Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing astaxanthin, and application of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae
A technology of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low astaxanthin production, achieve the effects of optimizing fermentation conditions, good industrial application prospects, and improving production and purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
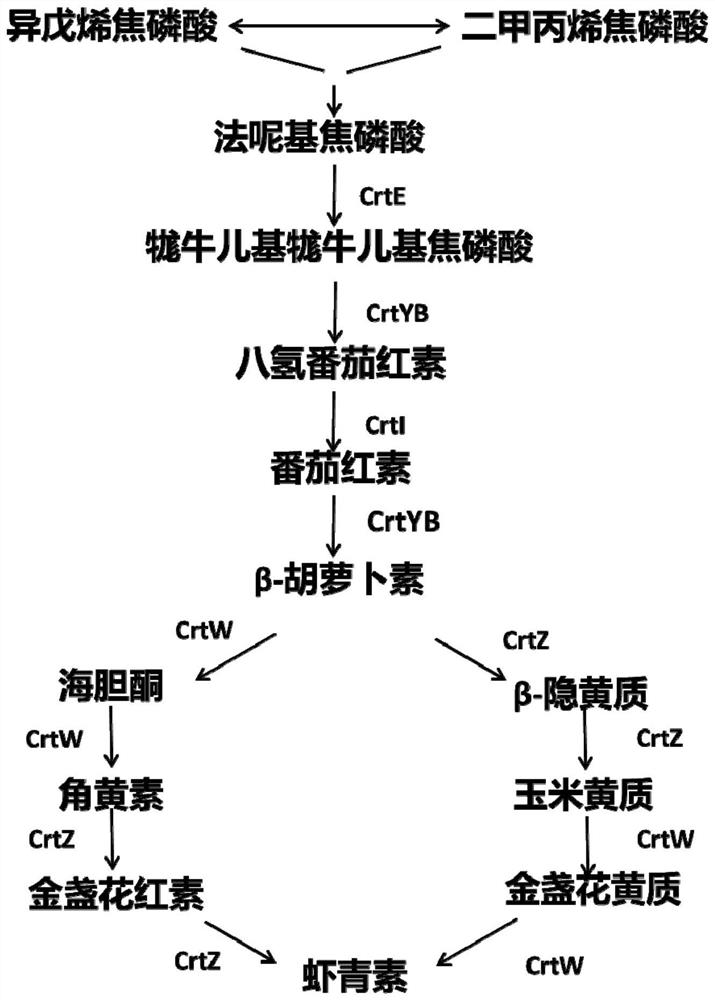
[0044] Example 1: Construction of an engineering strain producing high-purity astaxanthin using Saccharomyces cerevisiae producing β-carotene as a chassis strain
[0045] 1. Construction of gene expression fragments of CrtW and CrtZ
[0046] (1) Using the promoter TDH3p (SEQ ID NO: 1), the gene CrtW (SEQ ID NO: 2), and the terminator TDH2t (SEQ ID NO: 3) as templates, the TDH3p-CrtW-TDH2t fragment was constructed by OE-PCR , the sequence of the TDH3p-CrtW-TDH2t fragment is shown in SEQ ID NO:10.
[0047] OE-PCR system (50μl reaction system) is as follows:
[0048] Promoter TDH3p, gene CrtW and terminator TDH2t templates 1 μl each, upstream primers 1 μl, downstream primers 1 μl each, 10×Buffer 5 μl, dNTP 4 μl, Pfu DNA Polymerase 1 μl, add ddH 2 O to make up the volume to 50 μl.
[0049] The primers used are as follows:
[0050] Primer 1-F: 5'-cagttcgagtttatcatttatcaatactgcca-3' (SEQ ID NO: 4);
[0051] Primer 1-R: 5'-tcattggagtaacagcggacattttgtttgtttatgtgtgtgttattcg-3' (SE...
Embodiment 2
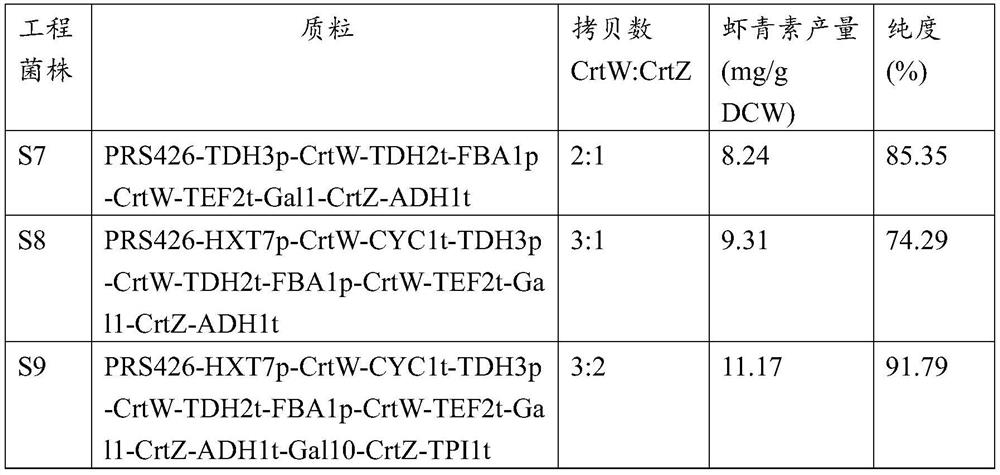
[0140] Embodiment 2: Shake flask fermentation produces astaxanthin
[0141] The Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strains S7, S8, and S9 constructed in Example 1 to produce astaxanthin were respectively inoculated into 5ml of SC-Ura liquid medium, and cultured overnight at 30°C and 250rpm to obtain first-class seeds, and then press 1-2% (v / v) inoculum size Inoculate primary seeds into fresh 5ml SC-Ura liquid medium, culture secondary seeds at 30°C, 250rpm to OD 600 =5-6, get the secondary seed. The transferred secondary seeds were inoculated into a 250ml shaker flask containing 50mL of 4% glucose-containing YPD medium (10g / L yeast extract, 20g / L peptone, 40g / L glucose, and the balance was water) for fermentation, and the initial OD 600 =0.1, temperature 30°C, rotation speed 250rpm, ferment for 42 hours, add D-(+)-galactose with a final concentration of 2% (2g / 100ml) to induce astaxanthin production, and ferment for 84 hours to obtain a fermentation broth.
[0142] Then, a...
Embodiment 3
[0155] Example 3: Effects of different inducer addition times on the yield and purity of astaxanthin during shake flask fermentation
[0156] The engineering bacterial strain S9 that produces astaxanthin is cultivated according to the seed culture method among the embodiment 2 and obtains secondary seeds, then it is inserted into five sets of 250ml shaking flasks that contain 50mL of YPD medium containing 4% glucose (each group is provided with two The fermentation culture was carried out in Y1, Y2, Y3, Y4 and Y5 in parallel), and the initial OD 600 = 0.1, temperature 30°C, rotation speed 250rpm, add D-(+)-galactose with a final concentration of 2% at the 30h, 36h, 42h, 48h, and 54h of fermentation to induce astaxanthin production, and the fermentation is over for 84 hours to obtain fermentation broth. Then, take an appropriate amount of fermented liquid, and carry out wall-breaking treatment to the yeast engineering strain wherein, then extract astaxanthin with acetone, then...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com