Method for preparing lithium salt by separating lithium concentrate roasting material and then acidifying or alkalizing roasting material
A roasting material and lithium concentrate technology, applied in the field of new energy lithium materials, can solve problems such as high production costs, loss of economic value, and increased production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
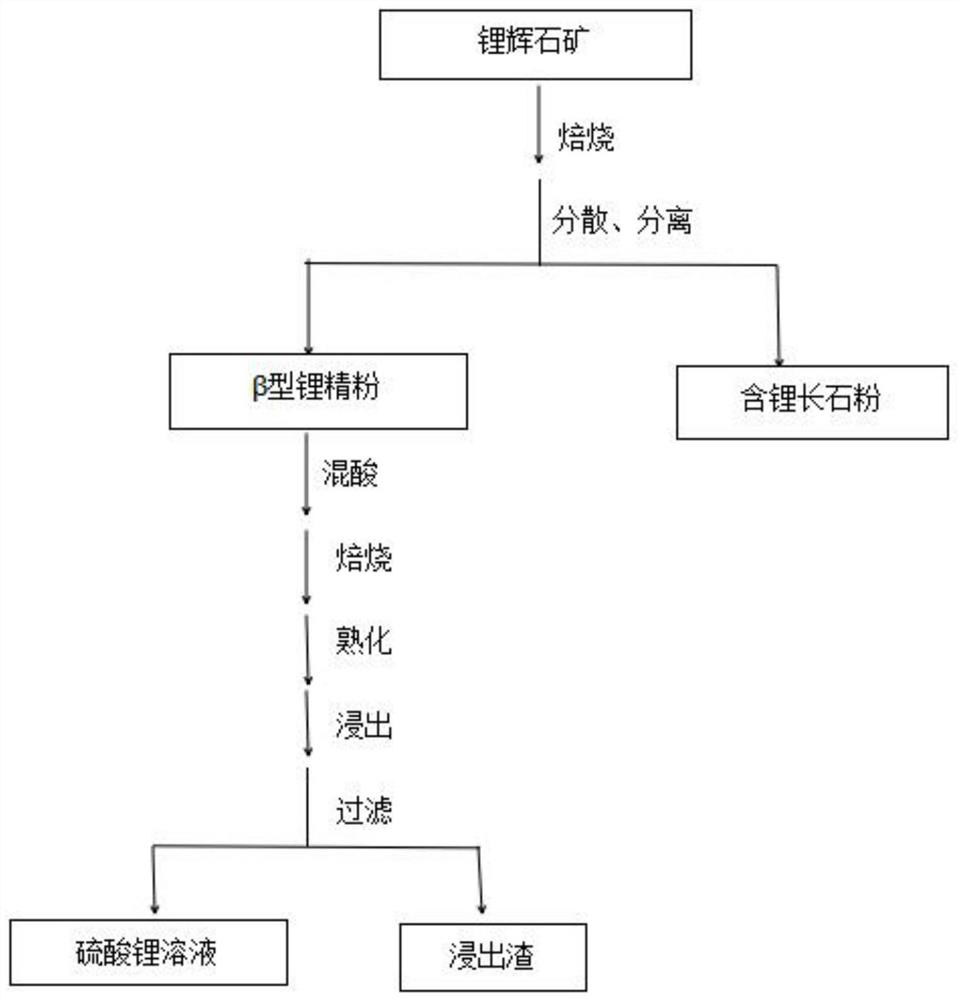
[0044] A method for preparing lithium salts through acidification or alkalization after separation of concentrate roasting materials, comprising the following steps:
[0045] S1, roasting: 100 g Li 2 The spodumene ore with an O content of 5% is placed in a roasting furnace, heated to 1050° C., and sintered for 40 minutes to obtain a roasted material;
[0046] S2, crushing and separation: the roasted material obtained in step S1 is crushed and separated by the airflow crushing and separation system; the fine powder under the 150-mesh sieve is the β-type lithium concentrate powder for lithium salt production; the coarse powder on the 150-mesh sieve The material is lithium-containing feldspar powder. The jet pulverization and separation system includes a jet pulverizer and a jet classifier; the gas pressure of the jet pulverization and separation system is 7kg / cm 2 , the supply frequency is 40 Hz.
