Pediococcus acidilactici derived from wolfberry enzyme and having uric acid reducing effect and application of pediococcus acidilactici
A technology of Pediococcus lactis and Lycium barbarum enzymes, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as patent publications that have not yet been found, and achieve obvious effects of reducing uric acid, reducing uric acid, and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Strain Screening:
[0034] Preparation of Lycium barbarum enzyme under natural conditions: Pack Lycium barbarum and sterile water in a sterile environment with a mass ratio of 1:5 in a sterile bottle, place in a cool place, and store sealed for 35 days. Take 1mL enzyme, 10-fold serial dilution to 10 -4 100 μL of each concentration was spread on the MRS selection medium, cultured at 37°C for 48 hours, cultured upside down and observed every 24 hours. A single colony with obvious calcium-dissolving circle was picked with a sterilized inoculation loop, streaked and purified on MRS solid medium, cultured at 37°C for 48 hours, and Pediococcus lactis strain GQ01 was isolated.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Strain identification:
[0037] According to the bacterial strain 01 that embodiment 1 obtains, identification method is as follows:
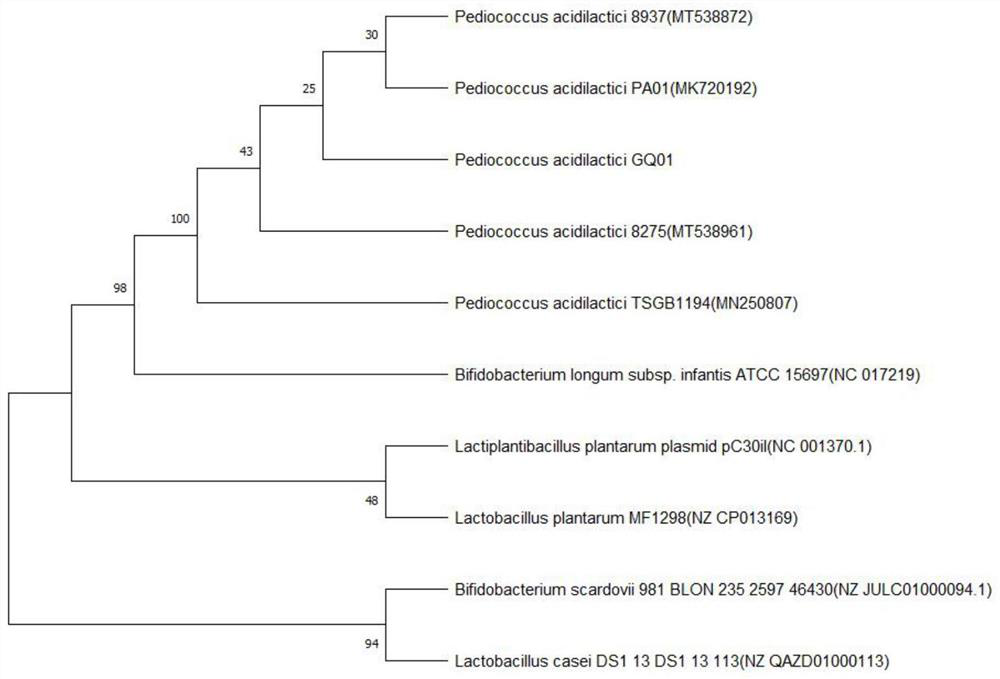
[0038] Genome extraction and PCR amplification were performed on the obtained single strain, and the PCR amplification products were sequenced. After genetic comparison, the similarity rate with the strain of Pediococcus lactis in Genebank was 99%. Based on the physiological and biochemical identification, it was identified as a strain of Pediococcus lactis and named as Pediococcus lactis GQ01, and the biological properties of the strain were studied. like figure 1 and figure 2 shown.
[0039] (1) Determination of growth curve
[0040] Select the strains at the end of logarithmic growth, inoculate them in MRS liquid medium at an inoculum of 1%, and culture them in a 37°C incubator for 36 hours, take samples every 2 hours and measure the OD 600nm .
[0041] (2) Determination of acid production capacity
[0042]Acid production rate...
Embodiment 3
[0045] Effect of Pediococcus lactis GQ01 intervention on blood uric acid level in mice with hyperuricemia:
[0046] The mouse model of hyperuricemia was established by intraperitoneally injecting the mice with potassium oxonate and supplemented with a high-purine diet. The experimental animals were 24 male Kunming mice, which were raised at room temperature and fed freely. After 1 week of adaptation After feeding, they were randomly divided into normal control group (NC), hyperuricemia model group (M), allopurinol (AP) treatment group and Pediococcus lactis treatment group (GQ01), 6 rats in each group. Except for the normal control group, the mice in the other three groups were intraperitoneally injected with 300 mg / kg·d of potassium oxonate-carboxymethyl cellulose suspension, and gavaged with yeast extract according to the standard of 10 g / kg·d. The mice in the GQ01 group were orally administered at 0.2 mL / d, and the mice in the AP group were orally administered at 30 mg / kg·d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com