Composite hydrogel for promoting wound healing as well as preparation method and application thereof
A composite hydrogel, wound healing technology, used in medical science, bandages, etc., can solve the problems of decreased performance and tissue adhesion, unable to support tissue regeneration, poor tissue adhesion, etc., to improve water solubility, increase new Collagen deposition and vascular remodeling, low cost effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
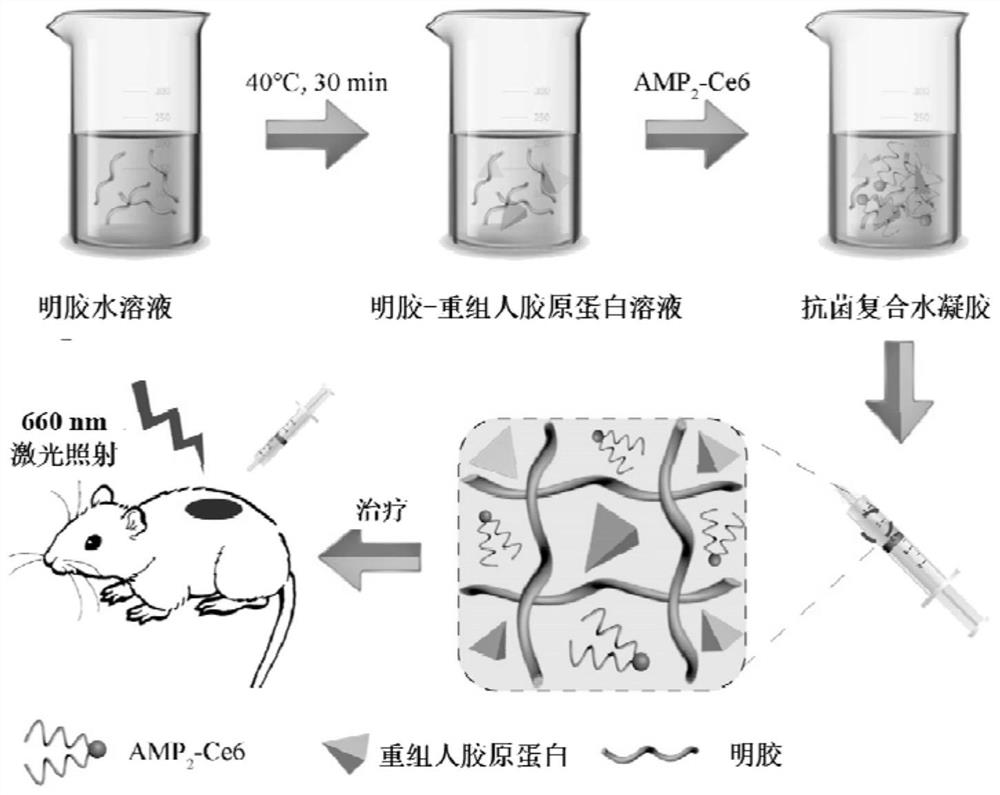
[0030] Embodiment 1 composite hydrogel preparation
[0031] Dissolve 1 g of gelatin in 10 mL of ultrapure water to prepare a 10% solution, heat the solution to 40° C. and stir for 30 minutes. Add 0.2g recombinant human type III collagen, mix and stir for 5 minutes, then add antibacterial photodynamic peptide AMP 2 - Ce6 (final concentration: 0.4 μM, 0.8 μM, 1.6 μM, 2.4 μM, 3.2 μM, 4 μM) was prepared into a gelatin-collagen mixed solution containing antimicrobial peptides. 1ml of 10% transglutaminase aqueous solution was added to 10ml of gelatin-collagen mixed solution to carry out biological enzyme cross-linking for 1 minute. Dispense it into a disposable gel injector mold and let it stand for 30 minutes to form a gel (save at 4°C for later use).