[0047] After separation, obtain 65 grams of lithium-containing feldspar powder...
Embodiment 2
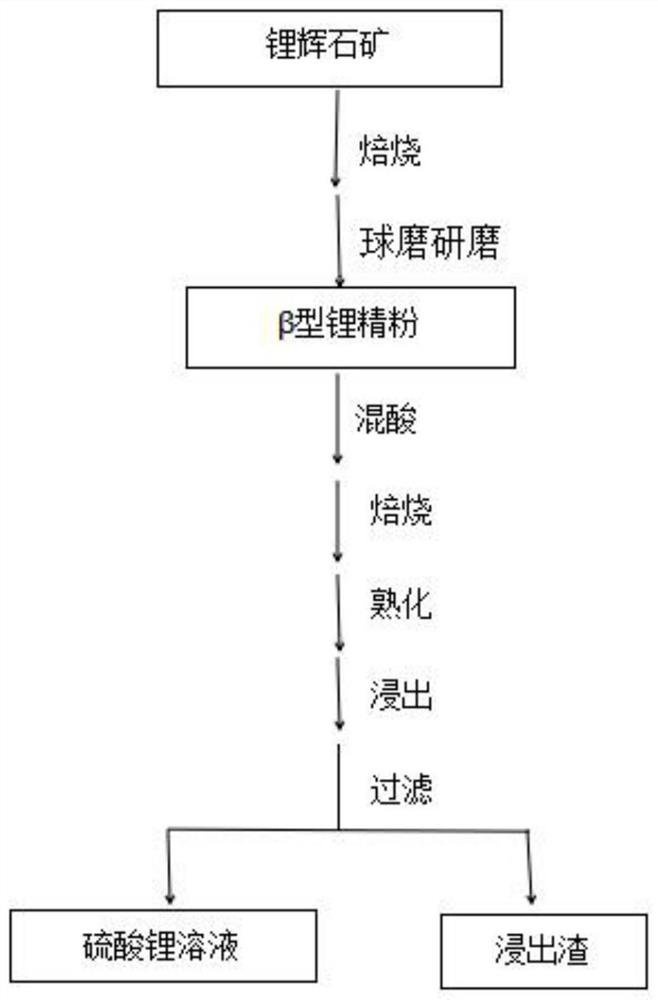
[0054] A method for preparing lithium salts through acidification or alkalization after separation of concentrate roasting materials, comprising the following steps:
[0055] S1, roasting: 100 g Li 2 The spodumene ore with an O content of 5% is placed in a roasting furnace, heated to 1000° C., and sintered for 1 hour to obtain a roasted material;
[0056] S2, Grinding and Separating: Grinding and separating the calcined material obtained in step S1 through the grinding and separation system; the fine powder under the 150-mesh sieve is the β-lithium fine stone powder for lithium salt production; the coarse powder on the 150-mesh sieve That is lithium-containing feldspar powder;
[0057] After separation, obtain 62 grams of lithium-containing feldspar powder and 33 grams of lithium salt production and use β-type lithium fine stone powder (the Li of β-type lithium fine stone powder 2 The O content is 14.62%; Li 2 The O content is ≤0.27%, which is directly used for ceramic prod...
Embodiment 3
[0064] A method for preparing lithium salts through acidification or alkalization after separation of concentrate roasting materials, comprising the following steps:
[0065] S1, roasting: 100 g Li 2 The spodumene ore with an O content of 5% is placed in a roasting furnace, heated to 1000° C., and sintered for 1 hour to obtain a roasted material;
[0066] S2, high-speed stirring and separation: the roasted material obtained in step S1 is stirred and separated at a high speed through the stirring and separating system; the fine powder under the 150 mesh sieve is the β-type lithium concentrate powder for lithium salt production; the coarse powder on the 150 mesh sieve is The powder is lithium-containing feldspar powder;
[0067] After separation, obtain 64 grams of lithium-containing feldspar powder and 31 grams of lithium salt production with β-type lithium fine stone powder (the Li of β-type lithium fine stone powder 2 The O content is 15.37%; Li 2 The O content is 0.27, wh...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com