Method for rapid in-situ detection of triphenylmethane chemicals in living biological tissue
A technology for in-situ detection of living organisms, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of various laboratory tests, high requirements for instruments and equipment, and unsuitable rapid detection, etc. , fast and efficient enrichment effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
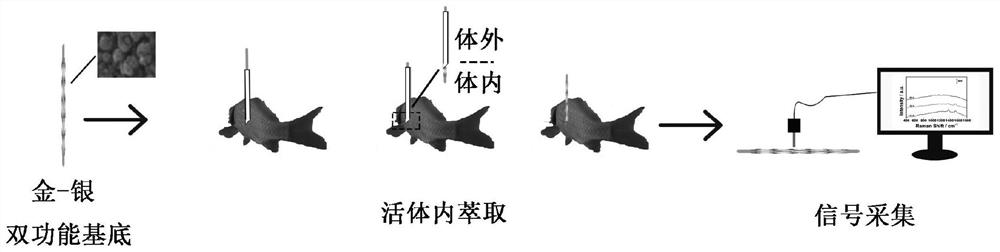
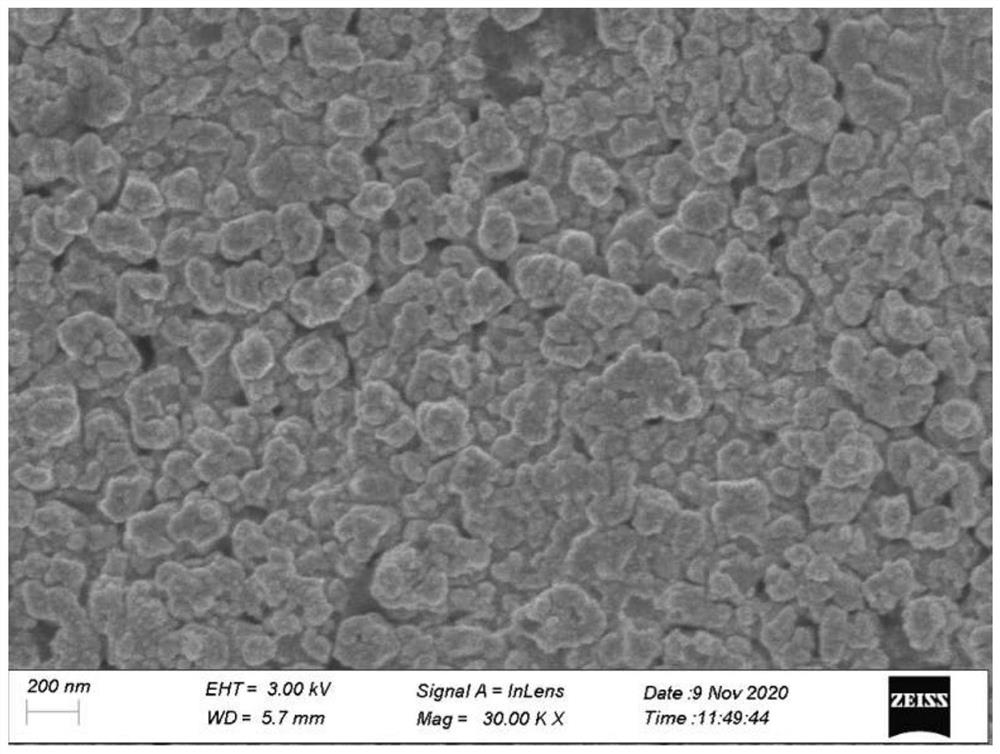
[0051] Preparation of gold-silver bifunctional substrate:
[0052] a. Preparation of porous silver extraction wire: cut a silver wire with a diameter of 0.15 mm to 6 cm long, wash it with acetone, ethanol and ultrapure water respectively, use the cleaned silver wire as a working electrode, and a silver / silver chloride electrode as a reference Electrode, the platinum electrode is the counter electrode to form a three-electrode system, placed in a 0.1mol / L hydrochloric acid solution prepared by ultrapure water and concentrated hydrochloric acid, using cyclic voltammetry, the voltage range is -0.2V-0.2V, and the sweep rate is 10mV / s , circulated 15 times, and washed the prepared porous silver wire with ultrapure water for 3 times.
[0053] b. Preparation of gold-silver bifunctional substrate: containing 0.1mol / L KNO 3 with 1mmol / L HAuCl 4 The mixed solution is used as the electrolyte, the porous silver extraction wire is used as the working electrode, the silver / silver chloride...
Embodiment 2
[0056] A method for rapid in-situ detection of triphenylmethane chemicals in living biological tissues, comprising the following steps:
[0057] 1) Insert the gold-silver dual-function base into the hollow cavity of the stainless steel hollow tube needle, firstly insert the stainless steel hollow tube needle with the base into the fish body with the tip of the stainless steel hollow tube needle, and then put the hollow tube jacket on the Then retreat, so that the gold-silver dual-functional substrate in the tube is exposed to the fish meat, and the triphenylmethane chemicals in the fish meat are extracted for 10 minutes;
[0058] 2) Take out the stainless steel hollow tube needle with the substrate, and use a portable Raman spectrometer to detect, the laser wavelength is 785nm, the laser intensity is 150mW, and the integration time is 1s to obtain the Raman spectrum.
experiment example 1
[0060] 1) Prepare malachite green standard solution with different concentrations, immerse the gold-silver dual-functional substrate in the malachite green standard solution for solid-phase microextraction, and then conduct Raman detection, parallel 3 times. With the concentration of malachite green in the malachite green standard solution gradually increasing, the Raman spectrum in the 1174cm -1 The peak intensity at the peak gradually increases accordingly. Select the intensity at the peak and the combined linear curve to realize the quantitative detection of malachite green. The linear relationship between the concentration of the malachite green standard and the intensity of the characteristic peak is as follows: image 3 shown.
[0061] 2) Prepare different concentrations of leuco-malachite green standard solution, immerse the gold-silver dual-functional substrate in the leuco-malachite green standard solution for solid-phase microextraction, and then conduct Raman detect...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com