Embodiment 2
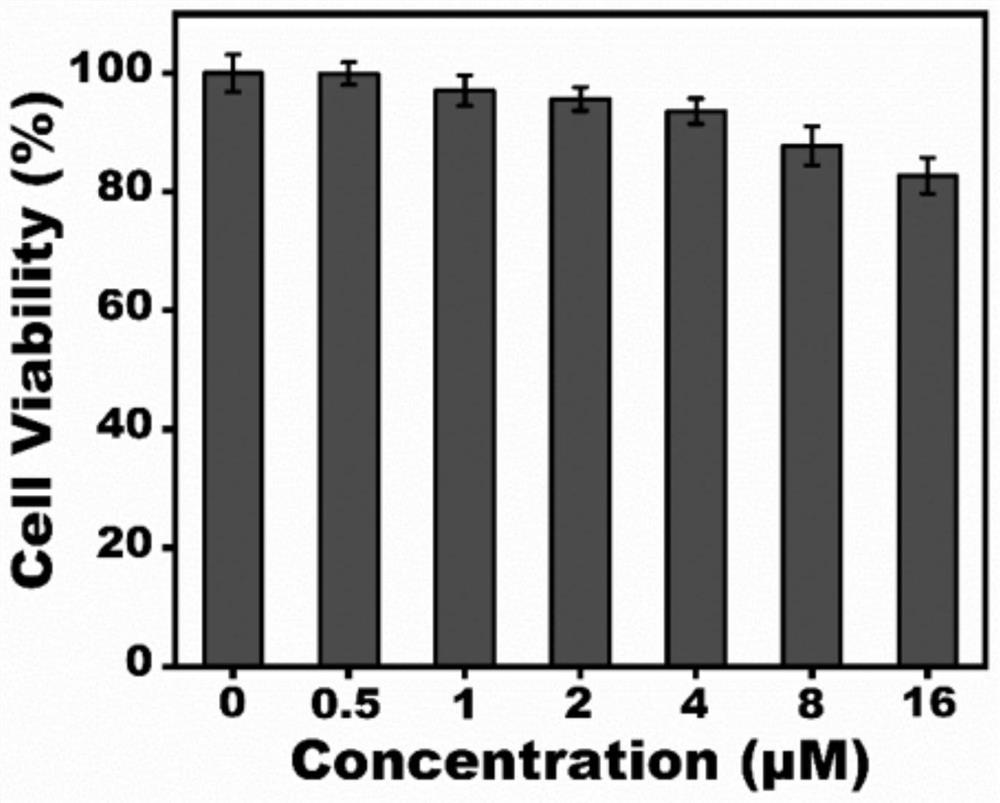
[0032] Example 2 Composite Hydrogel Toxicity Test
[0033] The biocompatibility test of mouse fibroblasts (L929) was carried out by MTT method. First, collect the logarithmic phase cells, adjust the concentration of the cell suspension by 10 4 Cells / well were seeded on a 96-well plate. After overnight culture, they were treated with different concentrations of composite hydrogels (0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 μM), incubated for 24 hours, and then treated with MTT solution. , cell viability was assessed by microplate reader assay (see figure 2 ).
Embodiment 3
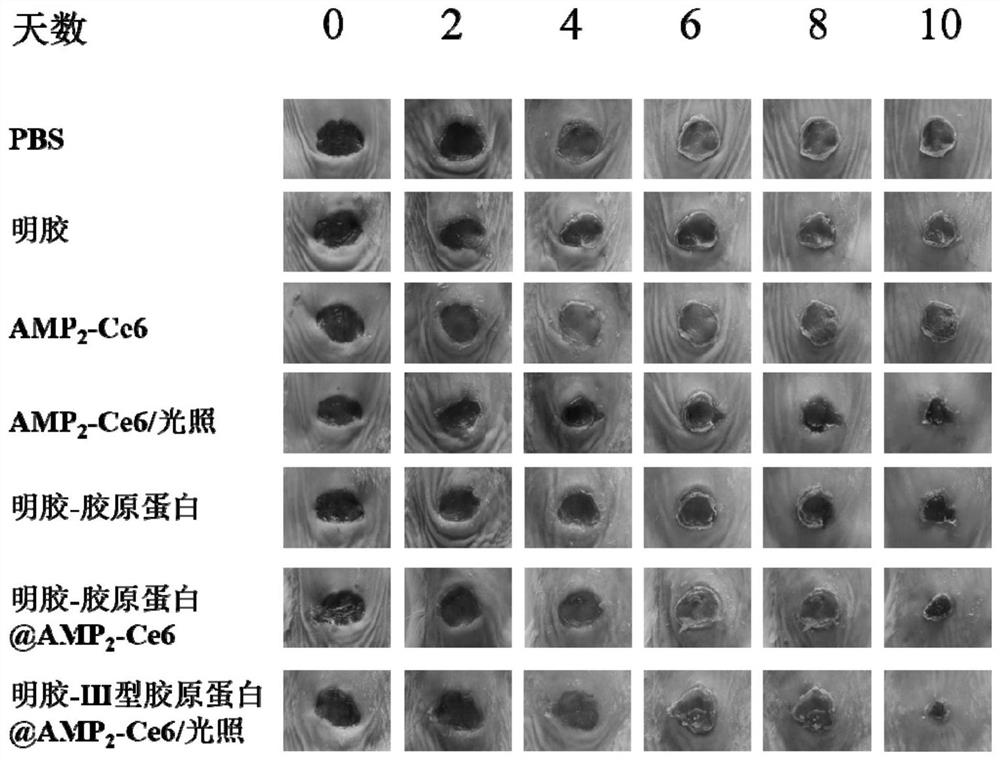
[0034] Embodiment 3 wound repair experiment
[0035] The specific experimental steps are:
[0036] (1) Mouse back trauma model
[0037] A total of 35 mice were similar in terms of species, age, and physique, and each mouse had one wound. First, a full-thickness wound with a diameter of about 1 cm was created on the back of Balb / c mice by surgical operation, and then bacteria were inoculated on the wound (10 5 CFU / mL of Staphylococcus aureus) for 2 days, in situ infection to form a biofilm. During the modeling period, the mice were housed in a single cage, accompanied by toys, and allowed to drink water and eat freely. After the modeling, there was no obvious difference in the wound of each mouse, the bacterial infection site was yellow, the periphery was red, and the surrounding tissue edema was obvious.
[0038] (2) Animal grouping
[0039] 35 mice were randomly divided into 7 groups:
[0040] Group A was the control group, and the dosage was 200 μL PBS / wound, applied e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com