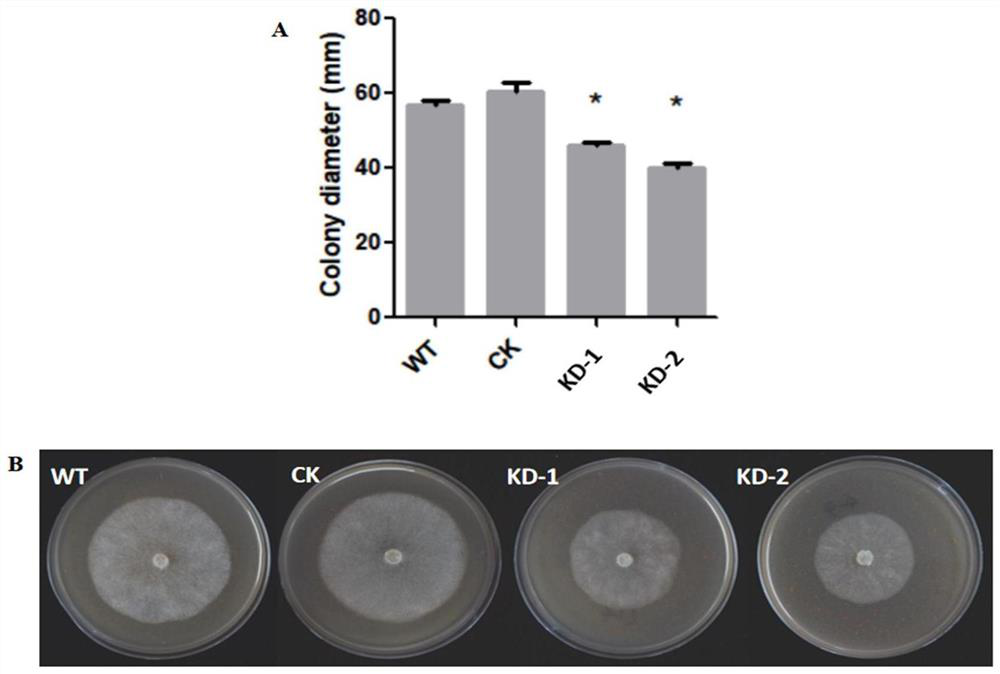
Key proteins for regulating and controlling secretion of extracellular vesicles from phytophthora capsici as well as coding gene and application thereof
A key protein, coding gene technology, applied in application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement and other directions, can solve the problems of limited varieties of resistant varieties and poor resistance stability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] Embodiment 1, acquisition of Phytophthora capsici Pcsec4-1, Pcsec4-2 proteins and their coding genes
[0091] In this embodiment, Phytophthora capsici Sec4 protein Pcsec4-1, Pcsec4-2 and its coding gene (or cDNA) can use the DNA (or cDNA) of Phytophthora capsici standard strain LT1534 as a template, obtained by amplification of the primers listed in Table 1 . Wherein, the material for DNA or RNA extraction can be the mycelium of Phytophthora capsici standard strain LT1534. Wherein, the coding gene Pcsec4-1 of Pcsec4-1 is shown as sequence 1 in the sequence listing, and the sequence 1 in the sequence listing is composed of 624 nucleotides; The sequence encodes the protein Pcsec4-1 shown in Sequence 2 in the Sequence Listing. The above-mentioned proteins or genes can also be artificially synthesized. The coding gene Pcsec4-2 of Pcsec4-2 is shown in the sequence 3 in the sequence listing, and the sequence 3 in the sequence listing is composed of 609 nucleotides; the 1st...
Embodiment 2
[0094] Embodiment 2, the construction of Phytophthora capsici Pcsec4-1 and Pcsec4-2 gene knockout vector
[0095] In this example, the CRISPR / Cas9-based gene knockout vector construction method and the sequence of the related vector and the NPT II gene sequence are described in the document "Fang, Y., and Tyler, B.M. (2016). Efficient disruption and replacement of an effector gene in the oomycete Phytophthora sojae using CRISPR / Cas9. Molecular plant pathology, 17(1), 127-139.” and “Fang, Y., Cui, L., Gu, B., Arredondo, F., and Tyler, B.M. (2017) .Efficient genome editing in the oomycete Phytophthora sojae using CRISPR / Cas9.Curr.Protoc.Microbiol.44,21A.1.1-21A.1.26." The pBluescript II SK+ homology arm vector plasmid (Donor vector), the sgRNA expression vector pYF2.3G-Ribo-sgRNA and the Cas9 expression vector pYF2-PsNLS-hSpCas9 used in this example were all donated by Professor Brett M. Tyler of Oregon State University, USA .
[0096] Donor vectors pBS-NPTII-Pcsec4-1 and pBS-...
Embodiment 3
[0104] Embodiment 3, acquisition of Phytophthora capsici Pcsec4-1 gene and Pcsec4-2 gene knockout transformants
[0105] Using CaCl 2 -PEG-mediated protoplast transformation method to prepare Pcsec4-1 and Pcsec4-2 gene knockout transformants, the method of oomycete genetic transformation is described in the literature "Fang, Y., and Tyler, B.M. (2016). Efficient disruption and replacement of an effector gene in the oomycete Phytophthora sojae using CRISPR / Cas9. Molecular plant pathology, 17(1), 127-139."
[0106] The knockout transformant was specifically obtained by combining the knockout gene Pcsec4-1 Donor vector pBS-NPTII-Pcsec4-1 obtained in Example 1 and its own sgRNA recombinant vector pYF2.3G-Pcsec4-1 and the Cas9 expression vector pYF2-PsNLS- hSpCas9; Pcsec4-2's Donor vector pBS-NPTII-Pcsec4-1 and its own sgRNA recombinant vector pYF2.3G-Pcsec4-2 and Cas9 expression vector pYF2-PsNLS-hSpCas9 (the respective homology arms and sgRNA vector and Cas9 expression After mi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com