Method for curing heavy metals in copper tailings by using industrial waste carbide slag and kaolin
A technology of copper tailings and heavy metals, applied in the field of solid waste resource utilization, can solve the problems of large energy consumption, air pollutants, secondary pollution, etc., and achieve the goal of alleviating environmental pressure, cheap and easy raw materials, and improving utilization rate Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
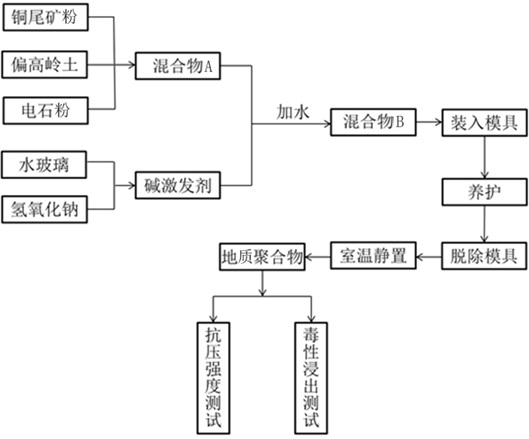
[0033] With calcium carbide sludge and industrial waste of copper tailings kaolin curing heavy metals, comprising the steps of:
[0034] Sl, industrial waste carbide slag dewatering to a moisture content of 20% and then dried 24h under vacuum at the temperature 100 ℃, crushed through a 200 mesh sieve to obtain powder electricity, kaolin dehydrated at 700 deg.] C to give metakaolin, copper tailings dried 15h under vacuum at the temperature 100 ℃, crushed through a 200 mesh sieve to obtain powder of copper tailings;
[0035] S2, the electrical powder, metakaolin, copper tailings powder mass ratio 0.15: 1 uniformly mixed to obtain mixture A;: 0.05
[0036] S3, and NaOH was added to stir the water glass, water glass modulus 1.2 modulation, and then allowed to stand at room temperature for 20 h, to give the alkali activator;
[0037] S4, the mixture A, the base and activator mixed water-cement ratio of 0.2: 1, the mixture ratio of the mass of the alkali activator is 100: 5 to obtain a ...
Embodiment 2
[0040] With calcium carbide sludge and industrial waste of copper tailings kaolin curing heavy metals, comprising the steps of:
[0041] Sl, industrial waste water content of carbide slag dewatered to 30%, and then dried 30h under vacuum at the temperature 110 ℃, crushed through 300 mesh sieve to obtain powder electricity, kaolin dehydrated at 800 deg.] C to give metakaolin, copper tailings dried 18h under vacuum at the temperature 110 ℃, crushed through 300 mesh sieve to obtain powder of copper tailings;
[0042] S2, the electrical powder, metakaolin, copper tailings powder mass ratio 0.25: 1 uniformly mixed to obtain mixture A;: 0.1
[0043] S3, and NaOH was added to stir the water glass, water glass modulus 1.8 modulation, and then allowed to stand at room temperature 24h, to give the alkali activator;
[0044] S4, the mixture A, the base and activator mixed water-cement ratio of 0.4: 1, the mixture mass ratio of the alkali activator is 100: 8 to obtain a mixture B;
[0045] ...
Embodiment 3
[0047] With calcium carbide sludge and industrial waste of copper tailings kaolin curing heavy metals, comprising the steps of:
[0048] Sl, industrial waste carbide slag dewatering to a moisture rate of 25%, and then dried 27h under vacuum at a temperature of 105 ℃, after passing through a 250 mesh sieve to obtain pulverized powder electricity, kaolin dehydrated at 750 deg.] C to give metakaolin, copper tailings 16.5h dried under vacuum at a temperature of 105 ℃, crushed through 250 mesh sieve to obtain powder of copper tailings;
[0049] S2, the electrical powder, metakaolin, copper tailings powder mass ratio 0.2: 1 uniformly mixed to obtain mixture A;: 0.075
[0050] S3, and NaOH was added to stir the water glass, water glass modulus 1.5 modulation, and then allowed to stand for 22h at room temperature, to obtain an alkali activator;
[0051] S4, the mixture A, the base and activator mixed water-cement ratio of 0.3: 1, the mixture ratio of the mass of the alkali activator is 10...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com