 r / min.
[0030] Fermentation culture:
[0031] Dried kelp is cut into small pieces with a diameter of 2 to 3 cm, added to 2216E liquid medium, and sterilized. Insert the seed liquid, ferment and cultivate for 7-10 days.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com