Antibacterial and osseointegration coating formed on substrate surface and method for preparing antibacterial and osseointegration coating on substrate surface
A substrate surface, osseointegration technology, applied in the field of orthopaedic biomedical materials, can solve the problems of poor structural stability, unsatisfactory antibacterial performance and osseointegration performance, short aging, etc., to achieve structural stability, intelligent controllable and instant sterilization effect. strong effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0065] The present embodiment is a method for preparing an antibacterial and osseointegrated coating on the surface of a substrate, comprising the following steps:
[0066] (1) soak the substrate in the adhesive;
[0067] In this embodiment, a square titanium sheet with a side length of 8 mm and a thickness of 0.5 mm and a titanium rod with a length of 1 cm and a diameter of 0.5 mm are respectively selected as the base materials, and are ground and polished step by step with #400, #800 and #1000 SiC sandpaper. Then use the solvent acetone, absolute ethanol and double distilled water to ultrasonically clean for 20min in turn, and dry for use;
[0068] Then, the cleaned titanium sheets (or titanium rods) and platinum foils were used as positive and negative electrodes, and immersed in a solution containing 0.27M NH 4 In the mixed electrolyte of glycerol / water (v / v=1:1) of F, the voltage was adjusted to 20V, and the titanium sheet (or titanium rod) was anodized for 60min to form...
Embodiment 2
[0092] This embodiment is a method for preparing an antibacterial and osseointegrated coating on the surface of a substrate, which is basically the same as that in Embodiment 1, except that step (5) is not included.
