Cloning, function research and marker mining of gene ZmRH4 for controlling corn kernel development
A gene and corn technology, applied in the field of cloning and application of the gene ZmRH4 related to controlling the grain size and quality of corn, can solve problems such as defects, lethality at seedling stage, and limited cognition
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1: ZmRH4 and the identification and gene cloning of mutants
[0039] Maize kernel development mutants show kernel abortion, growth retardation, etc., such as figure 1 As shown, its performance is as follows: the mutant has no normal and full starch grain structure, the endosperm is loosely composed, the filler is scarce, the development is severely hindered, the embryo structure cannot be observed, and the seeds are aborted. The present invention obtains a gene ZmRH4 that may control corn grain development, and obtains two EMS mutation mutants ems4-668a4 and ems4-66898 of the gene. According to the phenotypic characteristics of the above mutants, only the heterozygous normal grains isolated from the same F2 ear can be used for reproduction, and the mutant phenotypes were found to be stably inherited by selfing for many years and multiple generations. In addition, the allelic test (Aa×A'a') after crossing the two EMS mutants showed that the offspring showed a n...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2: Comparison of mutant and wild-type corn seed grain size and seedlings. Take the allelic mutant ems4-668a4 as an example. The ears of the EMS mutant showed an empty peel phenotype, showing a ratio of 1 / 4, as shown in Figure 1. Further observation of the mature seed structure revealed that the mutant grains could not see the embryo with the naked eye, and the deposition of endosperm was reduced. The seed coat was removed from the mutant grains on the 13th day after pollination, and it was found that the development of the endosperm was severely retarded, and the embryo could not be observed and separated. We took the normal grains and small grains on the ear, and carried out the standard germination experiment of seeds, and carried out the germination test with soil and MS medium as the medium respectively. The seeds were germinated with MS medium, all the wild-type seeds germinated, and none of the small seeds germinated. In the germination experiment with s...
Embodiment 3
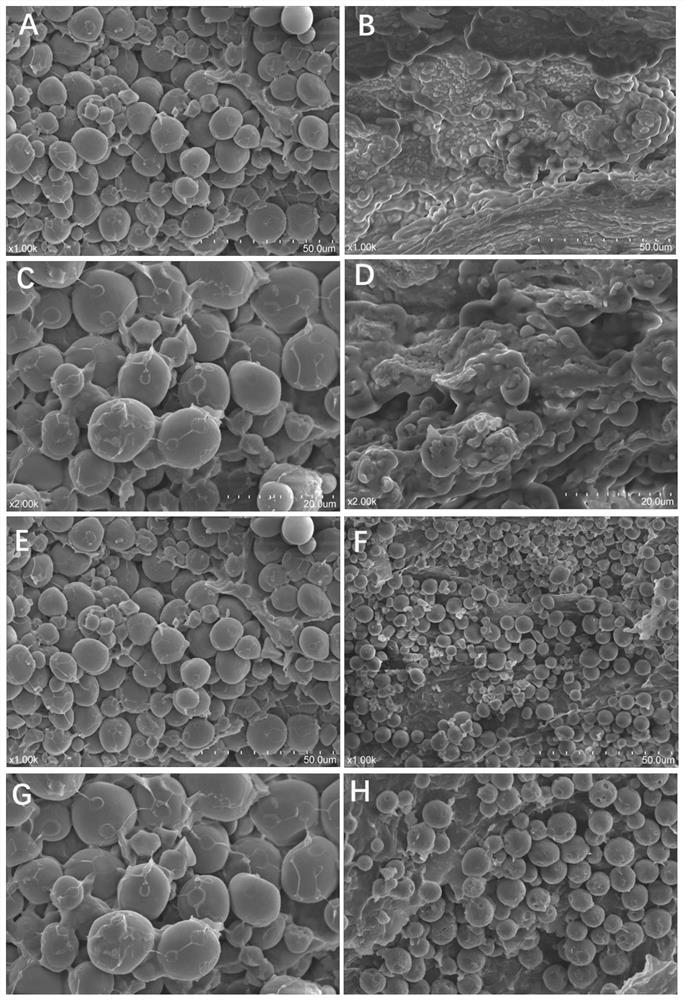
[0042] Example 3: SEM phenotype comparison of mutant and wild type grain endosperm.
[0043] Using scanning electron microscopy to observe the microstructure of the endosperm of normal and mutant grains, zmrh4-1, zmrh4-2 mutant starch grains and protein morphology are abnormal, irregular, such as Figure 4 . The phenotypes of the two mutants differ in degree. The zmrh4-1 mutant has no normal and full starch granule structure, the endosperm is loosely composed, the filling is scarce, and the development is severely stunted. The endosperm of the zmrh4-2 mutant had obvious starch grain structure, the starch grains were regular in shape, but significantly smaller, and the arrangement was loose, and the filler was scarce, and the developmental retardation of the grain of the zmrh4-1 mutant was less severe. In normal grains, the starch grains are full, tightly arranged, and filled with more fillers. The functional defect of this gene leads to the retardation of endosperm developm...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com