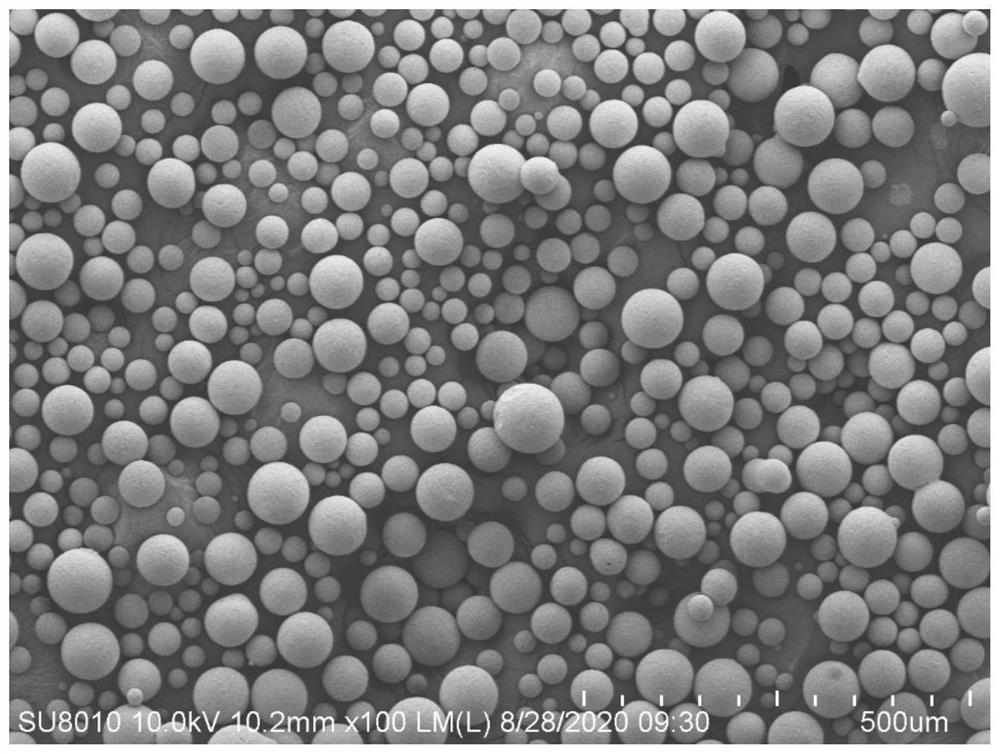
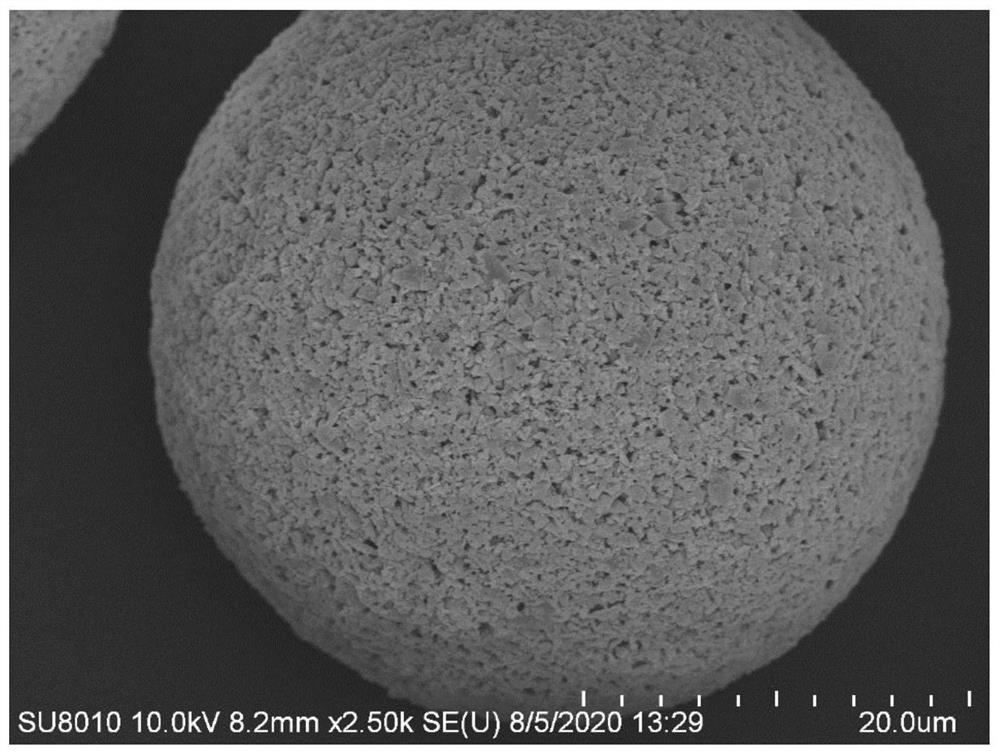
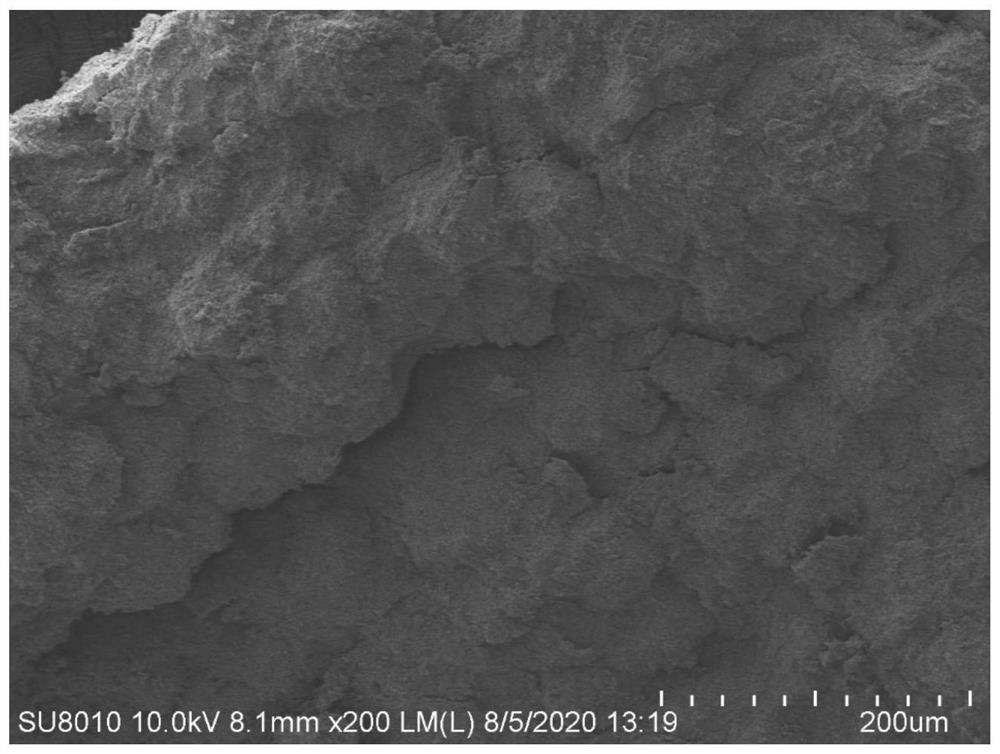
A kind of preparation method of nanoparticle toughened high-toughness SIC parts
A nano-particle, high-toughness technology, applied in the field of preparation of high-toughness SiC parts, can solve the problems of inability to achieve uniform dispersion, easy agglomeration and combination of nanoparticles, improve sintering driving force, simple operation equipment, and uncomplicated process flow Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0034] Embodiment 1: In this embodiment, a method for preparing a nanoparticle-toughened high-toughness SiC part is carried out in the following steps:
[0035] 1. Powder pretreatment:
[0036] The silicon carbide micropowder, silicon carbide nanopowder and sintering aid are respectively placed in an oven and dried at a constant temperature to obtain pretreated silicon carbide micropowder, pretreated silicon carbide nanopowder and pretreated sintering aid;
[0037] The particle size of the silicon carbide micron powder is 0.3 μm to 10 μm; the particle size of the silicon carbide nano powder is 1 nm to 200 nm;
[0038] 2. Micron powder dispersion:
[0039] adding the pretreated silicon carbide micron powder and the pretreated sintering aid into deionized water containing the aid, and dispersing evenly to obtain a micron powder slurry;
[0040] The mass ratio of the pretreated silicon carbide micron powder to the pretreated sintering aid is 1:(0.001~0.05); the mass ratio of th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0058] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the sintering aid described in step 1 is a mixture of one or more of carbon, boron and boron carbide; the constant temperature described in step 1 The drying temperature is 60°C-120°C, and the drying time is 2h-24h. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0059] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the auxiliary agent described in step two is tetramethylammonium hydroxide, polyvinylpyrrolidone, sodium hydroxymethyl cellulose, polyethylene glycol , phenolic resin, polyvinyl butyral, n-octanol, polyvinyl alcohol and polyacrylamide or a mixture of several. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com