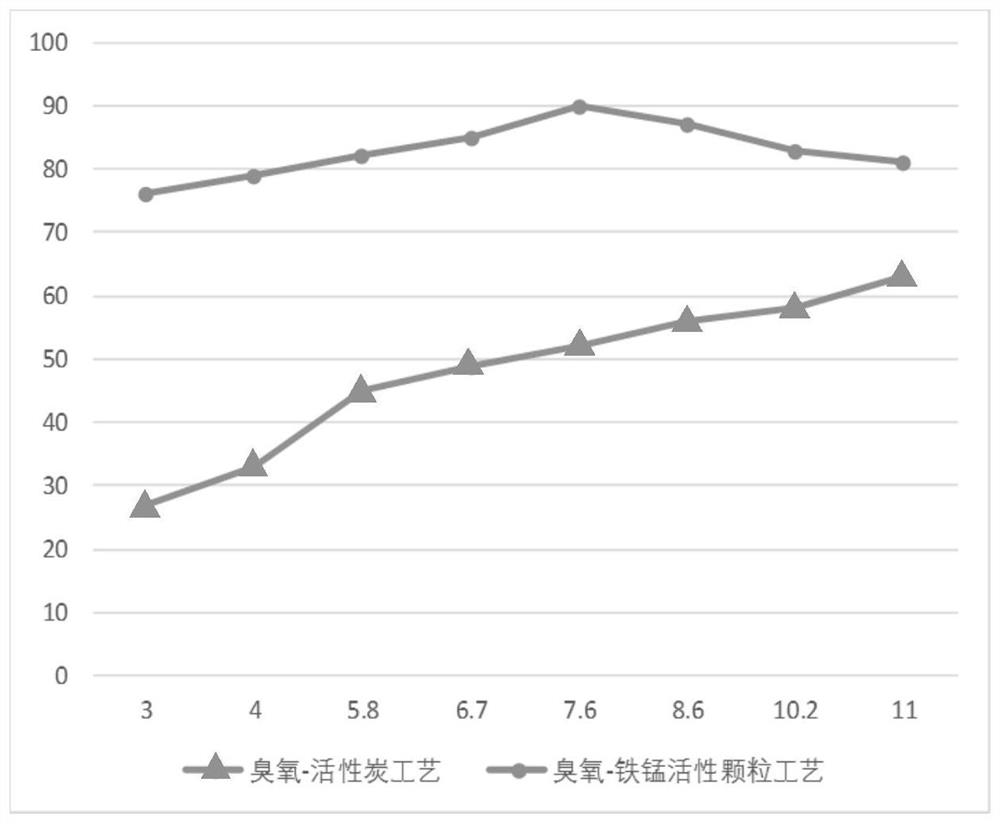
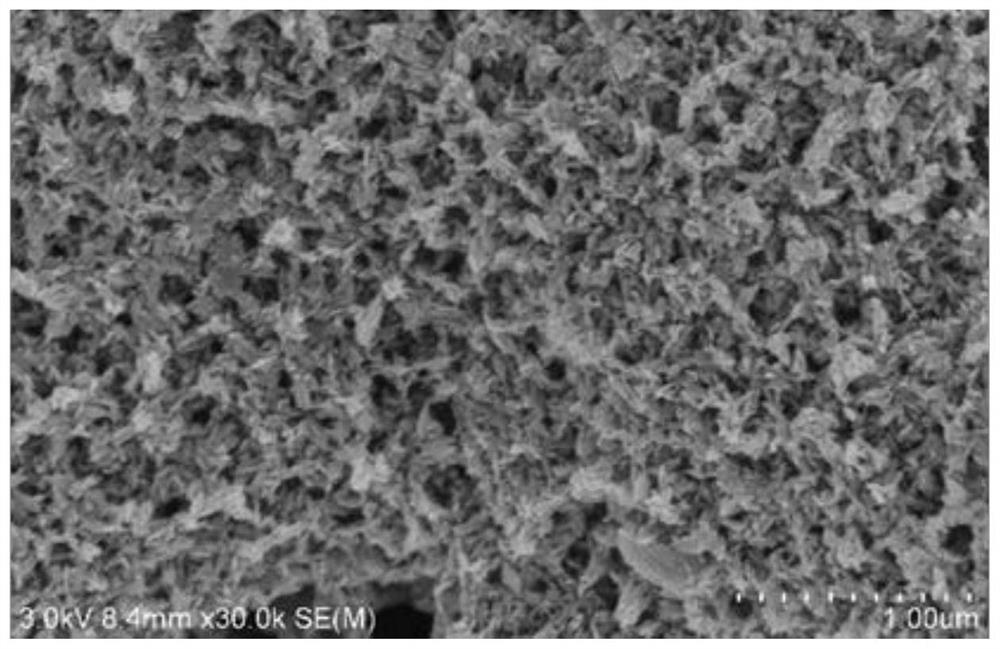
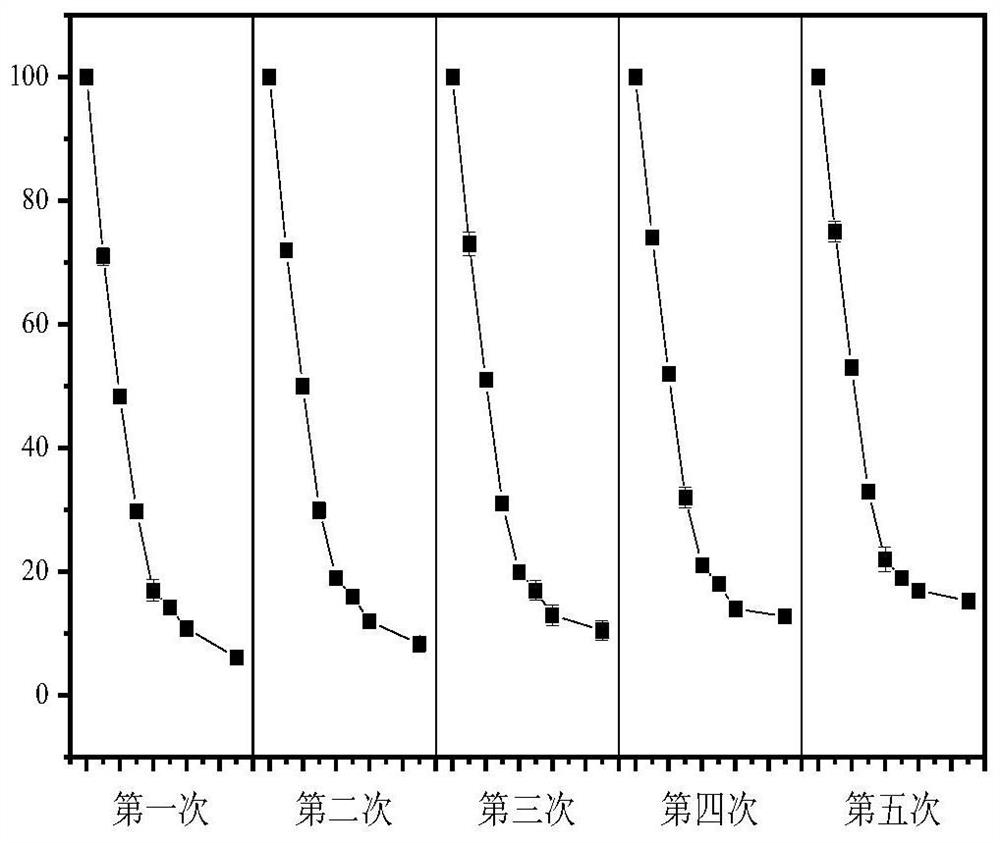
Preparation method of iron-manganese active granules for dye wastewater treatment
A technology of active particles and dye wastewater, applied in water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as easy deactivation, human health threats, animal and plant hazards, and achieve The effect of improving activity and stability, improving overall catalytic performance, and reducing the risk of deactivation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] This embodiment provides a method for preparing iron and manganese active particles for dye wastewater treatment, comprising the following steps:
[0046] Step 1: Take commercial granular activated carbon and 45 mesh sieved powdered activated carbon and mix them uniformly in the range of mass ratio 20:1 and put them in the container evenly. Add pure water, heat it in a water bath at 100°C for 5 hours, carry out deashing treatment, then take it out and place it in an oven at 105°C to dry to constant weight, add 45% activated carbon after drying according to the volume ratio of 1:5 Mixed solution of nitric acid and 60% sulfuric acid, the volume ratio of nitric acid to sulfuric acid is 3:1; take it out after constant temperature stirring at 65°C for 5 hours, filter and rinse with pure water until the pH value does not change.
[0047] Step 2: Add the stannous chloride gelling agent solution with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 5 grams per liter of hydrochloric acid to the deash...
Embodiment 2
[0053] This embodiment provides a method for preparing iron and manganese active particles for dye wastewater treatment, comprising the following steps:
[0054] Step 1: Take commercial granular activated carbon and 325-mesh sieved powdered activated carbon and mix them evenly in the range of 5:1 by mass ratio, and place them in the container evenly. Add pure water in proportion, heat in a water bath at 100°C for 10 hours, carry out deashing treatment, then take it out and place it in an oven at 105°C to dry to constant weight, add the activated carbon after drying according to the volume ratio of 1:20 Mixed solution of 45% nitric acid and 60% sulfuric acid, the volume ratio of nitric acid to sulfuric acid is 5:1, take it out after constant temperature stirring at 65°C for 12 hours, filter and rinse with pure water until the pH value does not change.
[0055] Step 2: Add the stannous chloride gelling agent solution with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 10 grams per liter of hydrochl...
Embodiment 3
[0061] This embodiment provides a method for preparing iron and manganese active particles for dye wastewater treatment, comprising the following steps:
[0062] Step 1: Take commercial granular activated carbon and 100-mesh sieved powdered activated carbon and mix them uniformly in the range of 7:1 by mass ratio and place them in a container, and mix them according to the volume ratio of pure water to mixture of 3:1. Add pure water in proportion, heat it in a water bath at 100°C for 8 hours, carry out deashing treatment, then take it out and place it in an oven at 105°C to dry to constant weight, and add the activated carbon after drying to a volume ratio of 1:10. Mixed solution of 45% nitric acid and 60% sulfuric acid, the volume ratio of nitric acid to sulfuric acid is 4:1, take it out after constant temperature stirring at 65°C for 8 hours, filter and rinse with pure water until the pH value does not change.
[0063] Step 2: Add the stannous chloride gelling agent solution...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com