Application of covalent organic nanosheet material
A covalent organic and nanosheet technology, applied in the field of radionuclide excretion agents, can solve the problems of short biological half-life, high biological toxicity, poor membrane permeability and selectivity, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
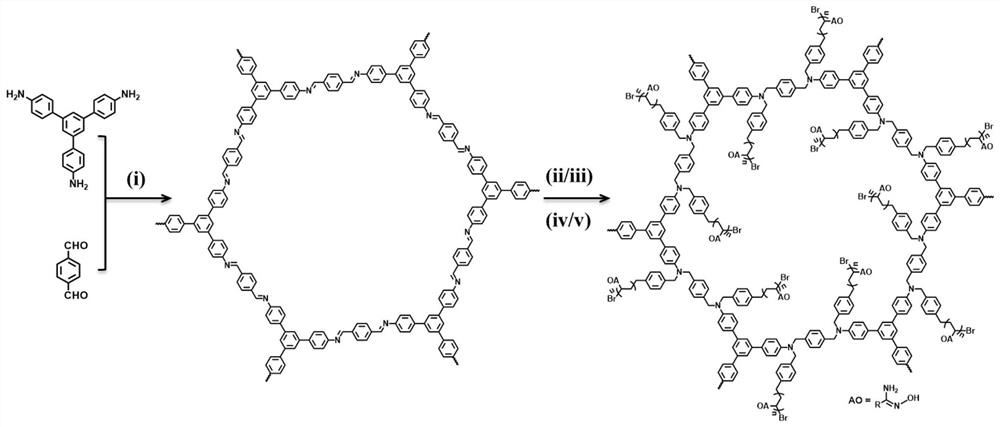
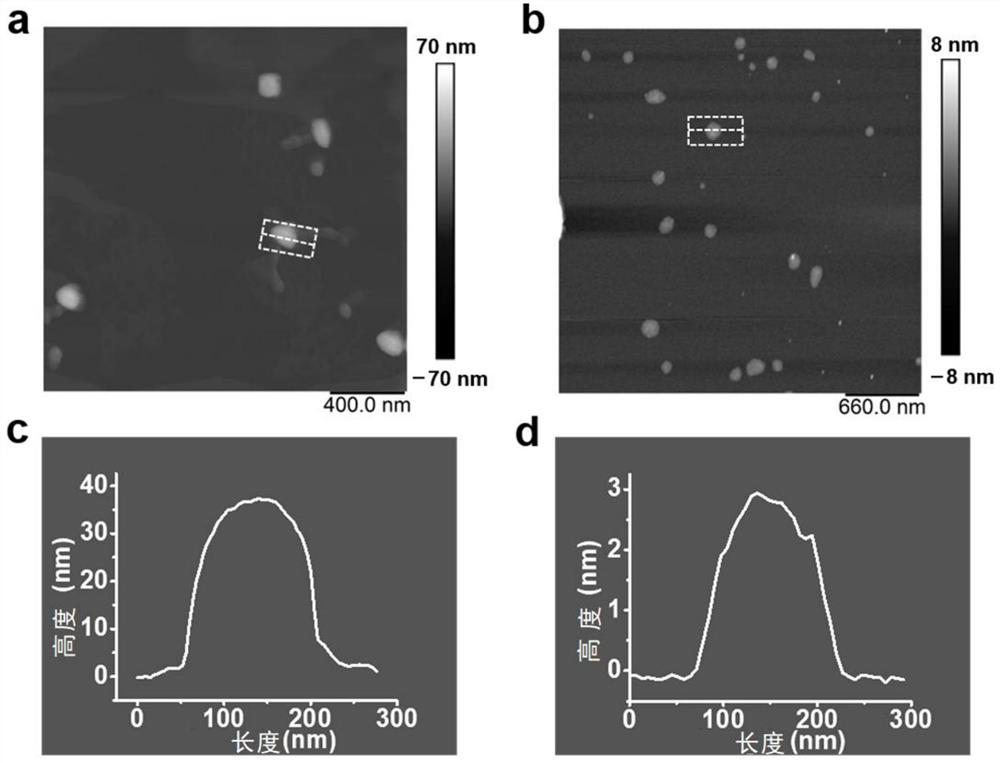
[0034] see figure 1 , this example prepared amidoxime-modified nanosheets CON-AO through a step-by-step post-modification synthesis method. The synthesis steps of CON-AO are as follows:
[0035] (1) Synthesis of COF-Imine: Weigh terephthalaldehyde (32mg, 0.24mmol) and 1,3,5-tris(4-aminophenyl)benzene (56mg, 0.16mmol) into a heat-resistant Schlenk glass tube (10mL) mmol), slowly added solvent o-dichlorobenzene (0.5 mL), solvent n-butanol (0.5 mL) and catalyst acetic acid (0.1 mL, 6M). After ultrasonication for two minutes, the reaction test tube was frozen in liquid nitrogen-vacuumized-filled with nitrogen, and cycled three times, filled with nitrogen protection and then sealed. Placed in an oven at 120°C for 72 hours, a yellow solid was generated. The solid was separated by centrifugation, washed with tetrahydrofuran and ethanol, activated by Soxhlet extraction with tetrahydrofuran for 24 hours, and dried in a vacuum oven at 50°C for 6 hours. The reaction scheme is as follo...
