Silicon-based rhodamine fluorescent staining reagent as well as preparation method and application thereof
A silicon-based rhodamine and fluorescent dyeing technology, applied in the fields of immunology, organic chemistry and biochemistry, can solve the problem of small Stokes shift of antibody-labeled dyes and difficult application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
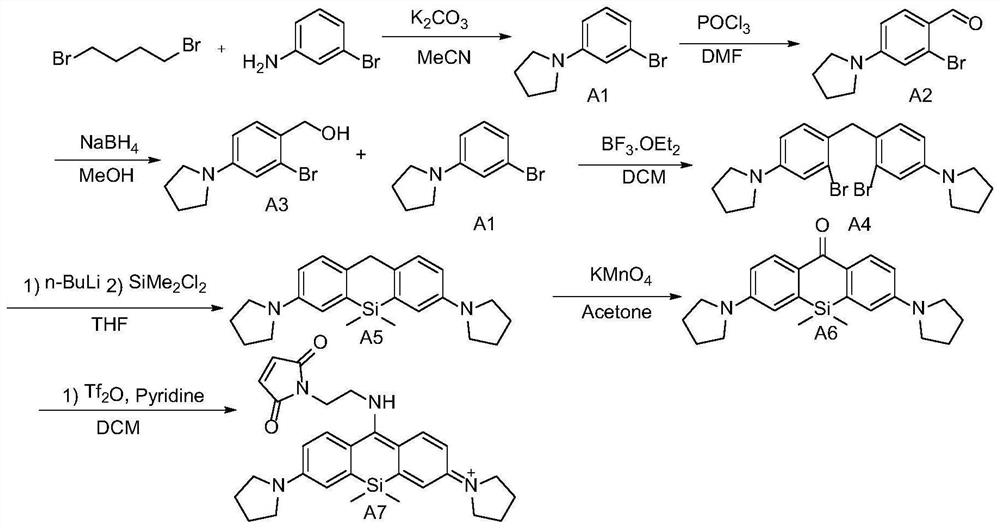
[0106] The present embodiment has the preparation method of the silicon-based rhodamine fluorescent dyeing reagent of formula (I), comprising the following steps:
[0107] (1) Synthesis of intermediate A1
[0108] The synthetic route is as follows:
[0109]
[0110] m-Bromoaniline (1.0 mmol), 1,4-dibromobutane (1.5 mol) and potassium carbonate (3.0 mmol) were mixed and stirred in acetonitrile (5 mL) for 12 hours, then 100 mL of water was added. The organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (30 mL×3). The organic extracts were washed with brine and treated with Na 2 SO 4 dry. After the solvent was removed and distilled under reduced pressure, it was purified by 200-300 mesh silica gel column chromatography. Eluted with petroleum ether / ethyl acetate (20:1), the intermediate A1 was obtained as a light yellow liquid with a yield of 68%.
[0111] (2) Synthesis of Intermediate A2
[0112] The synthetic route is as follows:
[0113...
Embodiment 2
[0137]This example is basically the same as Example 1, except that the starting material is replaced by the B intermediate obtained by 6-bromoindole, and its synthetic route is shown in Figure 1 (b), which includes the following steps:
[0138] (1) Synthetic Intermediate B1
[0139] The synthetic route is as follows:
[0140]
[0141] 6-Bromoindole (1.0 mmol), iodomethane (1.5 mol) and potassium carbonate (2.0 mmol) were mixed and stirred in acetonitrile (5 mL) for 12 hours, then 100 mL of water was added. The organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (30 mL×3). The organic extracts were washed with brine and treated with Na 2 SO 4 dry. After the solvent was removed and distilled under reduced pressure, it was purified by 200-300 mesh silica gel column chromatography. Eluted with petroleum ether / ethyl acetate (10:1), the intermediate B1 was obtained as a light yellow liquid with a yield of 75%.
[0142] (2) Synthesis of interm...
Embodiment 3
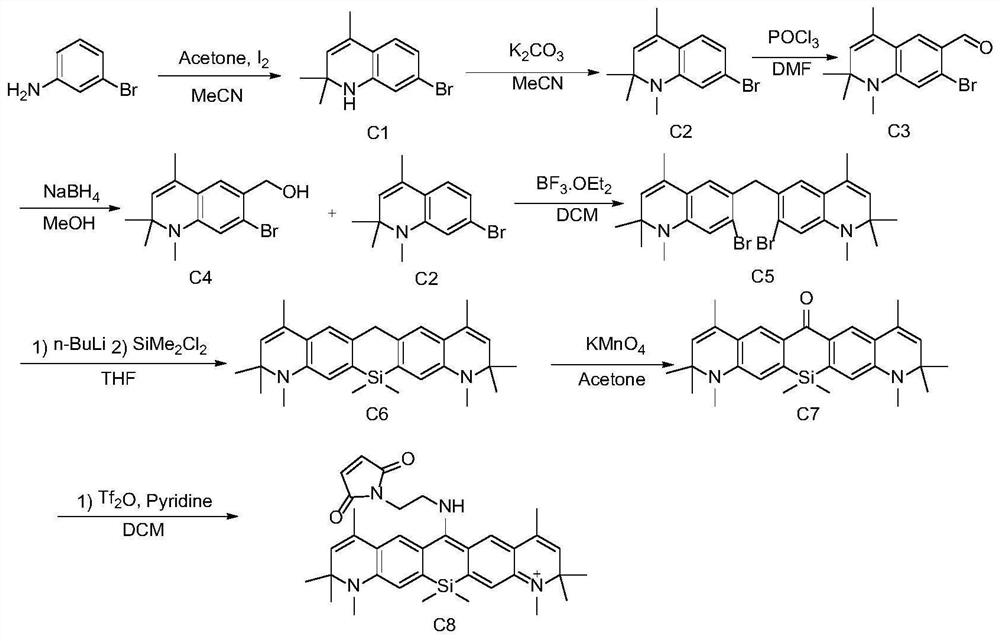
[0171] This example is basically the same as Example 1, except that the starting material is replaced by the C intermediate prepared by m-bromoaniline, and its synthetic route is shown in Figure 1 (c), which includes the following steps:
[0172] (1) Synthesis of intermediate C1
[0173] The synthetic route is as follows:
[0174]
[0175] m-Bromoaniline (1.0 mmol), acetone (10 mol) and iodine (0.01 mmol) were mixed and stirred in acetonitrile (5 mL) for 12 hours, and then 100 mL of water was added. The organic layer was separated, and the aqueous layer was extracted with ethyl acetate (30 mL×3). The organic extracts were washed with brine and treated with Na 2 SO 4 dry. After the solvent was removed and distilled under reduced pressure, it was purified by 200-300 mesh silica gel column chromatography. Eluted with petroleum ether / ethyl acetate (10:1), the intermediate C1 was obtained as a light yellow liquid with a yield of 47%.
[0176] (2) Synthetic intermediate C2 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com