A Largemouth Bass Iridescent Virus and Its Application
A largemouth and virus technology, applied in the field of largemouth bass iridovirus, can solve problems such as outbreaks of disease and economic losses, and achieve the effect of high protection rate and good immunogenicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
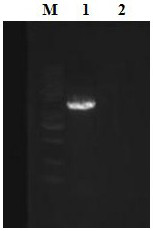
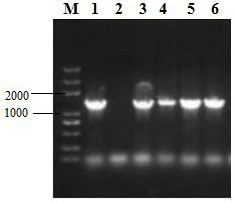
[0035] Example 1. Isolation and identification of largemouth bass iridovirus
[0036] 1. Collection of largemouth bass iridovirus-infected samples
[0037] From June to July 2019, a large-scale disease of largemouth bass broke out in a farm in Nanyang City, Henan Province. The main symptoms were black body color, lack of vitality, mild abdominal swelling, mortality rate as high as 70%, and dying fish. After necropsy, symptoms of acute peritonitis, necrosis and inflammatory lesions appeared in the surface part of liver, stomach, intestine and spleen, but the deep part appeared normal, there was fibrin exudate on the contact surface of swim bladder and abdominal cavity, mucosa of gastrointestinal tract There were localized necrotic lesions in the epithelium, which were in line with the symptoms associated with largemouth bass iridovirus infection. Twenty largemouth bass with ulcer symptoms were collected from the farm. The collected samples were stored separately in sealed bags...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Example 2. The preparation method of largemouth bass iris virus N-LBIV-201907 inactivated vaccine
[0057] Step 1, culture of EPC cells: subculture EPC cells in M199 medium containing 10% (V / V) fetal bovine serum at 25°C, 5% CO 2 Incubate at constant temperature until the cells are confluent, grow into a monolayer, and the number of cells is > 10 6 / mL
[0058] Step 2, Proliferation of Largemouth Bass Iridescent Virus N-LBIV-201907: Aspirate the culture medium in the EPC cells, and then add the virus suspension of N-LBIV-201907 (10 5 TCID 50 / mL), after the virus was adsorbed to the cells for 1 h, M199 (pH 7.2-7.5) maintenance solution containing 2% (V / V) calf serum was added for virus proliferation.
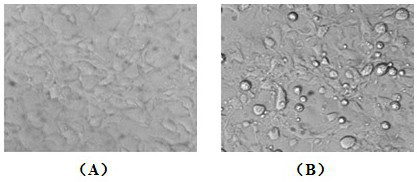
[0059]Step 3: Virus harvesting: The virus is continuously cultured for 4 to 7 days, and observed under a microscope. When 80% of EPC cells show typical cytopathic effects, they are placed in a -80°C refrigerator for freezing, and after freezing, they are taken out and ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3. Safety inspection and immune efficacy evaluation of largemouth iridovirus inactivated vaccine
[0067] 1. Safety inspection of inactivated vaccines
[0068] 1.1 Inactivation effect test
[0069] Take the prepared vaccine and inoculate EPC cells according to the above method of virus proliferation, and set up a negative control (freezing and thawing supernatant of EPC cells without virus) and observe for 7 days. If cytopathic effect occurs, it indicates that the virus inactivation is incomplete; If no cytopathic effect is seen, blind pass 3 more times. If cytopathic occurs in blind pass, it means that virus inactivation is still incomplete.
[0070] Sterility testing
[0071] Take the vaccine prepared above, inoculate the brain infusion bacterial culture medium (BHI) plate, spread the plate with streak method and cultivate at 37 °C for 15 days. Use after membrane filtration sterilization; if no colonies grow, the vaccine is sterile.
[0072] fish safety in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com