Device and method for degrading gaseous organic pollutants by electrochemical method
An organic pollutant, electrochemical technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, separation methods, gas treatment and other directions, to achieve the effect of increased service life, excellent lasting stability, and a wide range of applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
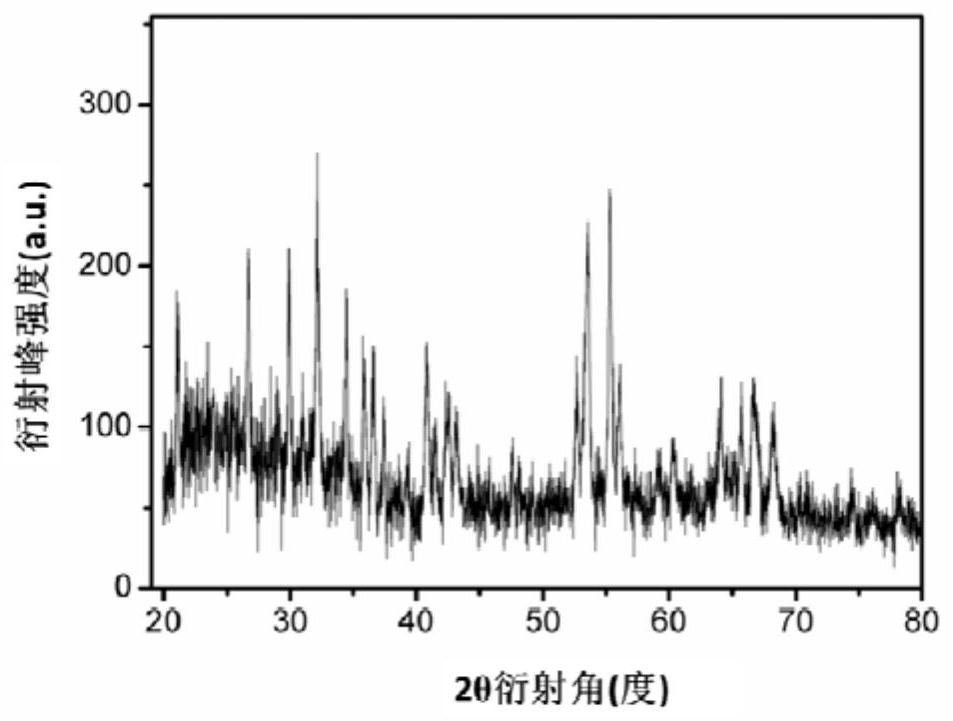
[0053] (1) Preparation of the anode: Titanium oxide was loaded on a foamed titanium sheet with a filtration accuracy of 50 μm as the substrate. First put the titanium foam into acetone for ultrasonic degreasing and washing with water, then immerse in 10wt% oxalic acid solution at 90°C for 2 hours to remove the oxide layer on the titanium surface, and at the same time form a roughness of about 5 μm on the titanium surface; then put the treated foam titanium The sheet is fixed on the metal baffle, and the titanium dioxide is sprayed on the foamed titanium by plasma spraying method, the spraying power is 30KW, and the spraying thickness is controlled at about 20μm by adjusting the spraying amount. The sprayed titanium foam is washed with ethanol and then dried to obtain titanium foam supported by titanium oxide, which is used as an anode for subsequent gas-solid phase electrochemistry.