Embodiment 2
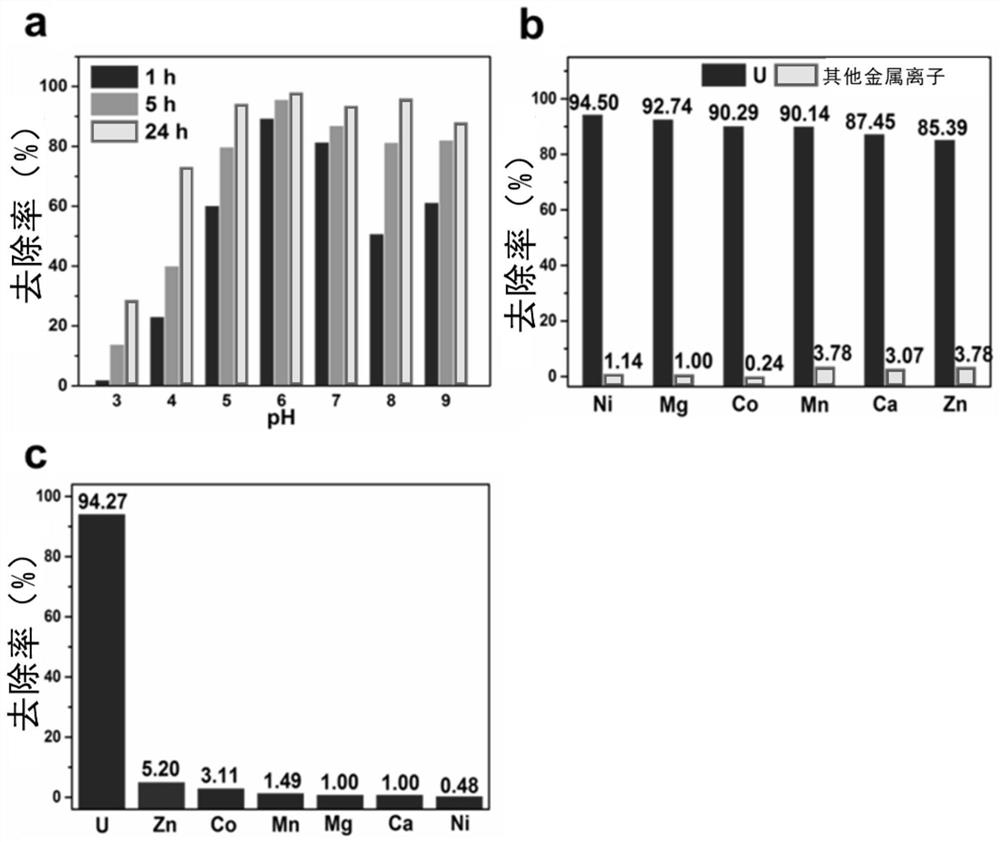
[0049] In order to study the influence of physiological pH and solution pH on adsorption, the present invention also studied the adsorption capacity of CON-AO prepared in Example 1 at pH 3-9 to uranyl.
[0050] The uranium solution (10mL, 8.0ppm) of CON-AO (5.0mg) was shaken and dispersed, and the shaking time was 1h, 12h and 24h respectively. When the pH value of the uranium solution was between 3 and 9, the effect of CON-AO on UO 2 2+ (8ppm) removal rate. Such as image 3 As shown in a, as the pH value increases from 3.0 to 6.0, the removal rate of uranium increases significantly, and the maximum removal rate reaches 98% at pH 6.0, and then decreases slightly. This phenomenon is due to the enhanced binding of uranyl due to the deprotonation reaction of the active binding sites (hydroxyl groups) on the nanoflakes. At physiological pH 7.4, the uranyl removal efficiency was about 90%, indicating that CON-AO is suitable for the removal of uranyl ions in vivo.
Embodiment 3
[0052] The selectivity between uranyl ions and other divalent metal elements in vivo is a key factor to evaluate the quality of uranium chelating agents in vivo. To this end, the adsorption selectivity of CON-AO for uranyl in vitro was verified.
[0053] The first set of selectivity experiments used the UO 2 2+ (10ppm) and respectively and different divalent metal ions (50ppm, Mg 2+ , Ca 2+ 、Co 2+ , Mn 2+ 、Ni 2+ and Zn 2+ ) composed of bimetallic component HEPES buffer solution; the second set of selectivity experiments is UO 2 2+ (4ppm) and mixed divalent metal ions (10ppm, Mg 2+ , Ca 2+ 、Co 2+ , Mn 2+ 、Ni 2+ and Zn 2+ ) multi-component HEPES buffer solution.
[0054] From image 3 It can be seen in b that although the concentration of other ions is UO 2 2+ 5 times, but in each group UO 2 2+ The removal rate of CON-AO is 85.39%-94.5%, while the removal rate of other divalent metal ions by CON-AO is only 3.78%. The second group of selective adsorption expe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com