Milling method for double-sided frame part
A technology for milling and parts, applied in the field of milling of double-sided frame parts, can solve the problems of high cost, cumbersome use, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., and achieve the effect of stable processing and increased manufacturing cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
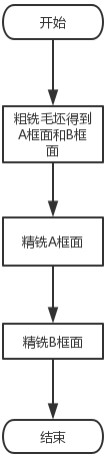
[0042] A milling method for double-sided frame parts, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0043] S1: A frame surface and B frame surface are respectively obtained on the upper and lower sides of the rough milling blank, and the process allowance reserved for the B frame surface is greater than the process allowance reserved for the A frame surface;
[0044] S2: Stress-free clamping, fine milling of the A frame surface, machining to the theoretical size, no process allowance;
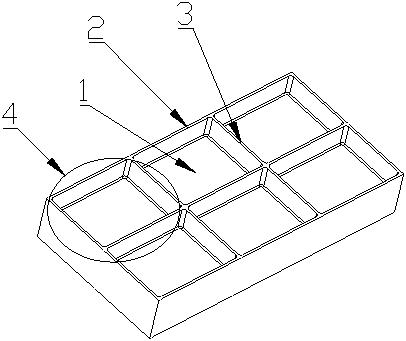
[0045] S3: Finish milling of the B frame surface, locate the rib 3 and the top surface of the edge 2 of the A frame surface after finishing milling in step S2, and when processing the web 1, use axial milling without delamination and use the B frame surface The center of the sash 4 is the starting point for milling the web 1 from the inside out. Such as Figure 9 As shown, the axial milling without delamination refers to the processing method of sequentially processing the web 1 h...
Embodiment 2
[0049] This embodiment is optimized on the basis of embodiment 1, such as Figure 5 and Figure 6 As shown, in the step S1, the process margin h1 reserved for the A frame surface is 1-5 mm, and the process margin h2 reserved for the B frame surface is 5-10 mm. In the finishing milling process, the A frame surface is firstly fine-milled, and the B frame surface is secondly fine-milled. When finishing milling A frame surface, due to the larger process allowance reserved for B frame surface, the conventional tooling method can be used for fine milling A frame surface; the small process allowance reserved for A frame surface is easier to finish milling ; On the other hand, when finishing milling the B frame surface, the larger process margin on the B frame surface can ensure the strength of the web 1 and prevent the vibration of the web 1 during fine milling.
[0050] Other parts of this embodiment are the same as those of Embodiment 1, so details are not repeated here.
Embodiment 3
[0052] This embodiment is optimized on the basis of embodiment 1 or 2, and said step S3 comprises the following steps:
[0053] S3.1: Positioning the rib 3 and the edge 2 of the A frame surface after finishing milling in step S2, first finish milling the rib 3 and the edge 2 of the B frame surface, and process them to the theoretical size;
[0054] S3.2: Then, if Figure 7 , Figure 8 As shown, use an end mill with a diameter D≤20mm to fine-mill the web 1 of the B frame surface, start from the center of the web 1, and use the spiral cutting method from inside to outside for milling. The end mill has no axial direction. Layered milling with radial milling width a e =(1 / 3~1 / 2)D, where D is the diameter of the end mill.
[0055] Position the ribs 3 and edge 2 on the surface of frame A after finish milling, without using special fixtures, first finish milling the ribs 3 and edge 2 of frame B to the theoretical size; then finish milling frame B The web 1 on the surface, when fi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com