[0054] X-ray diffraction spectrum test is carried out on the anode surface coating, the test ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Example 2: Influence of Intake Relative Humidity on Degradation Efficiency of Gaseous Organic Pollutants
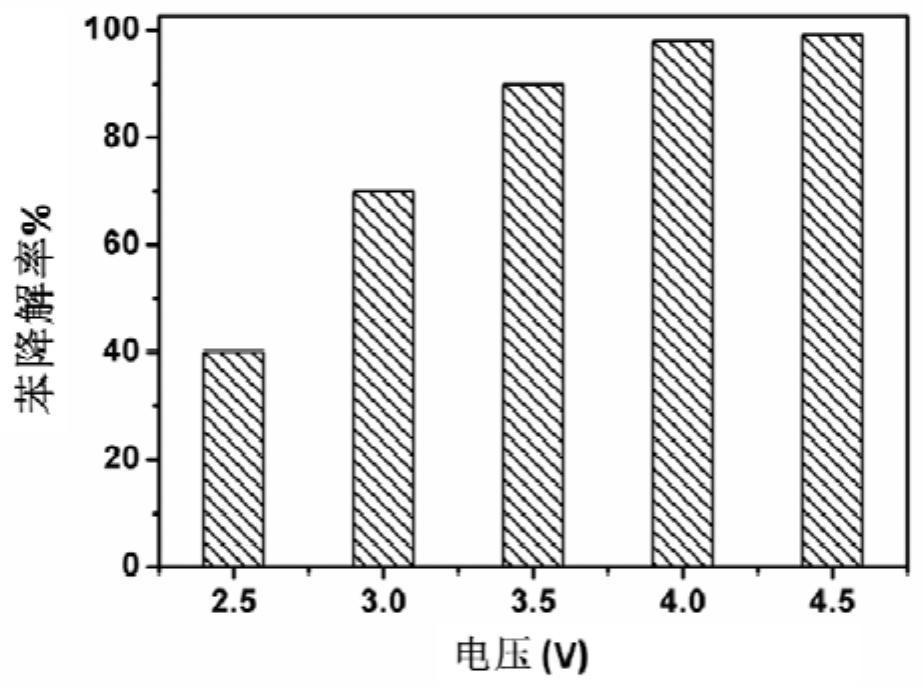
[0059] Using the anode, cathode and assembled electrochemical reaction device in Example 1, the relative humidity of the intake air in the anode area is controlled from 40% to 90%, the concentration of benzene in the intake air is 10ppm, and the gas flow rate is 20mL / min. At the same time, the relative humidity of the air entering the cathode area was controlled to be consistent with that of the air entering the anode area, and the air flow rate was 20 mL / min. After 4 hours of continuous flow of gas on both sides, each component in the electrochemical reactor has reached the equilibrium state of water vapor adsorption, and then a 4V voltage is applied between the anode and the cathode to detect the degradation rate of benzene under steady flow electrolysis, and the results are as follows Figure 4 As shown, the degradation rate of benzene is over 90% under differen...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Embodiment 3: Stability test of electrochemical method for degrading gaseous organic pollutants
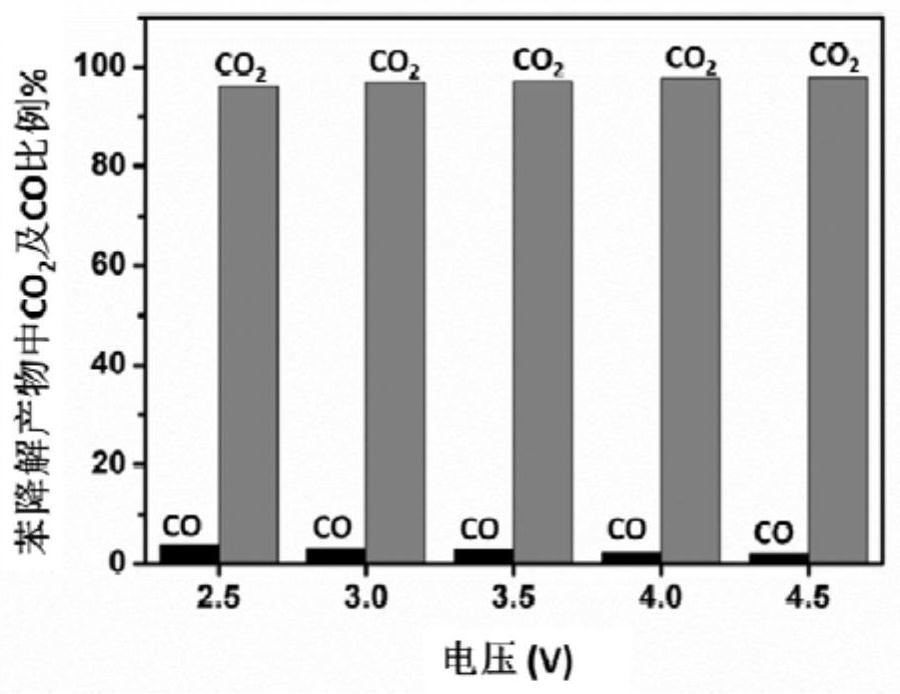
[0061] Using the anode, cathode and assembled electrochemical reaction device in Example 1, the gas (relative humidity is 60%) containing typical volatile organic pollutants-"benzene" is passed into the anode gas flow channel, and the concentration of benzene is 10ppm. The gas flow rate is 20mL / min. At the same time, air (relative humidity of 60%) was passed into the cathode air flow channel at a flow rate of 20 mL / min. Then apply a 4V voltage between the anode and the cathode, and monitor the concentration and current of benzene pollutants at the outlet of the anode airflow channel when it is stable. The relationship between the benzene degradation efficiency and current density and time under long-term continuous electrolysis is shown in Figure 5 . from Figure 5It can be seen that in the continuous degradation process of 60 hours, the degradation rate of benzene is m...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com