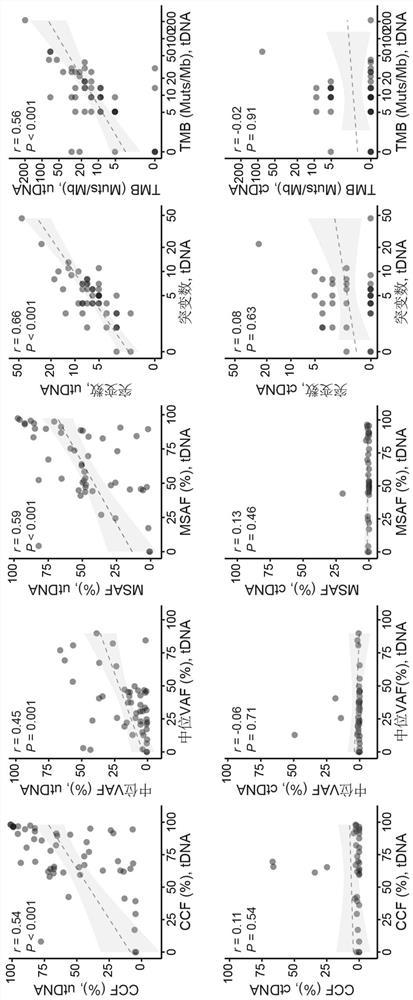
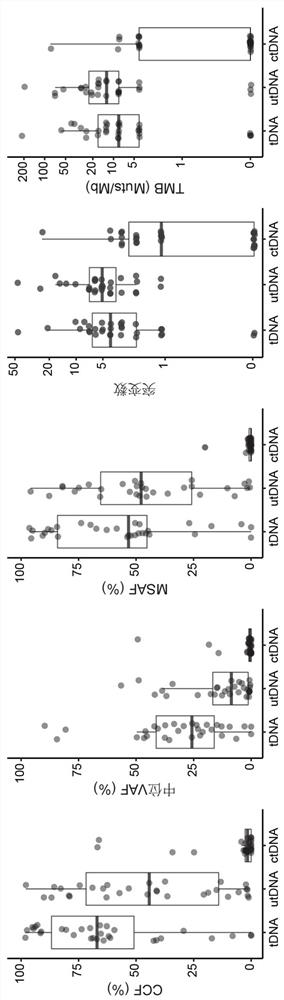
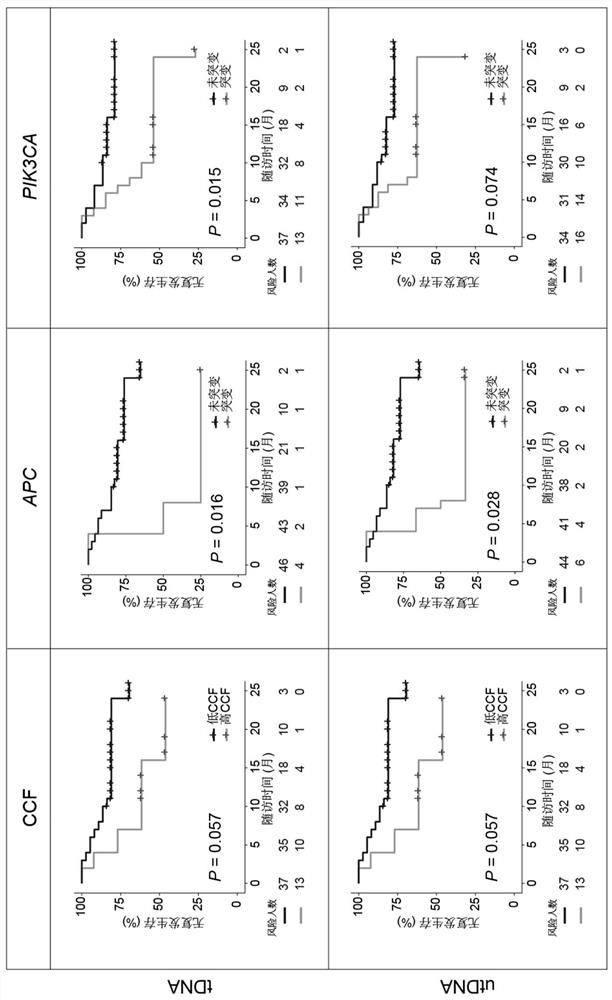
Application of bladder urothelium carcinoma detection combined marker
A technology of urothelial cancer and markers, which is applied in the determination/testing of microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., which can solve the problems of increased levels and low specificity, and reduce the workload of sequencing , Improving the detection efficiency and accuracy, and the effect of good diagnostic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Embodiment 1: Sample collection and processing.
[0044] This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Renji Hospital. The research process complied with the requirements of the American General Rules of Ethics. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. A total of 119 newly diagnosed subjects with suspected UBC were prospectively recruited in Renji Hospital. 40 ml of first morning urine was collected at home before surgical intervention. At clinical visits, 10 ml blood samples and paired peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) controls were collected for sequencing. In addition, fresh-frozen tissue specimens are obtained during diagnostic biopsy or curative surgery. Patients with an early diagnosis other than UBC or who did not receive urine / tissue samples were excluded.
[0045] Use a urine collection cup to collect the patient's morning urine and transfer it to four vacuum tubes, and thoroughly mix the urine sample with the pre-perfused prese...
Embodiment 2
[0046] Example 2: DNA extraction, library construction, capture and sequencing.
[0047] Plasma cfDNA and urine cfDNA were extracted from blood and urine samples, respectively, using the QIAamp Circulating Nucleic Acid Kit (Qiagen). Quantity and quality of purified cfDNA were checked with Qubit Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and Bioanalyzer 2100 (Agilent). For samples with severe genomic contamination extracted from intact cells, select DNA fragments using the magnetic bead method to remove larger diameter DNA fragments. Genomic DNA (gDNA) in PBMCs and frozen tumor tissues was extracted using DNeasy Blood Tissue DNA Extraction Kit (Qiagen). 250 ng gDNA was digested and purified.
[0048] Libraries were constructed using 20 ng of cfDNA extract or 40 ng of gDNA fragments, including end repair, dA tailing, and adapter ligation. The ligated library fragments were amplified by PCR with appropriate adapters. The amplified DNA library was further checked using Bioanalyzer...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: Analysis of gDNA sequencing data.
[0050] The gDNA data is analyzed using the in-house analysis pipeline developed by Huidu Medical, starting from the raw sequencing data (BCL file) and outputting the final somatic mutation call of the tumor DNA (tDNA). Briefly, the pipeline begins with adapter trimming, barcode checking, and correction. The cleaned paired FASTQ files were aligned to the human reference genome version hg19 using the BWA alignment tool. Identify candidate variants, including point mutations, small insertions, and small deletions, in target regions covered by the PredicinePLUS Assay Panel. Filters variants with low quality, location score, and other quality metrics. Variants with an allele frequency 0.5%, ExAC, gnomAD, and KAVIAR), and allele frequencies >5% Variants detected in paired PBMC samples. Candidate somatic mutations were further filtered based on gene annotations, identifying somatic mutations occurring in protein coding regions...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com