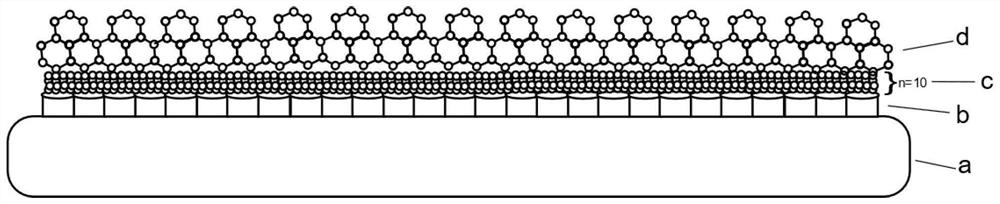
[0093] The structure of the antibacterial and osseointegrated coating formed on the surface of the substrate is as follows: Figure 10 In the figure, a represents the substrate, b represents the nanotubular layer of titanium dioxide, and c represents the copper sulfide nanoparticle coating.
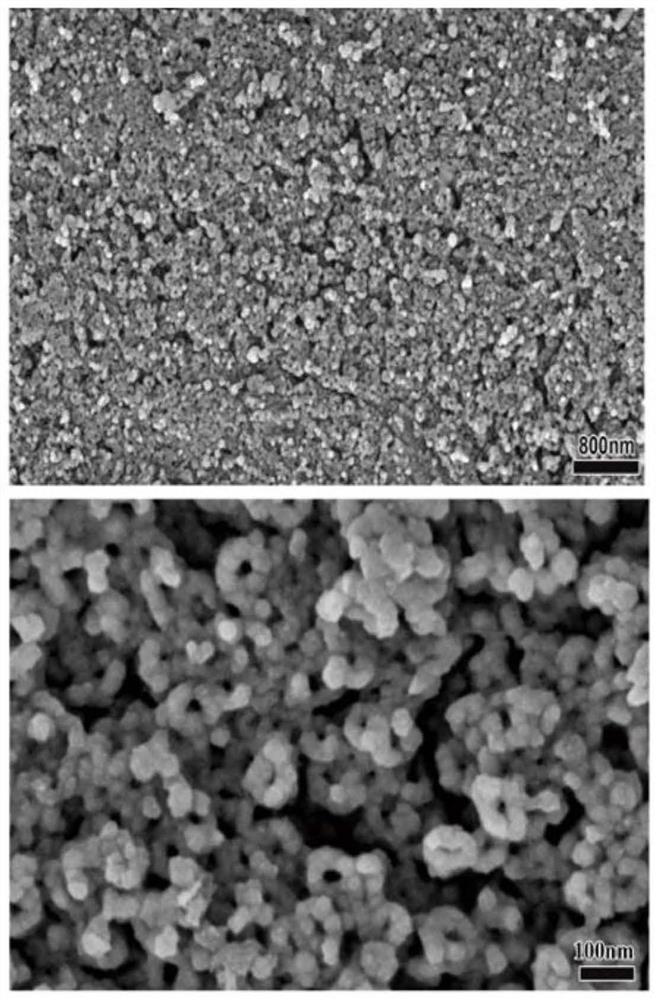
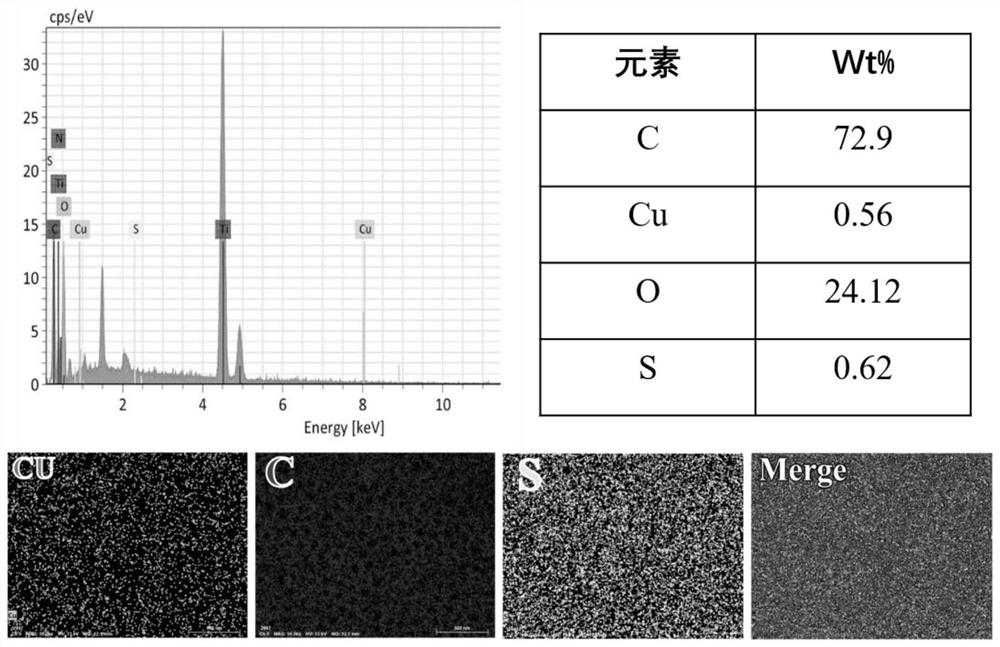
[0094] The antibacterial and osseointegrated coatings formed on the surface of the substrate were observed by scanning electron microscope, and the surface morphology was as follows: Figure 11 As shown, the XPS analysis results are as follows Figure 12 shown.
[0095] Depend on Figure 11 and Figure 12 It can be seen that the surface of the titanium sheet (or titanium rod) has been modified with copper sulfide nanoparticles.
[0096] The titanium sheet (or titanium r...
Embodiment 3
[0101] A method for preparing an antibacterial and osseointegrated coating on the surface of a substrate in this example is basically the same as that in Example 1, except that in step (4), repeating step (2) and step (3) 5 or 8 or 12 times.
[0102] Taking the titanium sheet (or titanium rod) without any surface modification as a control, the antibacterial properties and osseointegration properties of the titanium sheet (or titanium rod) coated with copper sulfide nanoparticles with different assembly layers were tested respectively. The results are shown in Table 1.
[0103] Table 1
[0104]
[0105] It can be seen from Table 1 that with the increase of the number of copper sulfide nanoparticle layers, the antibacterial properties and osseointegration properties of the antibacterial and osseointegrated coatings are continuously improved.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com