Sponge fiber, preparation method and application
A fiber and sponge technology, applied in the field of fibers, can solve the problems of insufficiently dense structure, low degree of orientation, and single structure.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0076] The present embodiment has prepared a kind of sponge fiber, and concrete process is:
[0077] S1. configure the mixed aqueous solution of phytic acid and sodium sulfate to obtain mixed aqueous solution I, wherein the concentration of phytic acid is 7.5wt%, and the concentration of sodium sulfate is 5wt%;
[0078] S2. Weigh 80g of lithium hydroxide and 150g of urea, add 770mL of ultrapure water, stir and dissolve to obtain the mixed aqueous solution II;
[0079] S3. Place 500g of the mixed aqueous solution II (solvent) and 29.1g of cotton linters (natural cellulose) at -25°C for cooling for 2h;
[0080] S4. Mix and stir the mixed aqueous solution II and cotton linters after cooling in step S3 (rotating speed 1500rad / min, time 5min) to obtain a transparent cellulose solution;
[0081] S5. centrifuging the cellulose solution obtained in step S4 to obtain a supernatant A, wherein the centrifugation speed is 8000 rad / min, the time is 30 min, and the temperature is 0° C.;
...
Embodiment 2
[0089] This embodiment has prepared a kind of sponge fiber, and the difference of concrete process and embodiment 1 is:
[0090] (1) In step S6, the addition ratio of crosslinking agent epichlorohydrin is 1.5mL crosslinking agent / 200g supernatant A;
[0091] (2) In step S8, the propulsion speed of the cooled supernatant B is 220 μL / min; the propulsion speed of the mixed aqueous solution II is 500 μL / min; the propulsion speed of the mixed aqueous solution I is 500 μL / min.
[0092] (3) In step S10, the drying method is freeze drying, and the drying time is 3 hours.
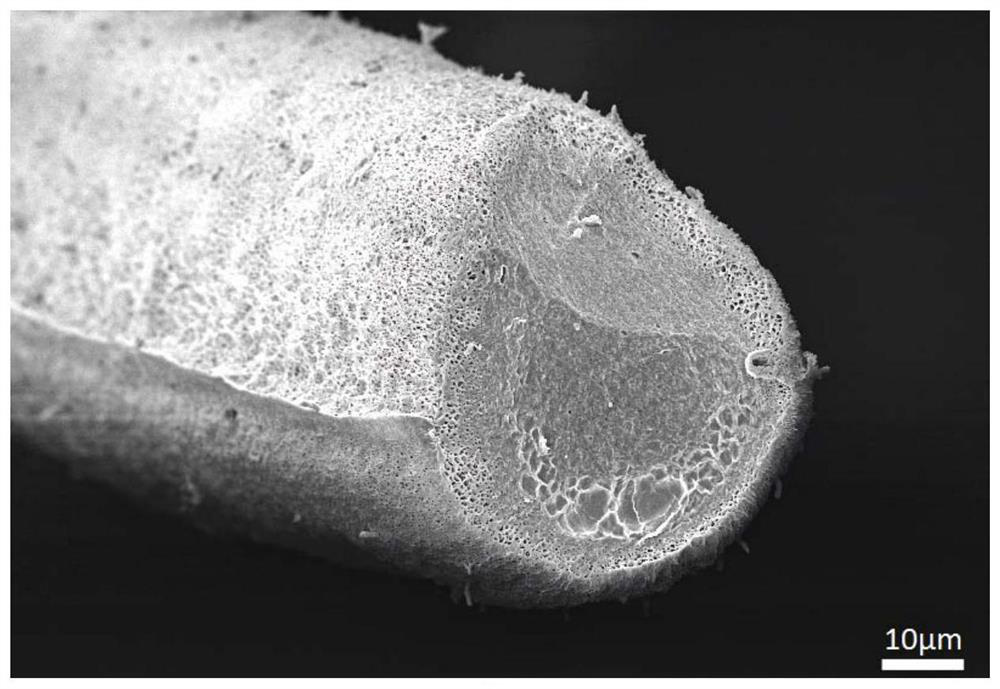
[0093] The SEM figure of the sponge fiber obtained in the present embodiment is as follows Figure 4 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0095] This embodiment has prepared a kind of sponge fiber, and the difference of concrete process and embodiment 2 is:
[0096] (1) In step S3, the quality of cotton linters is 31.9g;
[0097] (2) In step S6, the addition ratio of crosslinking agent epichlorohydrin is 3mL crosslinking agent / 200g supernatant A;
[0098] (3) In step S6, the stirring time is 2h;
[0099] (4) In step S8, the propulsion speed of the cooled supernatant B is 150 μL / min; the propulsion speed of the mixed aqueous solution II is 300 μL / min; the propulsion speed of the mixed aqueous solution I is 400 μL / min;
[0100] (5) In step S10, freeze-dry for 6 hours.
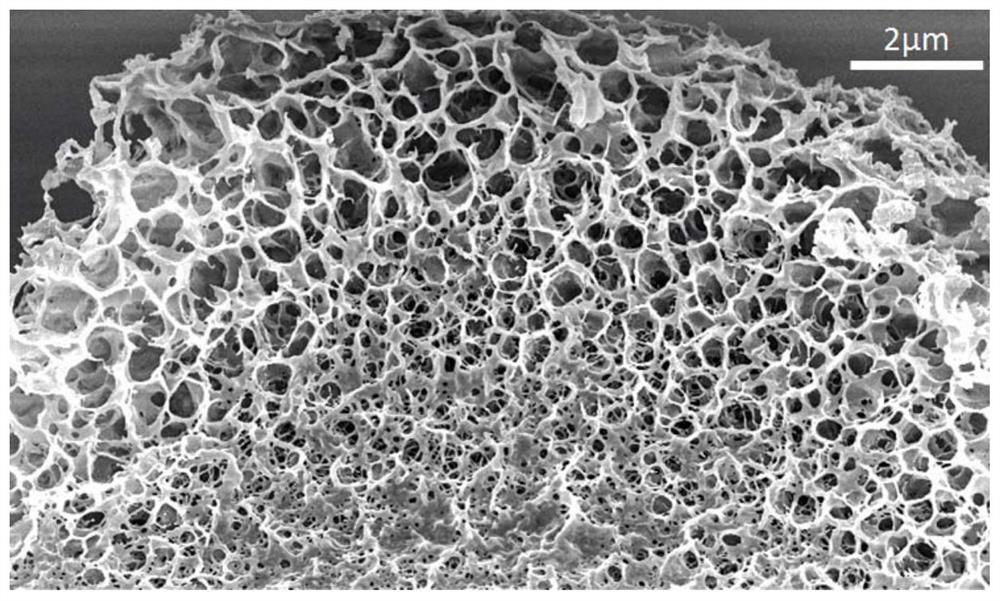
[0101] The SEM figure of the sponge fiber obtained in the present embodiment is as follows Figure 5 shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com