Automatic fault identification method for elevator landing door
An automatic identification and elevator hall technology, applied in transportation, packaging, elevators, etc., can solve problems such as frequent elevator failures, poor monitoring effects, and insufficient real-time performance, so as to improve efficiency, improve real-time performance, and reduce personal safety or property loss effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
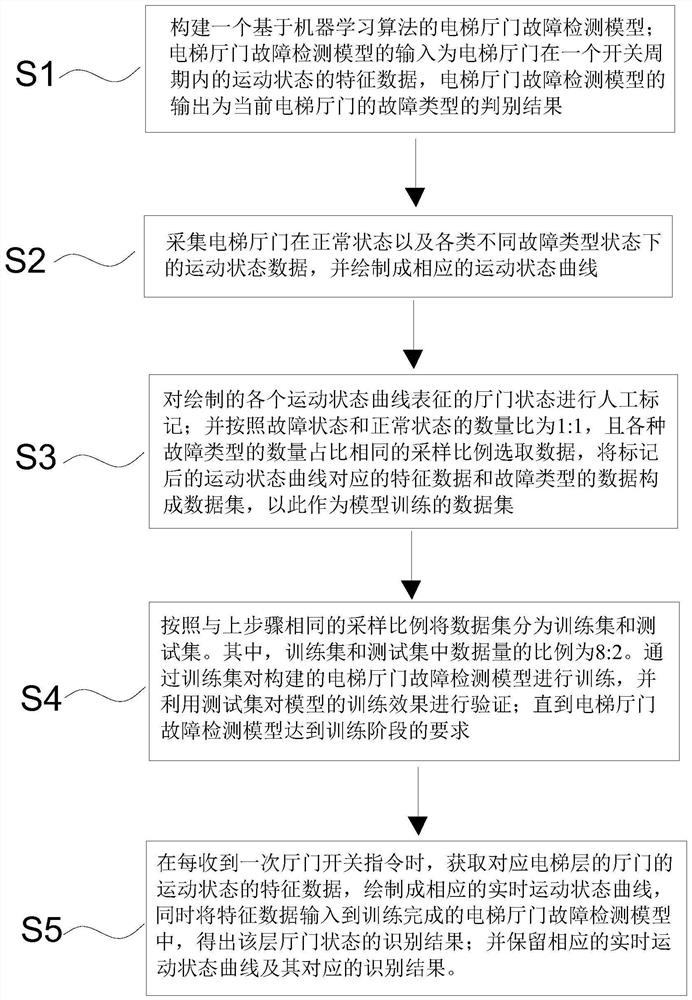
[0040] A fault automatic identification method for an elevator hall door provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0041] S1: Construct an elevator hall door fault detection model based on a machine learning algorithm; the input of the elevator hall door fault detection model is the characteristic data of the motion state of the elevator hall door in one opening and closing cycle. The input of the hall door fault detection model is the velocity, angular velocity and acceleration of the three axes of the elevator door. The output of the elevator hall door fault detection model is the judgment result of the current elevator hall door fault type.
[0042] S2: Collect the motion state data of the elevator hall door in the normal state and various fault types, and the motion state data is the input required by the elevator hall door fault detection model in the training or identification phase. In this embodiment, the relevant characteristic data is also drawn in...
Embodiment 2
[0060] This embodiment provides a fault monitoring system for an elevator hall door. The fault monitoring system adopts the automatic identification method for elevator hall door faults as in Embodiment 1 to identify the motion state of the hall door in each floor elevator, so as to realize the detection of various types of faults. timely monitoring. like Figure 5 As shown, the fault monitoring system includes: a hall door sensor, a signal transmission module, a data relay processor, a communication module, and a cloud server. The topology of the system is as Image 6 shown.
[0061] Wherein, the hall door sensor includes an inertial measurement unit and a displacement measurement unit. The inertial measurement unit includes three single-axis acceleration sensors and three single-axis gyroscopes; the inertial measurement unit is used to measure independent three-axis velocity signals, acceleration signals and angular velocity signals. The displacement measuring unit inclu...
Embodiment 3
[0072] This embodiment provides a fault monitoring system for elevator hall doors. The difference between the fault monitoring system provided by this embodiment and Embodiment 2 is that: Figure 7 As shown, the system in this implementation also includes a local data server and a local application server; all data received and generated in the cloud server are stored in the local data server; the local application server is used to respond to the request of the manager and provide Provides access to all data in the local data server.
[0073] Specifically, in this embodiment, the manager opens a browser in the local application server to access the server with a fixed domain name, or enters a password in the software to log in to the corresponding account, obtains the data in the local data server, and controls the movement of the hall doors of each elevator. Status to browse. On the local application server side, the real-time motion status of all elevators is displayed in ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com